MARKET OVERVIEW
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will expand beyond its conventional limits as companies transition towards more stringent environmental laws and increased sustainability promises. Placed in the environmental technology industry, this market will no longer be considered simply a wastewater management solution; it will be a focal point for industrial water management policies globally. Firms that after taken into consideration ZLD systems a regulatory requirement will begin to see them as lengthy-term investments, able to transform waste into assets and reduce environmental footprints.
Advances in membrane filtration, crystallization, and hybrid systems inside the future will revolutionize the manner ZLD technology are perceived, from value-additive frills to price-based investments. With increasing areas starting to enjoy freshwater shortages, the point of interest will step by step shift from compliance to conservation. Industrial players in electricity era, textiles, chemicals, and prescription drugs will increasingly more undertake ZLD systems no longer most effective to conform with environmental policies but additionally to beautify their deliver chain resilience and turn out to be less established upon municipal water components. This revolution will cause modern designs that provide modularity, power efficiency, and versatility throughout various geographies and weather situations.
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will sense a strong impact of virtual integration. With expanded adoption of clever monitoring gadgets and predictive preservation technologies, operators will be ready with immediately comments approximately device overall performance. Such virtual advances will not just make operations more efficient but also increase the lifespan of ZLD system and decrease unplanned downtimes. Moreover, algorithms used in the software will improve to maximize the rates of water healing and treat influent pleasant versions greater correctly, for this reason lowering the value and increasing the reliability of ZLD systems in the long term.
Looking beyond industry usage, municipalities and urban infrastructure developments will start investigating adoption of ZLD within the next few years. With urban areas struggling with wastewater disposal and water shortages, adopting closed-loop water treatment systems will go from being an option to a requirement. This transition into public sector utility planning not only will diversify the demand pool for ZLD solutions but will also force manufacturers to develop systems that are specifically designed for decentralized operations, rural environments, and urban wastewater systems.
Expansion will also extend to the circular economy. Upcoming ZLD systems will be built with greater emphasis on resource recovery not only water, but other valuable by-products like salts, metals, and nutrients. Such material recovery potential will confer economic value to ZLD processes, motivating industries to embrace them as waste monetization tools. Moreover, collaborations between technology developers, research organizations, and industries will incentivize pilot-scale innovations to become scalable commercial solutions.
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will keep reshaping itself as a strategic facilitator of sustainability. As its function becomes increasingly embedded in the larger context of industrial and environmental policy, this market will transcend reactive solutions to become a proactive solution. Its path will not be constrained by compliance structures but will be driven by innovation, demand, and a shared quest for water security and environmental accountability.
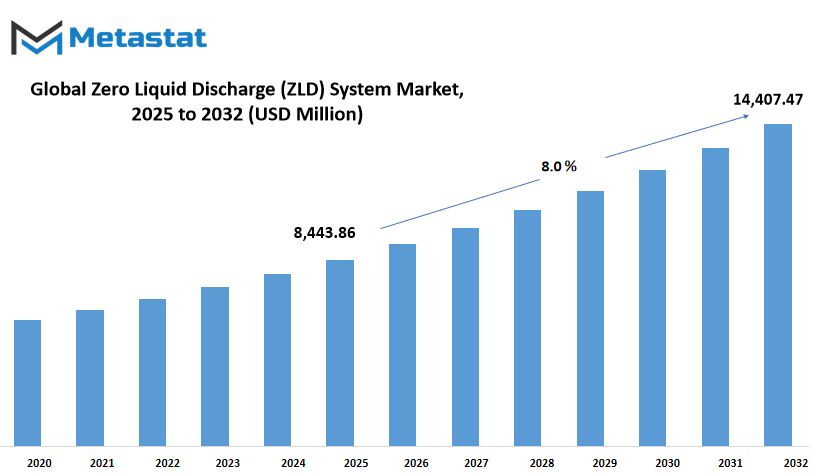
Global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market is estimated to reach $14,407.47 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 8.0% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will remain in the limelight as tougher industrial water pollution laws compel industries to adopt cleaner and more responsible wastewater treatment. ZLD systems, which treat and recycle each drop of liquid waste, will become more important as industries try to meet legal standards and stay away from penalties. Environmental regulations are no longer a choice for most countries they are a requirement. As governments make the regulations around discharge limits more stringent, companies will have to implement measures that guarantee zero liquid waste makes it out of their plants untreated. Increasing pressure of this nature will automatically drive demand for ZLD systems higher, particularly in industries such as power generation, textiles, and chemicals, where water consumption and waste generation are high.
The increased scarcity of freshwater resources will be yet another major driver. Numerous regions are actually experiencing extreme water stress as a result of climate alternate, population increases, and accelerated industrialization. Recycling dealt with wastewater the use of advanced ZLD systems is now not simply a sustainable alternative it is increasingly becoming a required one. The systems permit industries to recycle and reuse wastewater for the duration of their tactics, minimizing their reliance on outside assets of water. This gain will render ZLD generation ever extra compelling, in particular in water-strapped areas wherein corporations need to be ingenious about handling with out in addition draining already-scarce sources.
Even with these perks, the global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market still has some impediments. One of the most important is the exorbitant cost of strolling and installing the systems. From the initial capital outlay for device to normal renovation and energy fees, ZLD has been appeared as an steeply-priced proposition mainly in comparison with traditional wastewater remedy techniques. Such prices can function a disincentive to adoption, in particular amongst small groups with limited economic sources or uncertain returns on funding. Many companies may be reluctant to continue unless they are incentivized in the form of subsidies, tax remedy, or regulatory requirement.
Furthermore, the technical complexity involved in incorporating ZLD systems into the current operations is another issue. This is particularly the case for small and medium-scale enterprises (SMEs), where such upgrades might be beyond their technical capacity or available resources. ZLD systems may have various stages such as pre-treatment, evaporation, and crystallization, all of which should function in a smooth manner. The process to control these steps, in addition to the requirement for expert knowledge, could discourage smaller businesses from applying them unless more low-cost, user-friendly alternatives are developed.
Still, the future of the global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market is not bleak. Advances in thermal and membrane technology will have an important influence in enhancing performance while lowering overall costs. As makers and researchers keep pushing the boundaries, ZLD systems will be smaller, more energy-efficient, and easier to service. These enhancements will render the technology more attractive to a broader spectrum of industries. Technologies that use less energy, yield less waste byproduct, or are more flexible to various industrial processes will probably generate greater interest.
Additionally, developing nations also provide rich soil for the growth of ZLD systems. Most of these nations are quickly industrializing and are now starting to experience the environmental impact of uncontrolled water pollution. With advances in infrastructure and governments that impose more stringent controls, industries in the region will seek means of controlling wastewater more efficiently. This presents possibilities for ZLD providers to increase into new markets and create location-particular answers. Those nations in Asia, Latin America, and quantities of Africa are in all likelihood to become key members to destiny market increase.
In brief, while the destiny avenue for the Global ZLD System Market holds some financial and technical challenges, the strain for tighter environmental controls and the necessity to shop water with haste will hold strong call for. Technological improvements and expansion in rising economies will keep to extend the horizon of opportunity, making the marketplace now not simply attentive to regulation but increasingly proactive in its environmental stewardship.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By System Type
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market is heading toward a destiny in which sustainability and business performance are taking walks hand in hand. As industries become an increasing number of conscious in their water resource footprint, ZLD systems are more and more turning into a possible manner of reducing wastewater discharge. These structures get better nearly all the water from business effluent, restricting the reliance on clean water sources and minimizing the environmental effect of untreated waste. Although the technology of ZLD isn't new, its huge-scale implementation is simplest gaining momentum in recent times due to stricter environmental policies, accelerated water scarcity, and the necessity to meet sustainability dreams without any lack of commercial enterprise continuity.
ZLD systems are mainly of two types Conventional and Hybrid. The Conventional segment alone is expected to reach $5,084.29 million, demonstrating its massive presence and efficiency. Conventional ZLD systems usually involve conventional technologies such as thermal evaporators and crystallizers that find common application in various industries due to their efficiency in eliminating liquid waste. Yet, they are energy-intensive. Conversely, Hybrid systems integrate different processes in a manner that enhances energy efficiency and minimizes operational costs. These newer setups are starting to gain attention, particularly from companies seeking to comply with regulatory requirements without substantially adding to their environmental impact.
Increased significance of water as a limited and common resource will persist in influencing the course of industrial wastewater treatment. Governments and private organizations will be expected to encourage more sustainable water management practices, promoting the demand for both traditional and hybrid ZLD systems. With this change, the market will experience more and more research in scalable solutions suitable for energy-saving methods, better system integration, and large features as well as small people. Firms that can provide flexible systems with specific industry requirements will benefit, as no one solution works for all applications.
Though the path forward has its obstacles high installation expenses and technical know-how requirements the advantages of implementing ZLD systems greatly outweigh obstacles. Cleaner operations, enhanced water reuse, and lower environmental penalties make these systems a clever long-term investment. Over time, both kinds of ZLD systems will become more accessible and affordable with developments in process engineering and material science, ensuring that it becomes simpler for industries across the board to make the switch to a zero-liquid discharge future.
By Technology
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market is progressively advancing towards better solutions, particularly for the technologies employed. With increased emphasis on sustainable water treatment, industries are relying on two principal directions: thermal-based systems and membrane-based systems. Both have a unique mode of operation, offering industries choices depending on different demands and budgets. The decision between these two is influenced by the type of wastewater being treated, the quantity involved, and the level of recovery desired.
Thermal-based ZLD plants use evaporation to remove water from contaminants. This process tends to utilize heat to concentrate and then crystalize the remaining solids. These systems are accustomed to treating complex wastewater with high levels of dissolved solids. Though they are more energy-consuming, they are commonly chosen for their efficiency in generating a final dry waste product that is easy to handle. Power generation and chemicals industries, where waste streams are especially difficult to treat, mostly favor this approach in spite of the operational cost, due to its reliability and efficiency in accomplishing complete liquid waste destruction.
On the contrary, membrane-based ZLD systems utilize filtration technologies like reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration. These systems force water through layers of membranes that filter out the contaminants. They tend to be more energy efficient than thermal systems and are mostly applied in industries where the waste stream is not as highly loaded with contaminants. Nevertheless, membrane systems may not necessarily apply to all situations. They function most efficiently when the water has been pre-treated to some extent or when the solids concentration is fairly low. Nevertheless, their increasing popularity cannot be denied, particularly with continual advances in membrane and durability performance.
The future of the global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will be one where thermal and membrane technologies are utilized side by side, frequently in conjunction. Hybrid systems employing membranes for the primary separation and thermal treatments for the final treatment will likely increase. This will enable industries to lower their costs without compromising stringent environmental regulations. As industries develop better technologies, the efficiency and availability of both methods will improve, enhancing the use of ZLD systems across more industries. It's no longer just about compliance with regulations it's becoming a shrewd strategy for long-term resource stewardship.
By Process
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market is developing step by step with industries subjected to stricter surroundings rules and growing concerns regarding water shortages. ZLD structures treat and recycle wastewater to such an volume that no liquid waste is left at the back of, making them specially beneficial for industries including power era, chemical substances, prescription drugs, and textiles. Since businesses are striving to govern their water use in a more responsible way, the need for effective and cheap ZLD solutions will keep escalating.
By process, the global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market is also segmented as Pre-treatment, Filtration, and Evaporation/crystallization. Every phase of the process is crucial in ensuring the whole system is operated efficiently. Pre-treatment is aimed at eliminating big particles and toxic materials that may harm downstream apparatus. It's a required initial step, allowing the system to operate longer without shutdown. Filtration steps in next to trap tiny particles and impurities, getting the water ready for the most energy-consuming stage of the process. Evaporation and crystallization, which are the final steps, make sure that only solid waste is retained. Water is reclaimed in the form of vapor, condensed, and recycled, while solids are recovered for disposal.
As operations implement ZLD systems, energy efficiency and reducing the cost of operations will be the priorities. Improved layout and new technology will make those systems extra budget friendly for smaller operations. In the future, collaborative paintings between producers and water remedy corporations has the capability to boost up the improvement of modular, less complicated-to-install and maintain solutions.
Regulatory strain and network cognizance regarding environmental footprint will keep to dictate the rate of adoption. Early movers will not only escape fines but potentially also get a competitive advantage by demonstrating their sustainability commitment. Although the initial cost of establishing a ZLD system may be steep, savings over the long term from lower water use and waste disposal are likely to exceed the upfront expenditure.
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will not only increase due to regulations but also because clean water is becoming more expensive. Industries will look for systems that recover water with more efficiency while consuming fewer resources, propelling the market towards more intelligent, more responsive solutions. With the technology advancing and awareness growing, ZLD is set to shift from being a must to a norm in industrial water management.
By End Use
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will keep expanding steadily in various end-use industries with mounting pressure to limit the discharge of wastewater and ensure environmental compliance. Of all the industries embracing ZLD technology, the oil and gas sector is most prominent in its growing necessity to treat and recycle significant amounts of water consumed in exploration and refining. As regulations become stricter on the environment and water becomes more scarce in most drilling areas, these firms will end up investing more in closed-loop systems that leave no liquid waste untreated or released.
Pharmaceutical companies will also advance demand, as their own production involves generating complex wastewater containing active ingredients and solvents. Complete recovery of water not only balances sustainability issues but also eliminates chemical runoff into the surrounding ecosystems that could disrupt them. ZLD enables such plants to be safe by regulatory standards while reducing their water reliance.
In the energy and power industry, especially thermal power plants, water usage is enormous, and conventional treatment technologies frequently fail to cope. With ZLD, cooling system and boiler water can be recovered and utilized, minimizing environmental footprint as well as operational expense in the long run. This becomes useful especially in areas where fresh water is not readily available or while retrofitting aging power plants to comply with new environmental standards.
The petrochemicals and chemicals business also produces challenging effluents that cannot be released without sophisticated treatment. ZLD facilities will play an increasing part here by allowing the safe recovery and reuse of water, keeping dangerous chemicals out of groundwater or surface water supplies. As water is a critical utility in cooling, washing, and as part of the chemical reaction process, reuse via ZLD will be both environmental and economic imperative for them.
Aside from these dominant industries, other sectors like textiles, food processing, and mining are slowly heading towards complete wastewater recovery in order to decrease water expenses and address internal sustainability goals. The "Others" sector of the ZLD market demonstrates this increased consciousness and will comprise several new areas where industrial water consumption is substantial, yet water reuse strategies are still evolving.
In total, the global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will experience uptake in various industries, each for their own purpose compliance, cost, or going green. Clean water becomes a more valuable resource, and these systems will become not only useful but necessary, particularly for industries where water usage is high and needs to be handled responsibly.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$8,443.86 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$14,407.47 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
8.0% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
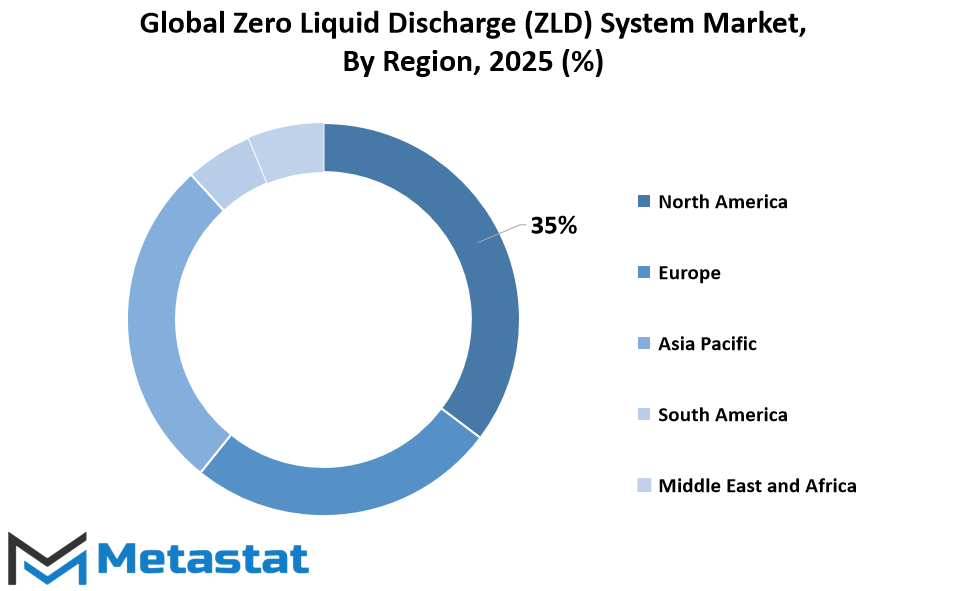
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market is encouraged by way of a vast geographical dispersion, and each region presentations distinct environmental guidelines, industrial necessities, and generation adoption tiers. In North America, nations like the U.S., Canada, and Mexico continue to be eager on eco-friendly water remedy technologies. The U.S., maximum drastically, is likely to preserve its emphasis on strict environmental guidelines and business compliance so that it will raise the wider utility of ZLD systems. Industrial sectors in Canada, mainly mining and energy, are maximum probably to do similar to water reuse needs grow. Mexico, alternatively, can cross directly to step by step boom its adoption as industrialization grows and environmental attention intensifies.
In Europe, countries consisting of the UK, Germany, France, and Italy are anticipated to continue to be good sized players inside the global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market. The countries have continuously invested in inexperienced technology to reap weather dreams as well as save you water wastage. France and Germany, with their stringent environmental regulations in addition to well-advanced engineering industries, will retain to generate call for for sophisticated ZLD technology. The Rest of Europe is also possibly to have a function to play, especially as greater uniform EU-huge sustainability policies come into impact across member states.
Asia-Pacific is possibly to experience dramatic transformation led by means of countries like India, China, Japan, and South Korea. India and China, given their emergent manufacturing and energy sectors, are underneath mounting stress to regulate wastewater discharge. The increasing industrial footprint and water shortages will compel these nations to employ ZLD systems more extensively. Japan and South Korea with their established technological ecosystems will tend towards enhancing system efficiency and energy use, leading the way for others in the region. The Rest of Asia-Pacific will also experience steady growth based primarily on increasing environmental awareness and regulation changes.
South America's participation in the ZLD system market comprises Brazil, Argentina, and neighboring countries. Brazil, being the region's industrial center, should take the lead in adoption, particularly in the food processing, petrochemicals, and pulp and paper industries. Argentina should follow with stepwise integration as understanding of water reuse grows. The Rest of South America would experience slower progress, contingent upon regulatory enforcement and industrial growth.
The Middle East & Africa region is split between GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and the Rest of Middle East & Africa. The GCC nations, with their desert environments and lack of freshwater, have historically recognized the significance of water conservation. This necessity will see demand for ZLD systems pushed by sectors, particularly oil, gas, and power generation. Egypt and South Africa, with their own water management issues, will also be interested in leading-edge treatment technology. Other regional countries will make the transition to ZLD solutions more slowly, contingent upon infrastructure preparedness and investment capacity.
Each geographic region exhibits varying levels of preparedness, economic emphasis, and environmental priority, all of which will determine the shape of the ZLD system market in the next few years.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will keep drawing increasing interest from industries that are facing mounting regulatory pressure to properly treat wastewater. Zero Liquid Discharge systems have been engineered to recover and reuse almost all wastewater generated by industrial processes, converting waste into available water and solid by-products. As companies like textiles, energy, foods and beverages, and pharmaceuticals are increasingly confronted with issues of water scarcity and environmental sustainability, ZLD technologies will cease to be a choice but a requirement. Companies will be able to satisfy rigorous discharge limits with their implementation while lessening reliance on water, particularly in those areas that are highly stressed for water.
The global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market will experience higher uptake in developing nations as governments strengthen pollution standards and incentivize industries to invest in clean technology. For most companies, deploying a ZLD system is not merely a compliance issue but also concerns the long-term efficiency. Reusing high-quality water on-site minimizes the dependence on natural sources or municipal supply, which expose the company to risks and increasing costs. Its operational advantages will increasingly outweigh concerns over upfront investment, particularly as developments shrink these systems to be more energy-efficient and smaller, and make them less difficult to integrate with current infrastructure.
Several companies are defining this market with their niche solutions. Major companies in the Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) System market are Veolia, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Aquatech International LLC, GEA Group, Alfa Laval, Encon Evaporators, Praj Industries Ltd, H2O Innovation, IDE Technologies, Thermax Limited, Samco Technologies, Inc., Condorchem Envitech, Kelvin Water Technologies Pvt. Ltd., Toshiba Water Solutions Private Limited, Aqualyng, Aquarion AG, and Arvind Envisol. Every one of these businesses possesses distinct capabilities from membrane- and thermal-based ZLD systems to modular, turnkey equipment adapted for particular markets. Some provide complete end-to-end services involving design, engineering, and maintenance, while others specialize in specific components such as evaporators or crystallizers.
As businesses become increasingly aware of their environmental impact, collaborations with such suppliers will continue to increase, promoting new service models that guarantee long-term ZLD system performance. This trend will also compel manufacturers to enhance the life cycle of their products, from material longevity to easier repairability and upgrades.
Although the outlook for demand is robust, operational cost and energy consumption concerns will continue to be a challenge. Yet, research and technological development will continue to enhance performance levels steadily. Hybrid processes, for example, will become increasingly popular by integrating various treatment strategies in order to achieve increased energy efficiency and water recovery. Consequently, businesses in various industries will no longer regard ZLD as a costly mandate but as an investment into the future that supports sustainability ambitions and operational steadiness.
In the coming years, the global zero liquid discharge (ZLD) system market not only will assist in environmental conservation but also will have a direct bearing on industrial productivity, particularly in areas with water scarcity. With appropriate partnerships and policy facilitations, the implementation of such systems will expand, bringing long-term value to companies, society, and the environment as well.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) System Market Key Segments:
By System Type
- Conventional
- Hybrid
By Technology
- Thermal Based
- Membrane Based
By Process
- Pre-treatment
- Filtration
- Evaporation/crystallization
By End Use
- Oil and Gas
- Pharmaceutical
- Energy and Power
- Chemicals and Petrochemicals
- Others
Key Global Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) System Industry Players
- Veolia
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Aquatech International LLC
- GEA Group
- Alfa Laval
- Encon Evaporators
- Praj Industries Ltd
- H2O Innovation
- IDE Technologies
- Thermax Limited
- Samco Technologies, Inc.
- Condorchem Envitech
- Kelvin Water Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
- Toshiba Water Solutions Private Limited
- Aqualyng
- Aquarion AG
- Arvind Envisol
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential





 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






