MARKET OVERVIEW
The Global E Waste Management market focuses on the industry-related aspect of one of the most prominent concerns in modern technology and the environment: the proper disposal and processing of electronic waste. As the global use of electronic devices is expanding, so is the rate at which discarded gadgets, appliances, and their components reach mind-boggling numbers. This includes the systems, processes, and services for managing these streams of waste, thereby recovering valuable materials while harmful substances are safely dealt with.
The Global E Waste Management market is defined by its essential role in mitigating the environmental and health impacts of discarded electronics. It addresses a diverse range of waste materials, including but not limited to consumer electronics, industrial machinery, and IT equipment. These products are comprised of precious materials like gold, silver, and rare earth metals, along with toxic elements such as mercury, lead, and cadmium. The industry guarantees that these elements are either reused, recycled, or disposed of in ways that minimize the damage. By using high-end recycling technologies and organized waste collection methods, this market enables sustainable practices.
The Global E Waste Management market is spread across various sectors. It is propelled by regulatory frameworks, technological advancement, and consumer awareness about sustainability. Its reach is not confined to developed regions but is increasingly involving emerging economies where electronic consumption is on the rise. Urbanization and the proliferation of smart devices are expected to fuel the demand for efficient waste management systems. This industry of e-waste disposal includes recycling firms, waste processing facilities, logistics providers, and policymakers working collaboratively to construct and maintain efficient systems for electronic waste disposal.
The market will have to face a series of challenges as electronic devices get increasingly complex. Of key importance in this regard will be the sourcing of valuable materials and proper handling of hazardous substances. In addition, this market is indispensable for developing circular economy models that are focused on conceptual design with recyclable elements in products. As streams of electronic waste diversify, Global E Waste Management companies will evolve innovative solutions to stay ahead of such an evolving need.
Advancements in automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence will determine the future of this industry as they are likely to revolutionize the sorting and material recovery processes. International partnerships and initiatives will also take precedence because e-waste is a global issue that requires a concerted effort. Cross-border collaborations will likely standardize practices and promote technology sharing, making the efficiency and effectiveness of waste management processes better across borders.
In the years ahead, the Global E Waste Management market will increasingly prioritize consumer engagement, aiming to educate individuals on proper disposal practices and the benefits of recycling. Governments and corporations are expected to invest in awareness campaigns and infrastructure improvements to address the challenges posed by growing electronic waste volumes. This will make the role of this market in the furtherance of environmental-friendly practices and resource depletion all the more critical as sustainability comes to the fore in industries worldwide.
Through its focus on innovation, collaboration, and responsible practices, the Global E Waste Management market will solidify its position as a key component of the global sustainability movement, balancing environmental responsibility with economic opportunity.
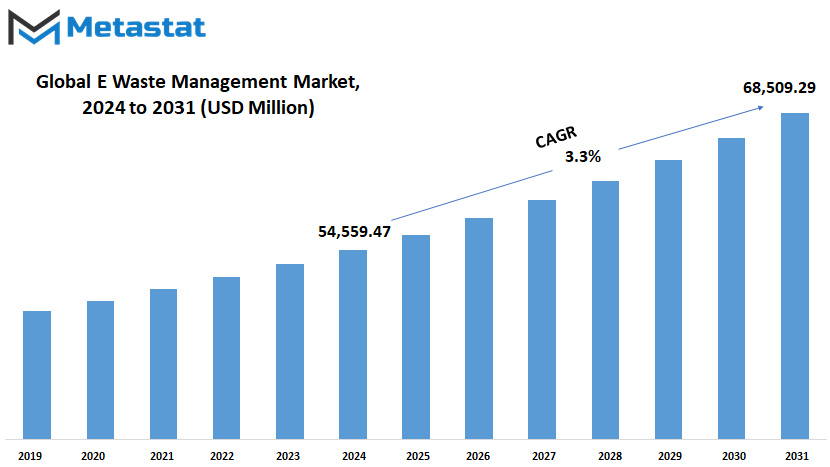
Global E Waste Management market is estimated to reach $68,509.29 Million by 2031; growing at a CAGR of 3.3% from 2024 to 2031.
GROWTH FACTORS
The global E-Waste Management market is likely to grow significantly as the awareness levels increase about the environment hazards caused by the improper disposal of e-waste. E-waste refers to electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and household appliances, that are disposed of. Since all these contain harmful elements such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, improper disposal leads to extreme issues in the environment and health. This awareness is coupled with the stringent regulations for sustainable recycling and disposal, and it is changing the future of the market.
Governments and environmental organizations across the world are taking the onus of controlling the risks posed by e-waste. There are regulations about proper collection, recycling, and reuse of materials in place, mainly in developed nations. Such efforts reduce landfill overflows and push toward a circular economy where all the valuable metals such as gold, silver, and rare earth are recovered and reused. Besides saving the environment, it gives considerable economic advantage as dependence on virgin resources would decrease.
Yet, challenges abound in the Global E-Waste Management market. Advanced recycling technologies are very expensive, and their high cost continues to be a significant barrier for many organizations and governments. It is also costly to build facilities that can recover materials efficiently; such facilities are usually only accessible to developed countries. In addition, public awareness and participation in e-waste recycling are still low in emerging economies. Absence of proper infrastructure and lack of knowledge about recycling benefits further fuels the problem and hampers the growth in these markets.
The market still holds promising opportunities despite these challenges. Innovations in recycling technologies improve the recovery rate of precious and rare materials. These innovations are making recycling more efficient and economical, which boosts public and private investments in the sector. For example, new technologies can recover valuable materials using less energy consumption and lower environmental impact, thereby making the process more attractive to stakeholders.
In the future, the Global E-Waste Management market will be on the increase as awareness and technology advance. More efforts in education and public outreach, especially in emerging economies, will promote participation. More countries adopting stringent environmental policies will create a larger demand for sustainable solutions. It, therefore, shows that the need to address current challenges and capitalise on opportunities to build an efficient e-waste management system worldwide is imperative for a more sustainable future.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Type
The Global E-Waste Management market is one of the major areas that has gained considerable interest in the past few years due to rapid technology advancement and a growing population with electronic equipment usage. Since the integration of technology into daily life has become the way of life, discarded electronic equipment are ever increasing in numbers, and pose both environmental and economic problems for the earth. Effective management of the waste will play a vital role in mitigating the harmful impacts while unearthing valuable opportunities in resource recovery.
By type, e-waste produced can be divided into metal, plastic, glass, and other components. Each of these types requires specific processing processes to recycling and reusing them effectively. For example, metals are one of the most important components in almost all electronic devices. Recycling of metals not only diminishes the need to mine more resources but also decreases the usage of energy in manufacturing. Plastic makes up the greatest proportion of e-waste; they should be reprocessed so as not to degrade the environment. Through reprocessing plastic material, industries are participating in the idea of a circular economy, which recycles waste material into a different product so as not to continue using raw material.
Glass in e-waste
Glass accounts for most the screens and monitors in e-waste. Recyclable requires a delicate approach so as not to separate any hazardous substances from the glass pieces. Recycled glass will eventually find application in new manufacturing activities and thus forms the beginning point in encouraging environmentally responsible business approaches among industrial ventures. Under “others” would come materials that would fall in batteries, circuit boards, which necessitates very radical solution concerning these toxins with very great worth to man’s technological prowess, an essential way that leads toward changing how humans do dispose of electronic wastes into the future.
Looking forward, the Global E-Waste Management market is expected to evolve, in light of tougher regulations, awareness, and technologies in recycling. Governments and other organizations worldwide have come to understand the need for sustainable practices, and thus research and infrastructure to deal with the problem are most likely to be invested in by them. An effective system is to be formed through the integration of industries, policymakers, and consumers that will ensure the proper disposal, recycling, and reuse of electronic waste.
This market, in turn, offers not just a solution to an environmental problem but also opportunities to harness valuable resources, generate jobs, and spur innovation. In addressing e-waste-related challenges, it can help take giant leaps toward a sustainable, resource-efficient future.
By Source
This global e waste management market has growing importance, for the increasing reliance of this world on technology. Electronic equipment, in short, has emerged to be the lifeline in everyone's day-to-day existence. The constant progression in the world of electronics coupled with less life span for each product along with the new consumer demand creates massive electronic wastes that need appropriate handling for a sustainable environment and saving nature. The current and potential future scenario for developing and innovative source reduction solutions in e-waste sources are crucial for the future of this industry.
The market is broadly categorized as per sources such as household appliances, consumer electronics, and industrial electronics. All these segments contribute to a significant amount of e-waste generation. Household appliances, which include appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, dominate this list. The old appliances are waste due to more house hold upgrading appliances to energy efficient models. Extracting valuable materials like copper, steel, and aluminum from appliances, effective management systems will focus on eliminating hazardous components in appliances and safely getting rid of them.
Another primary source is consumer electronics, including smartphones, laptops, and televisions. They are replaced, often before they have reached the end of their functional life cycle, because technology has advanced, and consumer demand has shifted. This creates millions of tons of waste, and many of those devices contain metals such as gold and palladium. The problem is to develop methods that are cost-effective to recover these materials but also minimize their environmental footprint.
Industrial electronics is also a group that contributes largely to e-waste, containing items such as medical equipment, machinery, and large IT systems. These parts are usually specific in nature, thus requiring the utmost care while being recycled. With industries making continuous upgrades towards better efficiency, this sector of waste is anticipated to grow exponentially. The latest recycling technologies, as well as policies that mandate manufacturers to incorporate recyclability, will be integral to this progress.
Looking forward, the Global E Waste Management market is going to change with new technological advancements and high regulations. The government and private sector may invest in research to develop more efficiency in recycling and reducing the overall impact of e-waste. Additionally, there will be massive awareness campaigns by consumers to dispose of e-waste responsibly and recycle. It is, therefore, a critical responsibility for the industry to take into account all of these challenges so that, with the proper application of its economic potential, recovered materials can help shape a sustainable future.
By Application
The global e-waste management market is poised for exponential growth with the growing need for a greener world along with technological innovations in the device industry. Electronic waste, more widely referred to as e-waste, has gained tremendous importance since devices like smartphones and computers are being used extensively. The pace of innovation is accelerating rapidly, and often, the device becomes less useful after a short period, resulting in an increase in electronic waste. Proper management of this waste is necessary to reduce environmental damage and make the best use of valuable resources. The future of the market depends on effective solutions for handling e-waste through recycling and disposal methods.
Recycling plays a vital role in extracting usable materials like metals, plastics, and glass, which can be reintroduced into manufacturing processes. This reduces the dependency on raw material mining, which is both costly and environmentally damaging. On the other hand, the share of e-waste categorized as trashed represents the continued burden of littering where people just dump these electronics into the landfills. This is proving to be a significant threat to health as well as the environment because some of these devices may possess hazardous substances. Forging into the future, the Global E Waste Management market shall witness advances in technology and infrastructure that enable enhanced collection, sorting, and processing of e-waste.
Improved efficiency shall also come in the identification and separation of varied components of e-waste through automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. The processes may well turn inexpensive and even an attractive opportunity for businesses and governments around the world to recycle waste more effectively. In addition, awareness campaigns and stricter regulations will likely encourage individuals and organizations to adopt more responsible disposal practices. Without government policies and collaborative efforts from industry, the Global E Waste Management market cannot thrive. Governments globally are enforcing policies to ensure companies take responsibility at end of life for how their products end up. Currently, companies start designing devices so as to be recyclable, hence there is an increased recovery of these valuable materials upon the product having reached its final stage.
In conclusion, the Global E Waste Management market stands at a crossroads. With emphasis now being placed on the ideals of sustainability and continual technological advancement, this market is on the brink of change. Perhaps it is through the improvement of recycling practices or a reduction in the volume of waste simply despatched, but this will certainly be the future of a more effective and environmentally-concerned way of dealing with e-waste.
By End-Users
The Global E-Waste Management Market is grabbing much attention around the world where societies are moving towards increased dependencies on electronic goods. Technological innovation and increasing product lifetimes are shortening drastically, leading to an unprecedented pile of electronic wastes, popularly known as e-wastes. This challenge that is building with time has sparked the creation of a robust market for efficient waste management and electronics recycling. This market has vast future development prospects, especially in how e-waste is being dealt with and reprocessed due to the advancing technological world.
Another critical aspect propelling the Global E Waste Management market is end-user segmentation. Various sources of electronic waste comprise industrial electronics, consumer electronics, household appliances, IT and telecommunication equipment, and medical equipment. Each category is a unique source of contribution to the e-waste stream, and managing these sources requires specialized solutions. For example, industrial electronics, which include heavy machinery and equipment, require methods that ensure safe dismantling and recovery of valuable materials. Consumer electronics, which include smartphones, tablets, and entertainment devices, contribute heavily to the volume of waste and often include components that can be repurposed or recycled into new products.
Household appliances, including refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, also contribute significantly to the market. These products are often bulky and contain hazardous materials, thus requiring careful handling to avoid environmental damage. IT and telecommunication equipment, including servers, computers, and networking devices, is another rapidly growing segment. As industries and consumers frequently upgrade their devices, this sector contributes significantly to the need for comprehensive e-waste management solutions. Medical equipment, though smaller in volume, is a critical area because of the precise and often hazardous materials involved.
Looking ahead, the Global E Waste Management market is poised for remarkable growth as regulations tighten and awareness spreads about the environmental and economic benefits of recycling. Innovations in recycling technology are expected to streamline the process, making it more cost-effective and accessible. The future of this market lies in creating collaboration between governments, industries, and consumers for sustainable practices of managing e-waste. By doing so, the industry addresses an important environmental concern while opening new economic opportunities by recovering and reusing valuable materials. Global E Waste Management, with dynamic end-user segmentation, will certainly be playing a significant role in building a sustainable future.
|
Forecast Period |
2024-2031 |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
$54,559.47 million |
|
Market Size by 2031 |
$68,509.29 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2024 to 2031 |
3.3% |
|
Base Year |
2022 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific Green, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Global E-Waste Management is critical to deal with the mounting environmental issues resulting from discarded electronic devices. Such discarded items, known as electronic waste or e-waste, consist of smartphones, laptops, televisions, and other electronic equipment. Proper management of this waste is crucial in reducing its impact on the environment and ensuring sustainable development. One of the leading factors in this market is that the amount of e-waste generated globally continues to rise. There is therefore a need to develop efficient ways of collecting and recycling or safely disposing of these wastes. There is an increasingly innovative approach that aims at lowering environmental pollution levels while recovering these valuable resources.
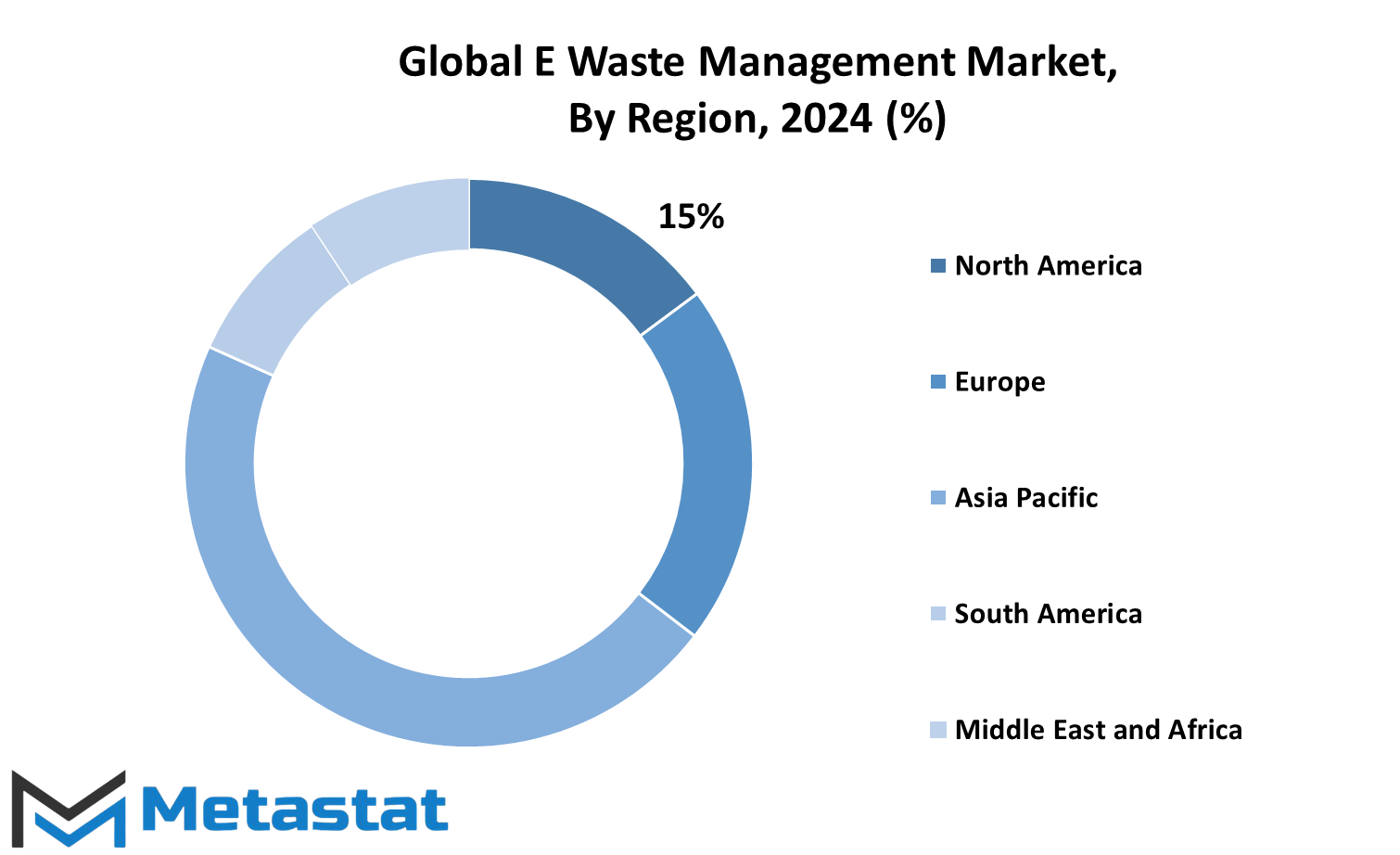
An important variation in terms of growth as well as adaptation is found from regional analysis within the global E-Waste Management market. North America, comprising of the United States, Canada, and Mexico, has shown more commitment to handling e-wastes through regulations imposed and recycling techniques used. Leading the region and the world through its policies relating to responsible recovery and disposal is the United States.
The European region is also at the forefront when it comes to e-waste management. These countries include Germany, UK, France, and Italy, which have become strict in enforcing policies and frameworks that foster recycling and wasting. European countries are keen on conducting public awareness campaigns and involving stakeholders so that even the reported levels of compliance with e-waste directives are very high. Europe's proactive approach leads one to believe that electronic waste should be minimized.
This region has the dynamic and large market comprising countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Rapid industrialization and increased demand for electronic devices in the region has increased e-waste generation; however, a few have established regulations while others are in the development process of frameworks related to the issues.". Initiatives to upgrade the recycling infrastructure and to open opportunities for resource recovery can turn the Asia-Pacific region into a hub of sustainable e-waste management.
In South America, Brazil and Argentina have started to enhance their waste management practices, although still much remains to be done as there is still inadequate infrastructure and awareness. On the other hand, the Middle East & Africa region, comprising the GCC countries, Egypt, and South Africa, is gradually becoming aware of the need for e-waste management. This region is, therefore, developing cooperation and building capacity to respond to the emerging challenge. And, hence, the global E-Waste Management market promises an environmentally safe and sustainable future after addressing the differences in other regions by providing region-specific customized solutions and concerted efforts.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The Global E-Waste Management market is expected to experience a tremendous boom as the world struggles with the mounting volumes of electronic waste. Electronic devices have been becoming obsolete with the rapid advancements in technology, and this has led to the increasing number of discarded gadgets, appliances, and other electronic equipment. This concern has made e-waste management an important industry, driven by a need for sustainable practices, stricter regulations, and the value of recovering precious materials.
This industry is characterized most prominently by a competitive landscape involving major players with an interest in tackling the environmental and economic burdens associated with e-waste. MBA Polymers, Inc., Stena Metall Group, Aurubis AG, and Boliden AB stand out as leaders in recycling and resource recovery. They utilize state-of-the-art technologies to extract metals, plastics, and other reusable parts from discarded electronics, thereby minimizing raw material mining. These initiatives serve not only for environmental conservation but also towards a more circular economy.
Some companies, like Electronic Recyclers International, Inc. and Sims Lifecycle Services, have become market leaders in electronic waste collection and recycling solutions. They ensure efficient processes where hazardous components are disposed of safely and valuable materials reclaimed. Global companies that are investing in innovative ways to expand their operations include Sembcorp Industries Ltd., Umicore SA, and Veolia Environmental Services, among others. The companies are actively involved in collaboration with the governments and local organizations to create awareness and enhance recycling rates.
The Global E-Waste Management market looks bright and promising as technology advances to further optimize recycling. New technologies, such as AI sorted systems and robotic disassembly units, are turning around the scene to make the industry more precise and efficient. Companies like Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd., Tetronics (International) Limited, and E-Parisaraa Pvt. Ltd. are already exploring this technological advancement to be positioned on the competitive ladder.
With rising consumer awareness and governments enforcing stringent policies, demand for effective solutions in e-waste management will grow. This is likely to give new opportunities to established players, while emerging ones will be nudged to come into the fray. The industry will play a vital role in shaping a sustainable future by aligning environmental goals with economic development through the challenges of electronic waste.
E Waste Management Market Key Segments:
By Type
- Metal
- Plastic
- Glass
- Others
By Source
- Household Appliances
- Consumer Electronics
- Industrial Electronics
By Application
- Trashed
- Recycled
By End-Users
- Industrial Electronics
- Consumer Electronics
- Household Appliances
- IT and Telecommunication Equipment
- Medical Equipment
Key Global E Waste Management Industry Players
- MBA Polymers, Inc.
- Stena Metall Group
- Aurubis AG
- Boliden AB
- Electronic Recyclers International, Inc.
- Sembcorp Industries Ltd.
- Umicore SA
- Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd.
- Tetronics (International) Limited
- Sims Lifecycle Services
- Global Electric Electronic Processing (GEEP) Inc.
- E-Parisaraa Pvt. Ltd.
- Veolia Environmental Services
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential





 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






