MARKET OVERVIEW
The future of Global Commercial Electric Vehicle market and its industry are meant to instigate a complete transformation of the transport systems with respect to logistics, public transport, and sustainable mobility for the players involved in this scenario. With stricter emission regulations imposed by governments or corporations endorsing clean alternatives, the segment will expand widely beyond conventional limits. While market growth, adoption trends, and environmental impact considerations are worshipped with much discussion, other aspects of this transformation lie beyond standard analyses.
One facet that tends to fall under the radar is the effect of mass electrification on the dynamics of the supply chain. Manufacturers will be constantly challenged with concerns surrounding lithium, nickel, and cobalt. They would have to innovate battery technologies that address such concerns as well as recycling methods. With environment-related matters steeping extraction processes and geopolitical relations affecting the availability of resources, companies will start to look toward alternative battery chemistries, such as solid-state and sodium-ion, to further diversify their reliance on these scarce materials. These considerations will not merely affect production costs but will also provide a clear path toward achieving long-term sustainability for commercial fleets.
The infrastructure around electric fleets would continue to evolve in rather unfamiliar but exciting ways. While charging networks are the prime focus of investments, grid stability and energy distribution will come to bear rightly, too. In context of large-scale fleet electrification, smart energy management systems integrating renewable sources and storage, together with dynamic scheduling for charging, will be required. Companies will collaborate with utilities to create microgrid designs so that reliability is assured without straining power grids. Bi-directional charging will be significant in this respect, allowing vehicles to send back surplus energy to the grid, strengthening the resilience of urban areas.
The unique challenges that will beset commercial vehicle autonomy, mainly known in the context of passenger cars, will be equally embedded within the commercial side. Self-driving technologies shall find their way into the domains of delivery trucks, freight carriers, and public transport, all in an effort to reduce operating costs and mitigate driver shortages. However, regulations and standards may keep lagging behind the pace of technological advancements. Safe deployment of these autonomous fleets will be influenced by safety standards, legal liability, and ethical considerations, which will require a great deal of testing and phased deployments over a variety of geographical areas.
Beyond logistics and freight, the workforce changes will be significantly affected. Skill needs in the transportation sector will change with the incorporation of electric and autonomous technologies as the new standard. Mechanics used to be trained on repair work for combustion engines, but the workforce will undergo reskill training programs toward performing software diagnostics, battery management, and maintaining electric drive trains. Besides reskilling, new job opportunities will be opened in fleet energy optimization and AI-enabled route planning, thus altering the job market of the industry.
In addition to this, financial models behind electric fleet adoption will also shift. From here forth, businesses will stop outright purchasing vehicles. Instead, they'd be leaning towards leasing structures; subscription models for the batteries; and frameworks for shared ownership arrangements. In that way, they capitalize on lowering the initial installation cost and will thus be more affordable for SMEs. Insurance policies will begin to take into account battery health and autonomous capabilities, changing premiums and risk assessment in ways local models are not structured to account for.
With the eruption of the Global Commercial Electric Vehicle Market, the market shall spread its tentacles deep into the domains of emission reduction and cost savings. The sphere of the industry thus intersects with energy management, workforce development, regulatory policy, and financial architecture, bringing a strong transformation to the face of commercial transportation. These transformations would hence determine how businesses are run, how urban environments are built, the utilization of resources, and the economic strategizing across the globe. The complete spectrum of these changes will reveal itself slowly over time, therefore sketching out the intricacies of an interdependent future that is far removed from the expectations of an ordinary market.
Global Commercial Electric Vehicle market is estimated to reach $455,347.56 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 26.9% from 2025 to 2032.

GROWTH FACTORS
The rapid rise of the commercial electric vehicle market is owing to innumerable factors. The increased support from governments on a global level constitutes one of the major factors for this growth. Countries working on various incentives and subsidies encourage businesses to shift towards electric commercial fleets.
These financial advantages, directly working against the upfront costs associated with electric vehicles, are making them an attractive offer for logistics and transport corporations. With sustainability gaining traction, eco-friendly transportation options have begun to see demand. The awareness among companies regarding their environmental effects is pushing them to look for cleaner options to traditional fuel-driven vehicles.
Nevertheless, there are certain obstacles that may hinder the industry's growth, thus keeping the optimism in the market. One of the primary concerns is the relatively high initial investment in commercial electric vehicles. Though government subsidies are reducing purchase costs, upfront costs still deter many businesses from going ahead. These businesses need to weigh the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance against the switch-out costs.
Another issue is establishing the infrastructure for charging, especially for long-haul trips. Electric commercial vehicle charging sites are not as abundant compared to traditional sites for fuel, resulting in halting operations or becoming inefficient. The expansion of charging points will be key to a smooth transition towards operating electric fleets.
On the other hand, advancements in battery technologies are expected to avail opportunities for market growth. Research and innovation have made batteries more effective and reliable, providing long ranges and short charging times. This present improvement firmly places electric vehicles in the market from a commercial standpoint and addresses some of the complaints businesses had about performance and reliability. Through better battery technologies, less downtime will result in greater operational efficiency for businesses.
With more and more companies adopting sustainable transportation solutions, the outlook for market growth remains almost certain. The fast-tracking of this transition will, however, continue to depend largely on government support, while other factors like improved battery performance will serve to lure more favorable attention toward electric fleets.
Overcoming current challenges with respect to costs and charging infrastructure is destined to make a world of difference in the widespread acceptance of electric vehicles. Businesses investing in electric vehicles today are likely to reap long-term savings and gain important competitive advantages as this market is gradually shifting toward sustainability.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Type
Driving factors of rising demand rapidly shifting towards the global commercial electric-vehicle market include an increase in demand for environmental transport and harsh emissions norms. Policy makers and businesses alike are becoming apparent about the transformation as it relates to the environment. All vehicles available within this market will contribute effectively to changing commercial transportation.
The electric bus segment is among the most important segments in the market, playing an important role in reducing pollution in urban areas and operational cost. The electric bus market has been valued at $40,263.48 million alone, a figure suggesting good global investment into and acceptance of electric buses. Carrying the worldwide trend, cities are integrating electric buses into public transport systems in an effort to curb fossil fuel use. Governments offer subsidies to encourage fleet owners to make the transition to an electric fleet-and this results in electric buses being an enticing option for public transport agencies.
Electric-truck models have been another extremely lucrative segment for transforming logistics and freight operations. Companies want more sustainable options of quickly transporting their goods while slashing fuel cost. Development in battery technology and charging infrastructure is, however, favourably impacting the feasibility of electric trucks for long-distance freight and urban deliverables. With these trucks being endorsed by some of the largest logistics companies around the globe, it is anticipated that there will be even more demand for the electric truck market.
Pickup trucks and vans are a significant segment within this up-and-coming industry. Industries that apply small commercial vehicles in daily operations-for instance, parcel delivery and maintenance-are transitioning to an electric model. Hence, these vehicles benefit from lower operating costs and lower maintenance requirements than gasoline or diesel. In addition, policies concerning clean energy transportation push for adoption, and electric pickup trucks and vans have therefore become a logical solution for most industries.
Electric vehicles are not only a matter of carbon reduction; electric commercial vehicles are about saving money in the long run and efficiency. There is continuous advancement in battery technology that guarantees longer driving distances with short charging times. Overall development in infrastructure, including an increasing number of charging networks, has eased the adaptation of electric vehicles in business operations. Therefore, growth in this global commercial electric vehicle market must be anticipated due to increasing innovations by the vehicle developers and supportive government policies.
Thus, we see the transition to electric commercial vehicles being led and facilitated by ever-increasing public and private support. Electric buses, trucks, pickup trucks, and vans will firmly shape the future of transport as businesses are becoming increasingly aware of the economic and environmental advantages.
By Propulsion System
The global commercial EV market trend consists of strong focus-shifting for organizations and governments on carbon emission reduction and clean energy targeting. The advancement of battery technology empowers that transition, and stricter environmental regulations and a sharp increase in the fossil fuel price renew that motivation to turn to electric fleets. Such an investment does not only promise to make the world a better place but will also offer organizations savings in their long-term cost of doing business, thus making investment in electric vehicles an admirable solution for industries.
By propulsion system segmentation, Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV), and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle classified the market. BEV runs purely on electricity and cannot work without rechargeable batteries to activate the motor. Maintenance costs are quite lower while the battery range and technology keep developing, which is why BEVs become extremely popular.
PHEVs switch between an internal combustion engine and an electric motor powered by a rechargeable battery. This is very useful for businesses that need longer driving ranges without the station being their sole supplier of energy because it allows the usage of either power source. Conversely, FCEVs run on hydrogen fuel cells that generate the power needed with water vapor being the sole emitted waste by-product. These vehicles should take a significantly shorter amount of time to refuel than battery-operated ones, but because of the dearth of hydrogen fuel cell recharging infrastructure, their use has been limited.
The demand for commercial electric vehicles is on the rise in various sectors like logistics, public transport, and construction. A growing trend in the present-day society is achieved through the use of electric vans and trucks to trim down operations costs and set sustainability targets among the delivery companies. Several municipalities have also gone toward electric buses to reduce pollution and improve the public transport service; now electric trucks are introduced into long-haul freight transportation because of advancements in battery technology that have rendered farther driving possible while increasing efficiency.
While government policy and incentives are critical to accelerating the pace toward this transition, many countries are providing tax cuts, grants, and subsidies for business investments in electric fleets. Heightened emission regulations are also motivating manufacturers to produce efficient and less price-tagged electric vehicle types. Advances in technology are bound to see a reduction in the price of batteries, thus making electric vehicles available to a wider market.
Adverse conditions, including charging infrastructure and the manufacture of batteries, still preclude the emergence of these innovations. Continued preparation in the way of investment and research with regard to clean energy application will make the gap even shorter. As more people become conscious of environmental realities and call for sustainable transportation, future decades will host a significant growth shift in the global commercial vehicle market, molded to change the complexion of transportation and reduce fossil fuel reliance.
By Capacity
Huge strides are now being made in the global commercial electric vehicle industry as companies are trying to promote a sustainable and cost-effective form of transport. With battery development and increased government incentives, electric vehicles seem poised to become a real contender against gasoline-powered alternatives. Companies from almost every sector began shifting to electric fleets to lower emissions and operational costs. Whereas environmental reasons were probably the primary motivator for the initial switch, the increasing economic viability of electricity over fossil fuels has now also become a key motivating factor for many companies to make the switch.
The classification of the market basically depends on capacity, and it has three segments: Less than 150 kWh, 150-250 kWh, and Above 250 kWh. Generally, vehicles of less than 150 kWh are used for short-haul transport, such as urban deliveries and small-scale logistics. They are suited to city operations, where the vehicle stops frequently and driver's mileage is lower.
The 150-250 kWh segment carries the medium-sized commercial vehicles servicing the business needing even more range without sacrificing their efficiency. Most operations usually involve regional deliveries and public transport, where distances might vary. Above 250 kWh consists of heavier electric trucks and buses meant for long-haul transport. They allow for high energy storage to be used for heavy load transfer and extended journeys, thus qualifying logistics and mass transit suitability.
Various metric factors, including increasingly stringent emission regulations and developments in the charging infrastructure, will increase the rate of adoption for electric vehicles. Electric mobility is starting to get traction all around the world due to incentives created by governments via grants, tax opinions, or subsidies to encourage businesses to make the switch. In conjunction with these policies, the fast-charging network minimizes consumers' concerns about charging times, thus weakening the practicality of operating electric fleets uninterruptedly.
Although witnessing growths in electric vehicles, massive challenges still remain toward their widespread adoption into commercial electric vehicles. Not only do sky-high initial costs and some regions having limited charging infrastructure put up hurdles to adoption, but also battery life is oftentimes an issue. Nevertheless, research and development in battery technology are steadily resolving such issues, thus leading to improved efficiency and better costs over a period of time. Hence, companies investing in electric fleets today will most probably cut back on costs arising from maintained fuel prices and maintenance with passage of time, thereby making the whole transition economically viable.
The result is that market growth is slowly engendering an increase in competition among manufacturers, thus stimulating their efforts to improve vehicle performance, range of batteries, and affordability. With the existent favorable policies and improvements in technologies, the future of commercial electric vehicles in ammunitioning the transport system towards a cleaner and more sustainable environment is bright.
By End Users
The world now turns to its stimulating engines, the global market of commercial electric vehicles, as if businesses and governments are up to the future of transportation. Everywhere companies look for electric vehicles as they continuously cut back on emissions and operating costs. The movement toward electric commercial vehicles is most visible in the commercial sector being transported for its operational processes, such as deliveries, logistics, and public services. Growing environmental concerns would render the alternatives of electric vehicles viable against conventional fuels.
Changing coalition delivery companies stand among the foremost companies to adopt commercial electric vehicles. Increasingly, companies are looking for economically viable methods of moving goods and these are aided by e-commerce. Electric delivery vans and trucks help save on fuel and maintenance costs and lead to reduced air pollution. Many companies nowadays are operating their electric fleets and truly look forward for a long-term savings effort despite the initial higher cost. Added incentives such as tax remits and subsidies from governments have also made the shift easier for businesses.
This also holds true of the logistics and transportation companies that drive the growth of this market. These companies need vehicles that can take on heavy payloads and handle long-distance journeys. Electric trucks have gained traction, thanks to the advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure that serve to eliminate the perceived barriers that would allow traditional diesel competitors to capture this market.
Several logistics companies are involved in trials or fleet implementations of electric fleets to lessen threats from fuel dependence and meet sustainability targets. Accelerating rate of adoption will be facilitated as battery range continues to improve. This scenario positions the electric truck as a feasible alternative for long-haul transportation.
Public transport is another major segment driving the commercial electric vehicle market. Cities from cities in the world are investing on electric buses, and their purpose is to better the quality of air while, at the same time, reducing pollution. To promote electric nature of buses, governments have imposed their rules, resulting in an increase in demand from transit authorities. Electric buses have fewer operational costs and less maintenance than diesel ones and are, therefore, an optimal choice for public transport systems. Some cities have already made a commitment toward ensuring that their entire bus fleet is electric in a few years.
Technological advances and government policies support every growth in the commercial electric vehicle market. Improved battery efficiency, charging network arrangement, and vehicle design are making electric models more competitive. Besides, the increasing stringency of emission regulations compels the company to consider electric options. Even so, high initial costs and limited infrastructure for charging remain obstacles; however, these barriers will soon be resolved through rapid and sustained advances.
With an increasing focus on sustainability by companies and governments, the movement towards commercial electric vehicles would only gain speed now. It is also about financially viable solutions and efficiencies over time. Electric vehicles, therefore, would be a major player in the future of commercial transportation, with innovation and support riding on a high tide.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$89,856.29 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$455,347.56 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2024 to 2031 |
26.9% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
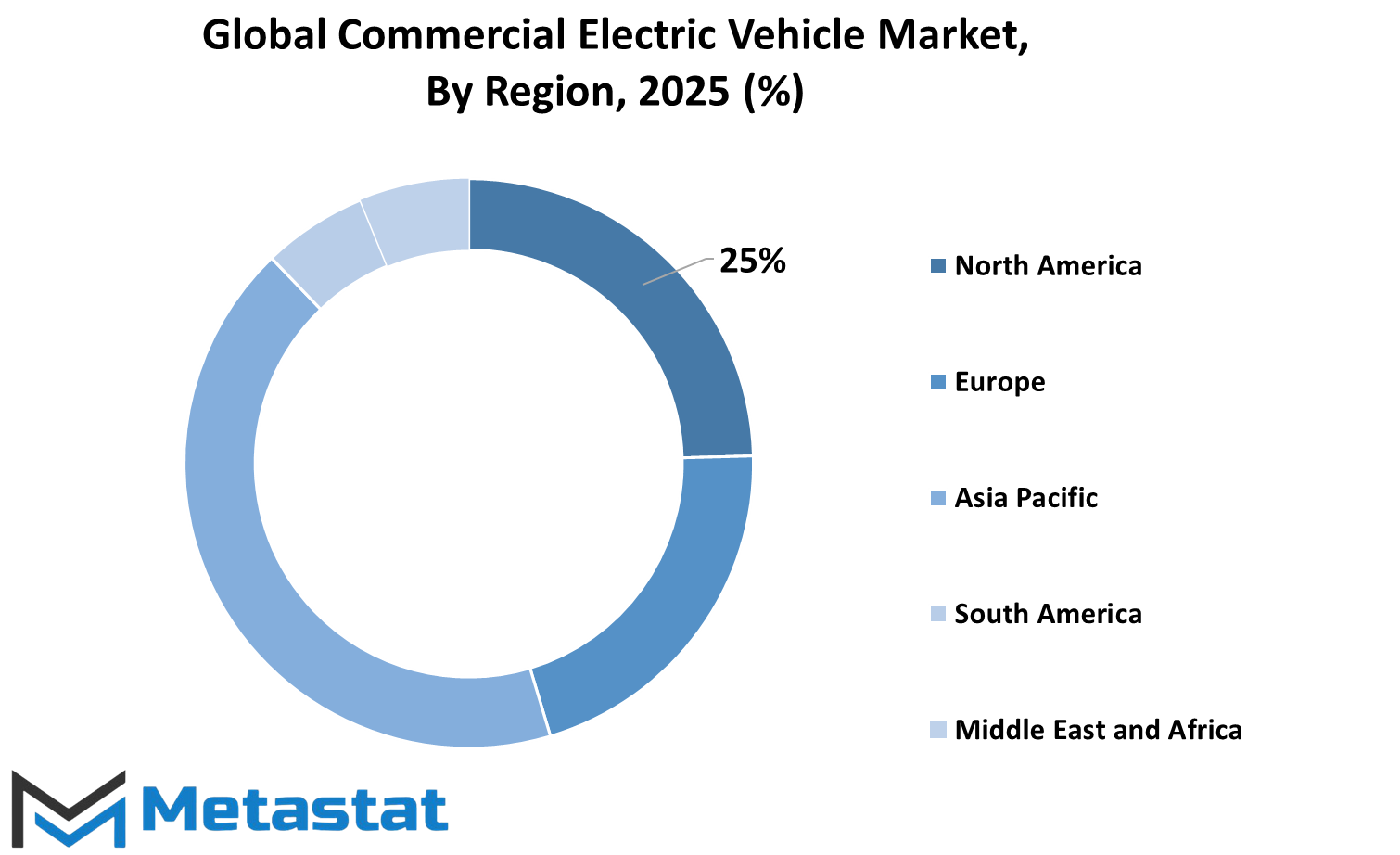
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The Global Commercial Electric Vehicle Market has recently had a marked growth owing to increasing cognitions of governments and organizations for emission reductions as well as more sustainable transport. The segmentation for this market types North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East Africa. Within North America, there are three distinct markets: the United States of America, Canada, and Mexico; Europe includes the UK, Germany, France, Italy, and the rest of Europe. Asia-Pacific further breaks down into countries like India, China, Japan, South Korea, and the rest of Asia-Pacific. South America likewise includes further breakdowns such as Brazil, Argentina, and the rest of South America, while the Middle East & Africa covers the GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and the rest of the Middle East & Africa.
The market of electric commercial vehicles is thriving with growing stringent emission norms coupled with advances in battery technologies. A number of countries are providing incentives for the promotion of electric commercial vehicles, thereby making them increasingly viable for businesses. Private firms that provide logistics, public transport, and freight are gearing up to their new electric models for lower operational costs and compliance in sustainability commitments. Electric trucks, vans, and buses are gaining more traction with the addition of charging infrastructure and battery efficiencies.
Electric commercial vehicles are booming in North America. By far, the majority of the activity occurs in the U.S. Governments are funding charging networks and giving incentives for companies to convert from traditional fuel-based fleets to electric vehicle fleets. Canada and Mexico are working on establishing their electric vehicle industry. In Europe, tough emission targets and grants have become the motor of adoption. The transition is being led by countries such as Germany, the UK, and France. The established automakers, producing electric vehicles, are further boosting the market in this region.
The Asia and Pacific region truly drive the electric commercial vehicle industry, wherein China is number one in government initiatives and a solid manufacturing base. Initiatives in India and Japan are also there, with investments in charging stations and battery technology. Reduction of air pollution- the real cause behind the growth of this region. South America opens the doors for electric commercial vehicles bit by bit, with Brazil and Argentina leading the charge. The region's future growth will depend upon economics and infrastructure development.
The Middle East and Africa are seeing slow but steady growth. The GCC countries, Egypt, and South Africa are all studying the prospect of adopting electric vehicles, driven by the sustainability agenda and rising fuel prices. Government policies are being developed to facilitate this transition. With advancing technology and decreasing production costs, the commercial electric vehicle market globally will continue to flourish, availing companies of efficient and environment-friendly transport.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The global commercial electric vehicles market is presently witnessing a profound transition due to the breakthrough initiative towards sustainable transit. The major factors that influence this paradigm shift are the growing demand for greener alternatives to carbon-based vehicles and heightened awareness on carbon emissions and incentives provided by the government, including advances in battery technology. Such demand for electric vehicles by various companies to cut carbon footprints will keep the competition going in the newest frontier of costs.
Some of these issues that are pushing the boundary with regards to this market include increased focus on sustainability. The imposition of stricter regulations for emissions worldwide has further resulted in the increase of adoption of electric vehicles within the commercial arena. Several governments worldwide are offering various benefits based on subsidies, tax exemptions, and other incentives to encourage the switch. Further, some developments in battery technologies have greatly improved the efficiency and range of electric vehicles, making them relatively practical for long-haul transport and heavy-duty applications.
Infrastructure is also growing to take the lead as a fueling fact for supporting market growth. The expansion of charging networks is attracting more companies into using electric vehicles in their operations. Charging stations are also being invested in by companies at hubs for logistics, warehouses and in commercial parking lots, which means fleets will always be able to function. The price of lithium-ion batteries has also been falling through the years, making electric vehicles cheaper and easier to attain.
Many great names and players are leading this industry, called the commercial electric vehicle industry. The significant companies in this electric commercial vehicle market include BYD Auto, Tesla, Inc., Volkswagen Group, General Motors, Stellantis N.V., Geely Auto Group, BMW Group, Hyundai Motor Company, Daimler AG, and Rivian Automotive. They are constantly coming up with newer models for battery life, charging capabilities, and superior vehicle performance. Some companies partner with technology firms to develop fully autonomous connected electrical vehicles that help to define the future of the industry.
However, the good growth periods are on the line of problems. Factors like high initial cost and limited charging infrastructure in some regions are hindrances to widespread adoption. However, these problems are likely to be minimized as subsequent technologies continue to develop and scale up production. Both government and private enterprises are working towards the joint solution of this issue to ensure that there is a smooth transition to commercial electric mobility.
As for the future of the market, it will continue to grow further as businesses realize the long-term benefits of electrics over time. Further, adoption will be driven by lower maintenance costs, lower dependency on fossil fuels, and adherence to stringent environmental regulations. The market for commercial electric vehicles will thus be a critical component in defining the future of transport alongside other advancements in battery efficiency and infrastructure.
Commercial Electric Vehicle Market Key Segments:
By Type
- Buses
- Trucks
- Pickup Trucks
- Vans
By Propulsion System
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
By Capacity
- Less than 150 kWh
- 150-250 kWh
- Above 250 kWh
By End Users
- Delivery Companies
- Logistics & Transportation Companies
- Public Transportation
Key Global Commercial Electric Vehicle Industry Players
- BYD Auto
- Tesla, Inc.
- Volkswagen Group
- General Motors
- Stellantis N.V.
- Geely Auto Group
- BMW Group
- Hyundai Motor Company
- Daimler AG
- Rivian Automotive
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential






 US: +1-(714)-364-8383
US: +1-(714)-364-8383






