
Mar 19, 2025
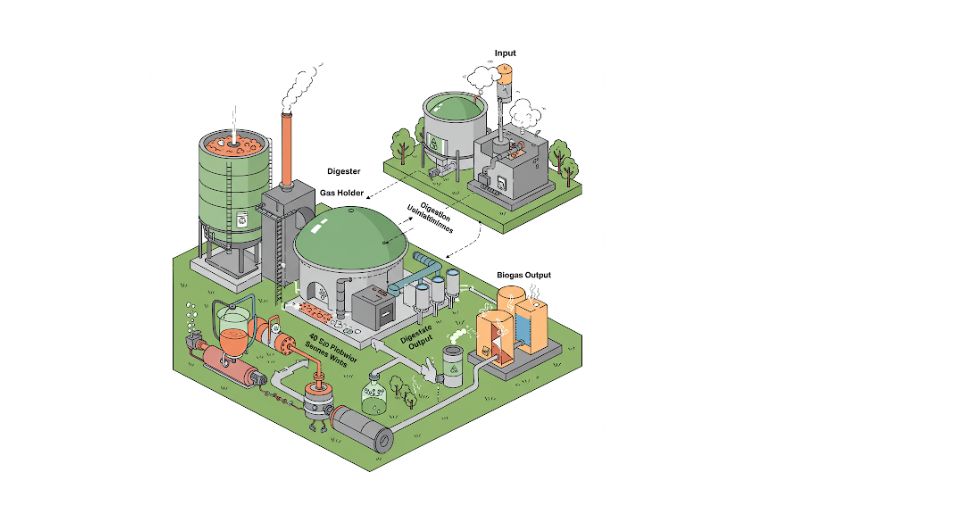
The Metastat Insight scout recently released a report that features the global biogas plants market weaving bright ventures, green commitments, and economic potential today. Biogas plants that convert the biomass from organic waste into renewable energy have become an integral part of the sustainable energy solutions wherein greening practices happen worldwide.
Production of biogas is based on the anaerobic digestion of organic stuff like agricultural residue, industrial waste, and municipal solid waste. Biogas is generated from this decomposition process as a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. It also results in the production of digestate, nutrient-rich material which is used as fertilizer. Biogas thus becomes emplaced for energy production as well as waste reduction, which makes it an integral part of circular economy strategies at global level efforts for reducing the environmental footprint.
Technology has been the much-needed differentiator improving biogas plant efficiency and economy of scale. Better digester designs such as continuous stirred tank reactors and plug flow digesters have made the breakdown of complex organic matter more effective and increased the yields of biogas. Co-digestion technologies enable the treatment of multiple feedstocks at the same time and improve the flexibility and economic efficiency of biogas operations. Also, advances in technology have made adaptation of biogas systems into all kinds of sites-from smaller rural setups to industrial facilities-possible.
Biogas plants are likely to be integrated into the mainstream agricultural and industrial systems. On the one hand, economies of scale are realized when biogas systems can treat and dispose of manure from livestock, along with crop residues, considerably reducing greenhouse gas emissions, while simultaneously providing a new revenue source to farmers by enabling the sale of energy. For example, food processing industries that produce organic by-products also installed biogas plants to treat their waste to sustain low energy costs. Thus, it proves that biogas technology can serve multiple purposes in both waste management and energy generation.
Hari and many others said it has helped so much for the global proliferation of biogas plants. Policy instruments like the feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and grants by different governments and by international agencies encouraged the development of the renewable biogas energy investment portfolios. With these mechanisms in place, immediate and high upfront capital has been made a hurdle and made more economically viable for investments and communities into biogas projects. Moreover, since these facilities would generate jobs in the construction, operation, and maintenance of biogas facilities, they are perceived within the socio-economic context.
The advantages of biogas plants, to be frank, actually go way beyond they being renewable energy generators. Among the many benefits that can be derived from biogas sources is the reduction of methane emissions, which adds up to being a greenhouse gas and thereby helps much in reducing climate change impacts. This can be done by diverting organic wastes from landfills. Besides, the digestion process produces a valuable co-product that can be used as an environment-friendly substitute for chemical fertilizers, enhancing soil health and lowered pollution from agricultural runoff. With these environmental advantages, it is no wonder that biogas is now considered an important feature in national and regional strategies for their sustainability goals.
Though they have so many advantages, the global biogas plants markets are going through some serious hurdles that need to be overcome before they can reach the efficiency they desire. An important issue which one will have to contend with is the availability and consistency of feedstock. Feedstock supply may sometimes be compromised by seasonal appeals of agricultural wastes or competition with other industrial applications of organic materials. This warrants the need for robust feedstock management plans and a search for other organic sources such as algae or dedicated energy crops, as well as other alternatives, to create a steady input source for biogas plants.
Public perception and awareness also contribute to the acceptance of biogas technology. It is most needed to educate the communities in the utility of biogas not just as a renewable energy source but also as a waste management solution to create awareness for support and participation. Successful examples are where such kinds of projects have been built in communities with people's involvement during the planning and operation of the plants. Such participatory approaches would be the future for wider applicability in terms of ownership and responsibility.
The possible future of the global biogas plants market is very bright as trends now emerging look to integrate them ever further into the overall energy landscape. There is a growing trend towards the upgrading of biogas for use as biomethane, a purified product that can be injected into natural gas grids or used as a vehicle fuel. This innovation diversifies further the use of biogas and opens it up to entirely new markets and applications, especially with regard to transportation, where increasingly serious efforts are being made to decarbonize operations.
Also, biogas hubs are types of harmonized biogas plants that are creating large interlinkages among biogas plants to really optimize the efficiencies of resource utilization as well as energy distribution. Then, they could share infrastructure, for example upgrading facilities and storage, which could lead to optimizing costs and efficiencies. They could also have models of collaboration, which could have farmers, industries, as well as municipalities, to come together so that biogas projects can be much more resilient and thus sustainable.
Drop us an email at:
Call us on:
+1 214 613 5758
+91 73850 57479