MARKET OVERVIEW
The global substation automation market will continue to revolutionize the functioning of electrical networks and future-proof them to meet future needs. The market will no longer be regarded as a set of systems for managing power flow but an integral component of the broader energy ecosystem. As urban areas grow and industrialization intensifies, electricity grids will need a more advanced way of monitoring and controlling transmission lines, substations, and distribution networks. The international market for substation automation will fill this gap by allowing operators to shift away from mechanical to digital systems that react in real-time to fluctuations in demand, supply, and weather conditions. This sector will be characterized by how it will combine power system engineering with communication technology.
Substations will not be mere static structures; they will be interconnected via smart devices that record information in real time and adjust accordingly before issues become too complex. These systems will assist operators in ensuring stability, minimizing outages, and guaranteeing safety in power grids. In most parts of the world, antiquated infrastructure will ultimately yield to automation systems that can communicate with smart grids, clean energy sources, and next-generation energy storage systems. The global substation automation market will also prove itself valuable by introducing efficiency to utilities under pressure to deliver reliable power at reasonable prices. Outdated methods used to entail hand inspection and delayed decisions, but automated networks will enable vital reactions to occur within minutes.
Reducing the likelihood of faults spreading across a grid, utilities will be in the position to uphold customer confidence and satisfy regulatory requirements without unwarranted interruptions. In the coming years, this market will not be exclusive to large-scale utilities. Industrial facilities, data centers, and even local energy generators will implement automation technology in order to safeguard their processes and limit downtime risks. The global market will stretch further by providing automation technology that can integrate with both intricate national grids and isolated, independent facilities.
This versatility will make automation a standard practice instead of a niche investment. Another significant area will be the integration of automation with sophisticated data analytics. Future substation automation will produce enormous amounts of information regarding energy flow, equipment health, and ambient conditions. With proper analysis of this information, it will lead operators to predictive maintenance and long-term planning. Rather than responding to failures, networks will foretell them and take action before interruptions happen.
This capability will place the global market at the heart of stable energy futures. Eventually, the sector will no longer be perceived as a behind-the-scenes support mechanism but as a strategic force for how societies control electricity. Its advancement will not only aid in the expansion of cities in the modern world but also guarantee that digital technologies and clean energy function smoothly. The global substation automation market will thus become an integral bridge between energy production and assured delivery, determining the manner in which power circulates around the globe in the coming decades.
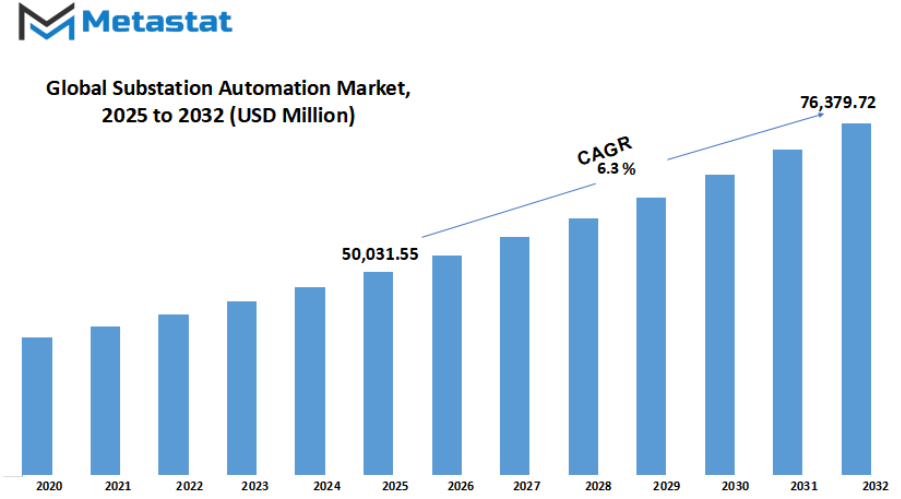
Gobal substation automation market is estimated to reach $76,379.72 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The global substation automation market is expected to witness steady growth in the coming years as countries work to strengthen power networks. Aging grid infrastructure necessitating modernization for reliability will be one of the main driving forces behind this growth. Many grids around the world are operating with outdated equipment that cannot keep up with rising energy demand. Modernization efforts will push utilities and governments to adopt automated solutions that can improve efficiency, reduce outages, and maintain stability in electricity distribution. Along with the need for modernization, there is also a growing focus on increasing grid resilience and integrating renewable energy sources. As renewable energy becomes a larger part of the global energy mix, the ability to manage variable inputs from solar and wind power will be essential. Substation automation will play a vital role in balancing supply and demand while ensuring stable operations.
Although the global market shows strong promise, certain challenges may hinder rapid expansion. High upfront capital investment and implementation costs remain significant barriers. Advanced systems demand considerable financial resources for installation, training, and maintenance, which may discourage adoption in regions with limited budgets. Another obstacle is the risk of cybersecurity vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure networks. As substations become increasingly digitalized and interconnected, the threat of cyberattacks targeting power infrastructure grows. Protecting systems from potential breaches will require continuous investment in robust security measures, which could slow adoption in some markets.
Despite these challenges, future opportunities for the global market appear promising. The deployment of advanced data analytics for predictive maintenance and optimization is set to transform how utilities operate. Predictive tools will allow operators to identify faults before they escalate into failures, reducing downtime and improving efficiency. These advancements will also optimize power flows, extend equipment life, and enhance decision-making through real-time insights. As energy networks become more intelligent, automation supported by data-driven solutions will create a more reliable, secure, and cost-effective power grid.
Looking ahead, the global substation automation market will play an important role in shaping the future of energy infrastructure. With modernization, resilience, and renewable integration driving adoption, and with technological innovations creating new opportunities, the market is positioned for long-term growth. While high investment requirements and cybersecurity risks may slow the pace, ongoing efforts to strengthen global power systems will ensure that automation continues to expand as a central element of future grid strategies.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Type
The global substation automation market is expected to play a central role in shaping how electricity networks function in the future. With growing demand for efficient energy management and increasing integration of renewable sources, automation in substations will not only modernize existing systems but also prepare infrastructure for the challenges of tomorrow. By reducing manual operations and enhancing monitoring, the market will improve stability, security, and reliability across power systems worldwide. This change will also allow faster decision-making, minimize downtime, and ensure smoother operation of power grids even under heavy demand.
The global market is further segmented into Transmission Substations and Distribution Substations. Transmission Substations will remain important because of the role they play in moving high-voltage electricity over long distances. Automation within these substations will ensure more accurate data collection, advanced fault detection, and stronger cybersecurity, all of which will keep large-scale transmission networks more secure and efficient. With renewable power plants often located in remote regions, transmission substations will benefit from automation by improving control and communication over vast areas.
Distribution Substations, on the other hand, will focus on ensuring that end users receive steady and reliable electricity. Automation in these substations will help balance local grids, integrate distributed energy resources such as solar and wind, and reduce outages caused by equipment failures. As smart cities continue to grow, the demand for efficient distribution substations will rise, creating opportunities for improved monitoring systems, intelligent sensors, and predictive maintenance solutions. The ability to respond quickly to changing demand at the local level will make distribution substations one of the strongest areas of growth in the market.
Future development in the global market will also be guided by the use of artificial intelligence, advanced communication networks, and Internet of Things technologies. These innovations will transform substations into intelligent hubs capable of handling complex tasks with minimal human intervention. Cost efficiency will improve as predictive systems identify potential breakdowns before they occur, while energy losses will be reduced through real-time adjustments. Such advancements will not only enhance performance but also support global goals of building sustainable, low-carbon energy systems.
In the years ahead, the global substation automation market will continue expanding as nations upgrade outdated grids and invest in renewable integration. Transmission and Distribution Substations will both see significant technological advancements, each contributing uniquely to the stability and modernization of power networks. The adoption of automation in these areas will lead to smarter, safer, and more sustainable electricity systems worldwide.
By Installation Type
The global substation automation market is set to experience steady growth as power systems continue to transform with modern technologies. Substation automation allows the control, monitoring, and protection of electrical networks to be carried out with greater accuracy and speed. With rising demand for efficient energy distribution and the integration of renewable power sources, this market will remain an important focus for utilities and industries worldwide.
By installation type, the global market is divided into new installations and retrofit installations. New installations will see significant adoption in regions where infrastructure development is expanding. Many developing countries are investing in building modern transmission and distribution networks to keep up with rising urbanization and industrialization. In such cases, fully automated substations with the latest digital systems will be implemented from the start, ensuring long-term efficiency and reducing maintenance needs. These new facilities will also be designed with smart grid compatibility, making them better prepared for future energy demands.
Retrofit installations, on the other hand, will play a vital role in regions where power networks are already well established but require modernization. Aging substations continue to be a concern for many countries, as older equipment often struggles to handle higher loads and advanced grid requirements. By upgrading existing facilities with digital protection systems, advanced communication tools, and automated controls, utilities will extend the lifespan of infrastructure while enhancing reliability. Retrofitting will also be cost-effective compared to building entirely new substations, making it an attractive choice for areas with budget limitations or space restrictions.
The future of the global market will be shaped by increasing reliance on renewable energy, growing urban demand, and the push for more reliable power delivery. Integration of intelligent sensors, real-time data analysis, and advanced communication networks will allow substations to operate with greater flexibility. Automated fault detection and remote control systems will minimize downtime and improve efficiency, meeting the need for uninterrupted electricity supply.
Both new and retrofit installations will benefit from advancements in digital technology and cybersecurity measures, ensuring that modern substations remain secure and resilient against threats. Governments and private sector players will continue to invest in automation as a way to meet energy challenges while reducing operational costs. With continuous innovation and strategic planning, the global substation automation market will stand as a cornerstone in shaping the future of electricity distribution and management.
By Component
The global substation automation market is moving toward a future shaped by digital transformation, smarter infrastructure, and growing energy demands. Substation automation plays an important role in ensuring reliable and efficient operation of power systems, making it a critical part of modern energy management. As urbanization increases and industries expand, the demand for more advanced and secure energy distribution methods will grow, directly boosting the adoption of substation automation technologies.
The global market, by component, is further divided into Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs), Communication Networks, and SCADA Systems. Each of these components will influence how power grids are managed in the future. Intelligent Electronic Devices will continue to evolve, bringing improved monitoring, protection, and control functions. With the ability to analyze data in real time, these devices will allow faster fault detection, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency. As energy infrastructure becomes more complex, IEDs will act as the foundation for predictive maintenance and intelligent decision-making.
Communication Networks will also play a major role in shaping the future of the global market. Reliable communication between substations and control centers will ensure that operators have immediate access to accurate data. The move toward high-speed, secure, and more resilient networks will become essential as the number of connected devices continues to rise. These networks will not only improve response times but also strengthen cybersecurity, which is becoming increasingly important with the rise of digital threats to energy systems.
SCADA Systems will remain vital for supervisory control and data acquisition, offering visibility across entire grids. In the future, SCADA platforms will integrate with advanced analytics and artificial intelligence, allowing operators to predict potential disruptions before they occur. This level of control will help reduce operational risks while improving energy reliability. By combining SCADA with cloud-based technologies, remote monitoring and management will become more efficient, cutting costs while ensuring continuous power delivery.
The future of the global market will also be driven by renewable energy integration. As more solar and wind projects come online, substations will need to manage fluctuating supply and demand. Automation will make it possible to balance these variations, ensuring grid stability and consistent power flow. Additionally, the shift toward smart cities will increase reliance on substation automation, as connected infrastructure requires steady and secure energy to function.
Overall, the global substation automation market will continue to expand as utilities and industries adopt more advanced technologies. By combining Intelligent Electronic Devices, Communication Networks, and SCADA Systems, the market will deliver a more reliable, efficient, and secure power grid that supports both present needs and future growth.
By End-user Industry
The global substation automation market has gained significant attention as industries increasingly focus on efficiency, safety, and real-time monitoring of electrical networks. Substation automation refers to the use of advanced control, monitoring, and communication technologies in electrical substations to improve reliability and operational efficiency. The market is projected to grow as industries adopt automation solutions to meet rising energy demands and stricter regulatory standards. With the integration of digital technologies, substations will not only manage power distribution more effectively but also provide predictive maintenance and enhanced fault detection, reducing downtime and operational costs.
By end-user industry, the global substation automation market includes utilities, steel, oil and gas, mining, and transportation sectors. Utilities remain a major driver due to the need for modernizing aging power infrastructure and ensuring uninterrupted electricity supply. Automation solutions in this sector will enable operators to monitor equipment remotely, control power flow, and respond quickly to any disturbances. The steel industry will increasingly adopt substation automation to manage high energy consumption efficiently, maintain consistent production processes, and enhance workplace safety. Real-time monitoring systems will allow steel plants to predict equipment failures and optimize energy use.
The oil and gas sector will also contribute to market growth, particularly in regions where energy distribution networks support large-scale extraction and refining operations. Automated substations will help reduce operational risks and ensure compliance with safety standards. In mining, automation technologies will allow better energy management in remote and high-demand environments. Monitoring and controlling electrical distribution will become critical as mining operations expand, with automated systems providing real-time insights and preventive measures. The transportation industry, including railways and urban transit networks, will adopt substation automation to ensure smooth and uninterrupted operations, enabling better control of power supplies and improved safety for both passengers and equipment.
The future of the global substation automation market is expected to be shaped by technological advancements such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and predictive analytics. These innovations will enable faster decision-making, enhanced grid stability, and smarter energy management. Increased investments in infrastructure modernization and energy-efficient systems will also drive growth across end-user industries. As global energy demands rise, the market will continue to play a crucial role in maintaining reliable and efficient power systems while supporting sustainable industrial growth.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$50,031.55 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$76,379.72 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
6.3% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific Green, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The global substation automation market is set to experience significant growth in the coming years, driven by the rising demand for reliable and efficient power distribution systems. Advancements in digital technology and smart grid applications are expected to transform the way substations operate, offering better control, monitoring, and maintenance capabilities. With the integration of modern communication networks and real-time data analysis, substations will become more intelligent, helping to reduce downtime, improve operational efficiency, and support the growing need for sustainable energy solutions.
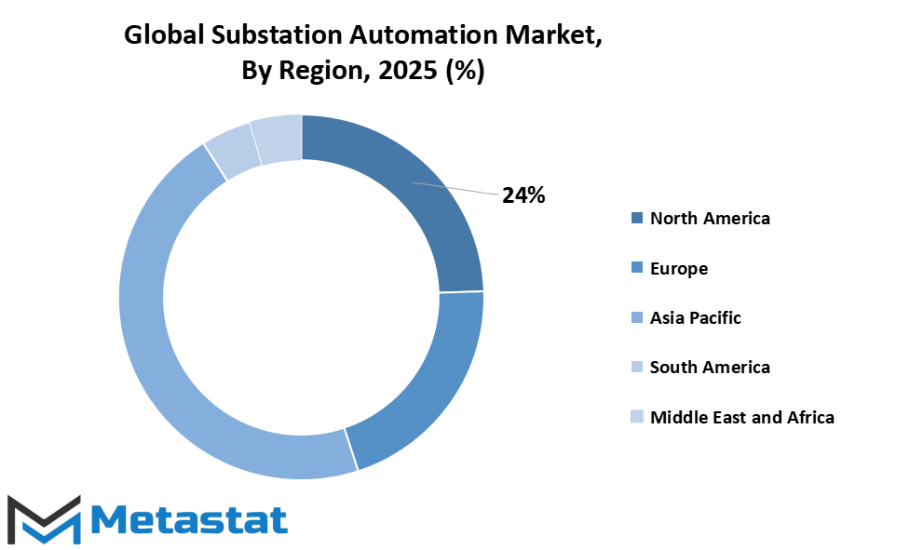
Based on geography, the global substation automation market will see varied growth patterns across different regions. North America, including the U.S., Canada, and Mexico, will continue to maintain a strong presence in the market due to ongoing modernization projects and investments in smart grid infrastructure. The U.S. will drive most of the regional growth with increasing upgrades in transmission and distribution networks, while Canada and Mexico will contribute through initiatives aimed at enhancing grid reliability and energy efficiency.
Europe, covering the UK, Germany, France, Italy, and the Rest of Europe, will witness steady growth, driven by the shift toward renewable energy sources and stricter regulations on energy management. Germany and the UK will lead with high adoption of automation technologies in substations, focusing on integrating advanced monitoring systems and predictive maintenance solutions. France and Italy will also see considerable investments in upgrading older infrastructure, ensuring better resilience and automation capabilities.
The Asia-Pacific region, which includes India, China, Japan, South Korea, and the Rest of Asia-Pacific, will emerge as a key growth hub for the global substation automation market. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing energy demand will fuel the deployment of automation systems. China and India will dominate with large-scale projects aimed at modernizing existing grids, while Japan and South Korea will focus on innovative technologies to optimize energy management and system performance.
South America, consisting of Brazil, Argentina, and the Rest of South America, will experience moderate growth, with Brazil leading due to investments in grid expansion and automation projects. Argentina will follow with selective implementation of advanced substation technologies, enhancing the efficiency and reliability of its power networks.
The Middle East & Africa region, which includes GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and the Rest of Middle East & Africa, will witness gradual adoption of substation automation systems. GCC countries will drive regional growth through smart city initiatives, while Egypt and South Africa will implement modernization programs to strengthen power infrastructure and reduce energy losses.
Overall, the global substation automation market will continue to expand across all regions, driven by the need for smarter, more resilient power systems and the growing focus on sustainability and technological innovation.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The global substation automation market has become a critical focus for the energy sector, as modern power systems require higher efficiency, reliability, and real-time monitoring. The development of intelligent substation systems will allow power operators to manage and control electricity distribution with greater accuracy, reducing downtime and operational costs. Automation in substations is expected to evolve significantly, driven by advanced communication technologies, IoT integration, and enhanced software solutions. These advancements will not only improve operational performance but also help utilities adapt to increasing energy demands and the shift toward renewable sources.
Competitive players in the global substation automation market will play a crucial role in shaping its future. Companies such as ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, General Electric, Schneider Electric, and Eaton Corporation have already established strong positions through innovative solutions and global reach. These players focus on developing scalable and interoperable automation systems that meet the diverse needs of modern power networks. In addition, specialized firms like ZIV Aplicaciones y Tecnología, S.L., Cisco Systems, Inc., and Black & Veatch Holding Company will continue to influence the market by providing advanced communication infrastructure, cybersecurity solutions, and project engineering expertise. Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. (SEL), Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Hitachi Energy, and Toshiba Corporation will contribute with intelligent protection and control systems designed to enhance substation efficiency and resilience.
Smaller yet strategic players such as Alstom Grid, Larsen & Toubro Limited, and SELTA S.p.A. are expected to strengthen the competitive landscape by offering innovative technologies tailored to regional energy requirements. The continuous investment in research and development by these companies will help drive next-generation substation automation, integrating predictive maintenance tools, real-time analytics, and AI-based decision-making. As the global substation automation market expands, collaboration among these key players will likely accelerate technology standardization, improve system interoperability, and optimize overall grid performance.
Looking ahead, the market will witness significant growth due to increased focus on sustainable energy, grid modernization, and smart infrastructure. The integration of digital technologies with automation systems will allow utilities to respond faster to network disruptions, improve energy efficiency, and enhance operational safety. Competitive players will continue to push the boundaries of innovation, making the global substation automation market an essential driver for the modernization of power systems and the transition toward more intelligent and reliable electricity networks.
Substation Automation Market Key Segments:
By Type
- Transmission Substations
- Distribution Substations
By Installation Type
- New Installations
- Retrofit Installations
By Component
- Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs)
- Communication Networks
- SCADA Systems
By End-user Industry
- Utilities
- Steel
- Oil & Gas
- Mining
- Transportation
Key Global Substation Automation Industry Players
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- General Electric
- Schneider Electric
- Eaton Corporation
- ZIV Aplicaciones y Tecnología, S.L.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Black & Veatch Holding Company
- Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. (SEL)
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Hitachi Energy
- Toshiba Corporation
- Alstom Grid
- Larsen & Toubro Limited
- SELTA S.p.A.
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential






 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






