MARKET OVERVIEW
A smart tracker is a very practical device, as it gives real-time information regarding the location, movement, or condition of objects or individuals. Utilizing technologies such as GPS, Bluetooth, or RFID, these trackers have become an important tool in various everyday situations. Their ability to relay accurate and timely updates makes them indispensable for asset tracking, personal safety, and vehicle monitoring. They satisfy the developing demand for comfort and effectiveness when handling personal as well as professional responsibilities.
Among other applications, tracking valuable belongings is one of the most common use of smart trackers. It makes sure that vital equipment is safe in the workplace. For instance, it avoids losing personal items like keys and wallets. Users can easily find an object by attaching a small tracker to it and then using the smartphone or a dedicated device to locate it. It saves time and eliminates the frustration that usually accompanies searching for misplaced objects.
Other than protecting possessions, smart trackers are also important in enhancing personal safety. For parents, these devices are helpful in monitoring their children's location, providing an added layer of security. Similarly, the safety of aged relatives can be assured by such devices in the event of an emergency through updates. The ability to trace where a person is or to send alerts during abnormal movement highlights the role these devices play in contemporary safety equipment.
Another area where smart trackers have proved useful is vehicle tracking. Companies that rely on transportation use them to monitor delivery trucks, ensure timely arrivals, and find the best routes. On a personal level, car owners use trackers to recover stolen vehicles or monitor young drivers in the family. The security and utility combination has made smart trackers a valuable asset for both businesses and individuals.
This makes smart trackers pretty popular as they meet our practical needs in a way that is quite simple yet effectual. Leveraging available technologies, smart trackers enhance on how essential items are to be followed up, ensures safety, and provides efficiency. Indeed, adaptability to diverse conditions marks out their importance and value to today's lifestyle. Life becomes easier in such circumstances because users value being convenient yet secure.
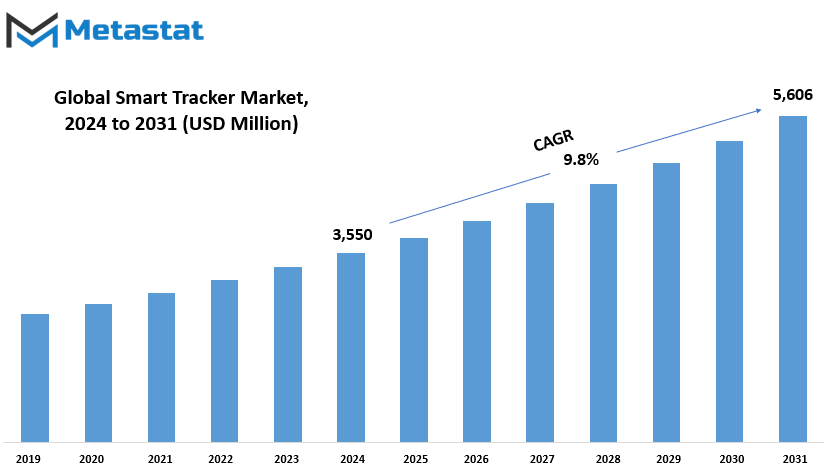
Global Smart Tracker market is estimated to reach $5,606 Million by 2031; growing at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2024 to 2031.
GROWTH FACTORS
The demand for security and real-time tracking has grown significantly across various sectors, including logistics, personal safety, and fleet management. This growth can be attributed to the increasing reliance on tracking systems to ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability. These systems enable businesses to monitor assets, individuals, and vehicles with greater accuracy, offering valuable insights and improving operational performance. In addition, adoption of IoT and smart devices further accelerates this growth as these allow easy connectivity and monitoring, thus making tracking more accessible and efficient for users.
However, despite all these, there are still some challenges remaining that can slow down the growth of this market. The major obstacles are related to privacy on location tracking and data security. Users are usually hesitant to employ tracking systems because of fears over the misuse or exposure of their sensitive information. Another problem is that high technology used in tracking and integration with already existing systems is expensive. The cost of such technologies, particularly for smaller organizations, is very unaffordable and can, therefore, not be easily adopted.
However, these challenges also lead to innovation and improvement. An affordable, energy-efficient, precise tracking technology could make systems more accessible to a wider base of consumers. Solutions will emerge that will reduce costs associated with privacy concerns, making both businesses and individuals want to acquire the system. These improvements would do more than enhance security and monitoring capabilities; they would promote larger-scale adoption.
With further technological advancement, the future of the market holds great promise. With proper solutions in terms of overcoming privacy risks and cost barriers, the tracking industry could be quite large in growth. With security and real-time tracking increasingly being prioritized by businesses and individuals alike, demand for innovative and reliable systems will continue to grow. With strategic developments in this field, the market could witness transformative changes, making these technologies a standard part of everyday life in the years to come.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Type
Tracking devices are quite very crucial in enabling the individual as well as businesses monitor whereabouts their assets are and even to track them. The devices come in many categories and most are categorized depending on the kind of technology used. The types that one can commonly identify are GPS trackers, Bluetooth trackers, RFID trackers, cellular trackers, and hybrid trackers, though with some features and applications being unique.
GPS trackers are one of the most widely used monitoring devices because of their great precision in tracking the location of something. They use the GPS system to indicate the specific location of a thing or a person. GPS tracking devices are the most frequently applied for tracking the vehicle, pets, and outdoor apparatuses. Since they allow tracking in real-time, this makes tracking the items easily over long distances. This type of tracker is ideal for people who want to monitor valuable goods or family members in real time. However, Bluetooth trackers provide a more localized solution when it comes to tracking objects close to them.
These trackers are used for personal items, like keys, purses, or wallets. They work through Bluetooth with a smartphone and can find lost things within range. While the Bluetooth tracker cannot trace items in real-time at long distances, they remain as a reasonable solution to track where household or office items have gotten lost for an inexpensive and reasonable cost. Then, of course, are RFID trackers.
The technology tracks the assets with the help of RFID trackers. Mostly, the inventory management and asset tracking systems for warehouse and retail environments use the trackers. RFID trackers use their system as follows based on the tags attached to objects. The GPS and Bluetooth track as do not rely on the source from the battery power. This can work over a wider range with an aspect devoid of any kind of direct line-of-sight requirement. Cellular trackers forward data over mobile networks. This makes them the best for tracking a large distance.
They can be used to track a car or monitor outdoor equipment that is located in remote areas. The advantages of cellular trackers are that they give live updates and can provide extremely accurate location data, even in areas where GPS signals may be weak or absent. Hybrid trackers incorporate two or more technologies like, GPS, Bluetooth, and cellular networks. Hybrid trackers could offer much greater versatility in the kind of tracking solution.
They would be designed to allow the best of both worlds, in providing for real-time location tracking, along with allowing users to operate in locations where signal coverage is either limited or altogether nonexistent.
Hybrid trackers are the best option for most users requiring a mix of different tracking methods in various situations or environments. In short, the choice of a tracking device depends upon the requirement and needs of an individual using it. Whichever it may be-g GPS, Bluetooth, RFID, cellular, or even a hybrid-they each come with unique advantages that must be considered to choose a right device according to its purpose.
By Connectivity Technology
Connectivity technology has changed how we live and interact with the world. This has led to several key technologies that change how devices talk to one another. The market of connectivity technology is divided into various segments based on the kind of technology used: GPS-based, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Wi-Fi-enabled, Cellular (4G/5G), RFID, and Ultra-Wideband (UWB).
GPS-based technology is one of the most used forms of connectivity, enabling the precise tracking and location of devices, critical to various industries such as transportation, logistics, and personal navigation. GPS-based systems can be found in smartphones, vehicles, and wearables, providing users with their location in real-time.
Bluetooth Low Energy, the next key player in connectivity technology. The main point is BLE offers low-power consumption of wireless communication; thus, its suitability ranges from applications for a fitness tracker to smart home and medical appliances. Through this, there will be speedy data transfer and conservation of energy and a seamless transmission of devices.
Wi-Fi-enabled connectivity is the basis to which people use the internet in their homes, offices, and public spaces. A Wi-Fi network allows faster data transfer over short-to-medium distances, giving reliable internet within homes, offices, or public places. Wi-Fi networks are essential for things like streaming, online games, and working remotely that make it an integral aspect of modern connectivity.
Cellular networks, 4G and 5G in particular, have completely transformed connectivity by providing fast, reliable internet access on the go. Today, 4G is widely used with high speeds and low latency for mobile phones and other portable devices. The future networks, 5G, will be even faster with a stable connection, further revolutionizing virtual reality, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
Another connectivity technology in wide use is Radio Frequency Identification, which is used very extensively in logistics and inventory management. RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Businesses are able to streamline their processes, reduce errors, and increase efficiency in the tracking of goods and assets through this technology.
Lastly, Ultrawideband technology has recently drawn attention because of its accurate location tracking capabilities as well as high-speed data transfer over relatively short distances. In various applications in asset tracking, smart homes, and augmented reality, UWB will be very useful and may surpass other technologies in certain respects.
Connectivity technologies are diversified. Each kind of technology provides some benefits over others in particular applications. From location tracking and low-power communication to high-speed data transfer and precise positioning, the future of device interaction and communication is taking shape with these technologies.
By Component
The market is broken into two major categories: hardware and software. These categories are also crucial to determine the overall landscape in that market. Hardware refers to devices and equipment; this can be as simple as servers and computers or as complex as keyboards, monitors, and printers used as peripherals. It is basically the tangible aspects of any infrastructure using technology. Without proper hardware, the most advanced software would be of no use and could not operate. So, hardware demand is still high due to technological improvements and the requirement for a more powerful, efficient device.
Software, on the other hand, refers to the applications or programs that run on the hardware. Software is simply a set of instructions telling the hardware how to perform particular functions. From operating systems that include Windows and macOS down to specialized applications for a business, entertainment, or educational purpose, software brings this hardware to life. It adds functionality that users rely on every day, whether it is handling data, creating content, or performing calculations. The increasing demand for software arises since more industries are coming into the realization that digital solution can help streamline operations and further productivity.
Hardware and software always go hand in hand. New software applications might require more powerful hardware to run effectively. Likewise, new hardware improvements could lead to the development of more advanced software. These two elements, therefore, are important to the technological advancement process. As an instance, when software is getting complex, it might necessitate faster processors, greater memory, and better storage capacity, which leads to the advancement in hardware design. Conversely, the latest hardware designs open up the opportunity to write more sophisticated programs that truly leverage the capabilities.
Competing for the most innovative product, in the hardware versus software environment, is an extremely demanding task. Hardware and software companies cannot help but continuously innovate while pushing the boundaries of what currently exists. Growth is spurred by new technologies like AI and machine learning. The increasing demand for connected devices and smart solutions further highlights how important having both high-quality hardware and innovative software remains. As more businesses and customers seek more holistic and integrated experience, the need to collaborate between those who are hardware and those who are software will continually grow, in turn shaping future market changes.
By Distribution Channel
The global Smart Tracker market is segmented into several distribution channels, each of which is very important in its growth and reach to consumers. Such channels include Online Retail, Offline Retail, Direct Sales, and OEM Partnerships. Each of these distribution methods has a specific purpose, providing different benefits to businesses and consumers.
Online retail is one of the most important distribution channels in the Smart Tracker market. In comparison, online shopping through various online platforms provides ease and wide accessibility for consumers. Since competition is highly prevalent online and prices tend to be cheap with many alternatives, buyers mostly flock online. With review access, price comparisons, and promotions on the online marketplace, the smart trackers were sold across the entire supply chain through this platform as well.
Offline retail is an important distribution channel for smart trackers. Most consumers still go to physical stores, and they prefer to see products before buying them. Such a direct experience, which can give a person the feel of handling a product, is much more valuable to people looking to assess the quality or functionality of a smart tracker in person. Brick-and-mortar locations like electronics shops and even department stores provide a mode of access and convenience beyond just the internet.
Direct sales is another key method of distribution, whereby the manufacturer or brand sells directly to the consumer. This model removes the need for intermediaries, and companies can have closer relationships with their customers. Companies can offer more personal experiences, provide customized solutions, and develop brand loyalty through direct engagement with consumers. Direct sales are usually used for premium products or special services where a closer connection with the consumer is useful.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) partnerships are also essential in the Smart Tracker market. This model involves partnering with other manufacturers or businesses to integrate the product into third-party devices or services. Such partnerships can reach a wider distribution and market penetration. Smart tracker manufacturers can reach a broader consumer base and increase their visibility in the market by partnering with established brands or large companies.
Ultimately, the global Smart Tracker market works best via a combination of these kinds of distribution channels to access buyers. Each has its distinct merits, whether it be convenient online retail, tactile exposure provided by offline shopping, intimacy through direct sales, or the additional reach brought in from OEM partnerships. As all these methods help deliver these products to a huge spectrum of consumers, these ensure that companies meet all customers' needs.
|
Report Coverage |
Details |
|
Forecast Period |
2024-2031 |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
$ 3,550 million |
|
Market Size by 2031 |
$5,606 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2024 to 2031 |
9.8% |
|
Base Year |
2022 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific Green, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
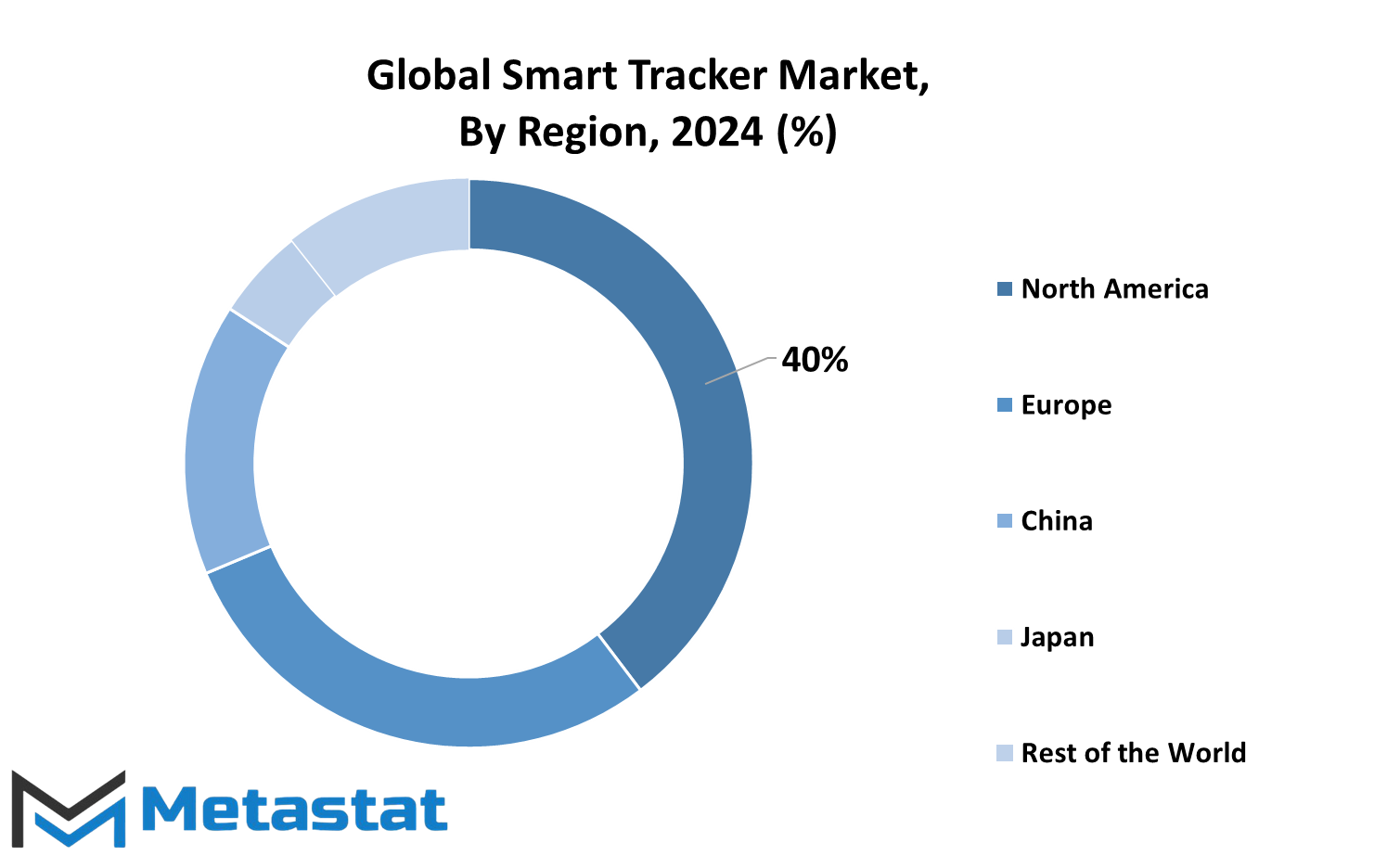
The Smart Tracker market is divided into different regions, each having its unique features. These regions include North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East & Africa. North America is further divided into three key countries: the United States, Canada, and Mexico. This division enables a detailed understanding of the market's performance and trends in each of these nations, reflecting their unique consumer behaviors and technological advancements.
Europe is another significant region, divided into several major markets. These include the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, and a broader category referred to as the Rest of Europe. Rest of Europe" comprises the smaller markets which may not individually be the most interesting but collectively may contribute toward the region's overall market size and potential growth. This segmentation gives a thorough view of the Smart Tracker market across the continent, considering leading economies along with emerging ones.
Asia-Pacific markets are further divided in this region into key countries including India, China, Japan, and South Korea. The "Rest of Asia-Pacific" category includes other countries within this region that do not enjoy the same market presence of these top nations but contribute towards market growth. This segmentation is important, as Asia-Pacific remains one of the fastest-growing regions for the Smart Tracker market, supported by growing consumer demand and technological innovation.
South America is also another region, where the market of Smart Tracker is mainly concentrated around countries like Brazil and Argentina. These two countries alone dominate the market in South America, but there is also another broader category for other nations that fall under the category Rest of South America. Such a broader category would highlight that growth in smaller markets is developing.
Last, the Middle East & Africa region is broken into the sub-regions: GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and the Rest of Middle East & Africa. Such regional divisions indicate varied economic patterns and different adoption levels of technologies within the Middle East and Africa regions. Segmentation by these categories will enable an easy grasp of regional differences and understanding of which aspects contribute to the growth of regions around the world. This geographical segmentation of the Smart Tracker market provides a clear and comprehensive overview of the industry’s dynamics across various regions.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
In recent years, the Smart Tracker market has grown rapidly with more big key players who still help promote innovation and competition within this market. They consist of devices that are intended to help users trace various kinds of personal belongings like keys, wallets, and even pets, which are popular among their customers because of the simplicity they offer. Companies like Tile, Inc. and Tracki have long been recognized for their contribution to this cause, bringing reliable solutions to consumers that want to keep track of important items. Apple Inc., with AirTag, joins the market, offering the advanced version of the tracker that fits well into the company's ecosystem of devices. Another leader is Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., which can be regarded as a global giant with its smart trackers, rivaling those in Apple terms of features and functionality.
The other companies emerged to compete on the market place, among them Chipolo and Spy Tec, which compete by giving their own varieties of tracking devices. For example, Chipolo is recognized for its colorful designs and easy interface, while Spy Tec specializes in more advanced tracking features for personal and business use. Jiobit is another key player in this niche, specializing in tracking devices for children and pets, with a smaller, more portable device designed for specific tracking needs. Other brands to mention include Vyncs, Trak-4, and Gpswox Ltd. Each contributes toward the industry by providing more specific tracking solutions that integrate GPS. They provide various specialized services such as vehicle tracking and fleet management. Some other companies like Locatify and Honeywell International Inc. have also introduced some newer areas like asset management and safety applications beyond what smart trackers could provide initially.
These producers further penetrate the market as HUAWEI Technologies Co., Ltd., Shenzhen Woxu Technology Co., Ltd., and Amaryllo Inc., among many others, create innovative looks towards giving the mass market, relatively low-cost variants without an associated compromise with quality and offer affordability and functional tracking as a package provided by Nonda Co., Ltd.
Such diverse products and innovative technologies at these companies will continue to mold the Smart Tracker industry, which shows no sign of slowing down. With increased adoption of these devices into everyday life, the market will probably expand, urging more companies to enter and develop products that meet this growing demand for security, convenience, and peace of mind.
Smart Tracker Market Key Segments:
By Type
- GPS Trackers
- Bluetooth Trackers
- RFID Trackers
- Cellular Trackers
- Hybrid Trackers
By Connectivity Technology
- GPS-Based
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
- Wi-Fi-Enabled
- Cellular (4G/5G)
- RFID
- Ultra-Wideband (UWB)
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
By Distribution Channel
- Online Retail
- Offline Retail
- Direct Sales
- OEM Partnerships
Key Global Smart Tracker Industry Players
- Tile, Inc.
- Tracki
- Apple Inc. (AirTag)
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Chipolo
- Spy Tec
- Jiobit
- Vyncs
- Trak-4
- Gpswox Ltd.
- Locatify
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Logistimatics
- HUAWEI Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Shenzhen Woxu Technology Co., Ltd.
- Amaryllo Inc.
- Nonda Co., Ltd.
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential








 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






