MARKET OVERVIEW
The global contingent workforce management market is a niche area of the workforce solutions market that will concentrate on the management, coordination, and optimization of non-permanent labor internationally. It will help handle the increased demand for companies to manage freelancers, temporary workers, independent contractors, and project-based teams across various regions and regulatory environments. Contrary to conventional employment management, it will incorporate sophisticated systems and models of service to manage short-term pools of talent with operational efficiency and compliance with differing local labor regulations.
Fundamentally, the global contingent workforce management market will act as a middle ground for organizations and the varied external talent they will need to respond to varying operational needs. It will bring together technology platforms, vendor management systems, compliance tracking, and analytics to better how firms source, onboard, manage, and compensate these workers. With organizations going global, the market will help businesses thrive by enabling them to remake workforce strategies quickly without the limitations of traditional permanent hiring models.
The global contingent workforce management market in the future won't just facilitate transactions but also give firms the actionable insights that will enable them to forecast talent requirements, determine cost structures, and avoid legal liability. The technologies and services provided will be tailored to consolidate processes across borders, where differences in tax structures, employment categories, and cultural practices might otherwise cause inefficiencies or exposure. An effectively managed contingent workforce strategy will assist companies in staying flexible while protecting compliance in a business world that will grow increasingly interconnected.
This market will also serve as a strategic partner to organizations making their way through the change towards more agile talent models. As project-based work and remote work will be more common, companies will depend on sophisticated platforms that unify the management of a varied external workforce. These platforms will deliver insight into worker performance, contract schedules, and budget use, so decision-makers will have the details to allocate assets effectively.
On a larger canvas, the global contingent workforce management market will represent the convergence towards operational styles wherein talent would be contracted on a skills-and-availability basis rather than geographic location or long-term contractual obligations. Firms will go beyond local pools of talent and access specialized skill sets across regions while having a unified oversight framework. The capacity to reconcile processes across continents will be a determining aspect in the success of this market.
As companies will further diversify their labor plans, the global contingent workforce management market will be a model for attaining scalability without compromising control or compliance. It will expand beyond being a procurement function to becoming a central corporate strategy component, driving the way businesses will strategize, implement, and modify their workforce models in an aggressive global marketplace. Within this changing environment, the value in the market will be its ability to marry dynamic talent needs with effective, compliant, and technology-driven workforce solutions.
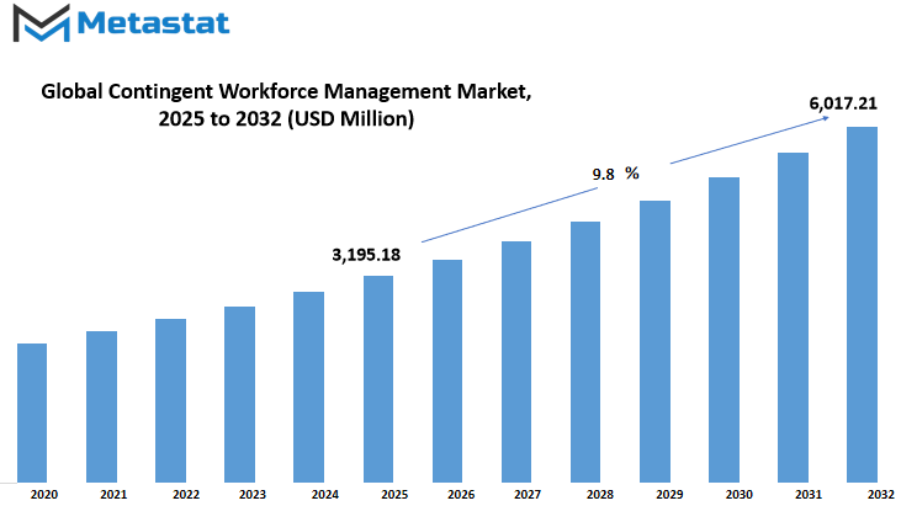
Global contingent workforce management market is estimated to reach $6,017.21 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The global contingent workforce management market is expected to register consistent growth in the future as companies continue to change with respect to workforce needs. Growth drivers such as growing adoption of flexible staffing solutions and advancements in workforce management technology are leading the change. Organizations are generally realizing the benefit of contingent workers in meeting short-term needs, reducing overhead costs, and gaining specialized knowledge. More businesses are expanding globally, increasingly requiring effective management of contract and temporary staff, thereby propelling the market into the upward trend. Technology integration is going to be one of the strongest drivers shaping the future of the market.
Digital platforms that automate recruitment, onboarding, performance tracking, and compliance processes are helping businesses manage their contingent workforce with greater ease. In addition, greater focus on data-driven decision-making is forcing companies to utilize analytics solutions to predict manpower needs, monitor employee performance, and increase operational efficiency. The need for greater workforce agility is also escalating as companies want to scale up their employees quickly in response to changing market conditions without making long-term commitments. However, some issues are hindering the development of the market. Regulatory compliance is a large concern, especially since labor laws change with geography and are subject to continuous updates.
Firms must make sure that the contingent laborers are correctly classified to avoid legal punishment and also reputational loss. A potential obstacle is a lack of integration among contingent workforce platforms and other human resource systems. With no connection, companies run the risk of inefficiency and data silos which hamper decision-making and overall performance.
There are promising developments on the horizon despite these challenges. Growing international acceptance of remote work is building a larger talent pool for businesses to draw from, regardless of geographical boundaries. Such a change allows business companies to obtain access to highly trained personnel from other regions while cutting on the costs associated with physical office space.
Moreover, the increasing use of artificial intelligence and automation in managing labor will further improve recruitment functions, improve workforce planning, and even enhance the overall employee experience. In the future, the global contingent workforce management market will gain as organizations require greater flexibility and efficiency in staffing processes. Even though compliance challenges and system integration must be overcome, technology innovation and remote job opportunities suggest good growth opportunities. With businesses still balancing flexibility and productivity, there will be a corresponding growth in the demand for effective contingent workforce management solutions.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Type
The global contingent workforce management market is gaining more attention as businesses continue to change how they hire and manage talent. This market focuses on strategies, tools, and services that help organizations handle both permanent and flexible staffing needs more effectively. By type, it is divided into permanent staffing and flexible staffing, each playing an important role in meeting the goals of modern companies. Permanent staffing ensures that businesses have a stable core team with long-term expertise, while flexible staffing allows them to adjust quickly to changes in demand, seasonal needs, or special projects. The balance between these two approaches is becoming more important as companies plan for the future.
In the coming years, the global contingent workforce management market will likely see strong growth because businesses want to be more adaptable. Technology will play a key role in making hiring faster, managing performance more efficiently, and connecting companies with skilled professionals anywhere in the world. Automation and artificial intelligence will help in screening candidates, matching skills to roles, and tracking productivity. At the same time, human decision-making will remain essential for building trust, understanding company culture, and supporting employee well-being.
Global competition for talent is increasing, and this will push organizations to rethink how they approach staffing. Permanent staffing will remain the backbone for critical roles that need deep expertise and consistent leadership. However, flexible staffing will become more valuable for handling unexpected changes, such as sudden market shifts or new business opportunities. This shift will also help companies reduce costs while maintaining access to a large pool of skilled workers.
From a futuristic viewpoint, the global contingent workforce management market will not just be about filling positions; it will be about creating an agile, resilient workforce. Companies will use advanced data analytics to forecast staffing needs before they arise. This will allow them to plan better, avoid skill shortages, and respond to global events more effectively. Flexible staffing will expand beyond temporary contracts to include highly skilled consultants, project-based experts, and remote professionals who can be onboarded within days.
In the long term, this market will shape how work is structured worldwide. As more businesses adopt hybrid staffing models, they will be able to innovate faster, enter new markets, and respond to customer needs with greater speed. The organizations that succeed will be those that use both permanent and flexible staffing in a way that supports growth, stability, and adaptability in an increasingly competitive environment.
By Organization Size
The global contingent workforce management market is steadily gaining importance as businesses look for flexible ways to meet their staffing needs. This approach allows companies to employ skilled professionals on a temporary, project-based, or freelance basis, giving them the freedom to adjust their workforce according to demand. By organization size, the market is divided into Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) and Large Enterprises, each having different needs and strategies when it comes to managing contingent workers. SMEs often use this model to fill skill gaps without committing to long-term contracts, while large enterprises adopt it to handle large-scale projects, seasonal requirements, or specialized roles.
Looking ahead, the future of the global contingent workforce management market will be shaped by the growing adoption of digital platforms and artificial intelligence to connect businesses with talent faster and more efficiently. For SMEs, advanced workforce management tools will make it easier to compete with larger companies for highly skilled professionals, as automation will reduce the time and cost involved in recruitment. These businesses will also benefit from analytics that help predict staffing needs, ensuring that they can respond quickly to market changes. Large enterprises, on the other hand, will continue to invest in integrated management systems that allow them to track performance, compliance, and productivity across a global pool of workers.
The rise of remote work will further expand the reach of the global contingent workforce management market. Geographic barriers will matter less, enabling businesses to tap into talent from anywhere in the world. SMEs will use this opportunity to access expertise that may not be available locally, while large enterprises will use it to build diverse and specialized teams for complex projects. This shift will also encourage the development of more secure digital infrastructures to protect sensitive business data when working with external contractors.
In the coming years, sustainability and ethical employment practices will also influence the market’s growth. Businesses will not only look for efficiency but also focus on creating fair and transparent working conditions for contingent workers. Technology will help monitor these standards, ensuring compliance with regulations in different countries. As more companies recognize the value of a well-managed contingent workforce, the demand for reliable management solutions will grow, pushing the industry toward continuous innovation.
The global contingent workforce management market will keep evolving to meet the needs of both SMEs and large enterprises. With technology, global connectivity, and changing work preferences shaping its path, it will become an essential part of modern business strategies in the years ahead.
By End-user Industry
The global contingent workforce management market is gaining attention as organizations increasingly look for flexible and cost-effective ways to meet their staffing needs. Businesses across different industries are relying on contingent workers such as freelancers, contract employees, and temporary staff to adapt to changing market demands. This shift is driven by the need for agility, specialized skills, and reduced long-term commitments. With rapid technological progress and evolving business strategies, the role of contingent workforce management will continue to grow, creating opportunities for companies to streamline operations while accessing a wider talent pool.
By end-user industry, the global contingent workforce management market is expanding across sectors such as Information Technology (IT) and Telecom, BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance), Healthcare and Life Sciences, Manufacturing, Retail and E-commerce, and other fields. In IT and Telecom, demand for contingent workers is rising due to the fast pace of digital transformation, frequent project-based work, and the need for specific technical expertise. In BFSI, contract professionals are being used for regulatory compliance, risk management, and customer experience projects, where skills must be updated quickly to match new regulations and technologies. Healthcare and Life Sciences benefit from contingent workers in areas like research, diagnostics, and patient care support, where demand can fluctuate depending on public health needs and medical advancements.
Manufacturing is seeing contingent workforce growth for roles in production, supply chain management, and maintenance, allowing companies to respond swiftly to demand spikes without overextending permanent staffing. Retail and E-commerce use flexible workers to handle seasonal peaks, order fulfillment, and customer service, especially with the ongoing expansion of online shopping. Other industries, including energy, education, and logistics, are also finding value in contingent workforce strategies, particularly in regions experiencing economic shifts or infrastructure development.
Looking ahead, the global contingent workforce management market will be shaped by advancements in workforce analytics, artificial intelligence, and digital platforms that connect companies with skilled workers faster than ever before. Businesses will increasingly use data to predict staffing needs, evaluate worker performance, and improve efficiency. The rise of remote work will make it easier for organizations to tap into global talent without geographic restrictions, while also encouraging new approaches to compliance, security, and collaboration.
This market’s future will not only depend on technology but also on how well organizations can balance flexibility with fair labor practices and worker satisfaction. Companies that adopt innovative, ethical, and data-driven workforce strategies will be better positioned to thrive in a competitive and changing economic landscape.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$3,195.18 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$6,017.21 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
9.8% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific Green, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
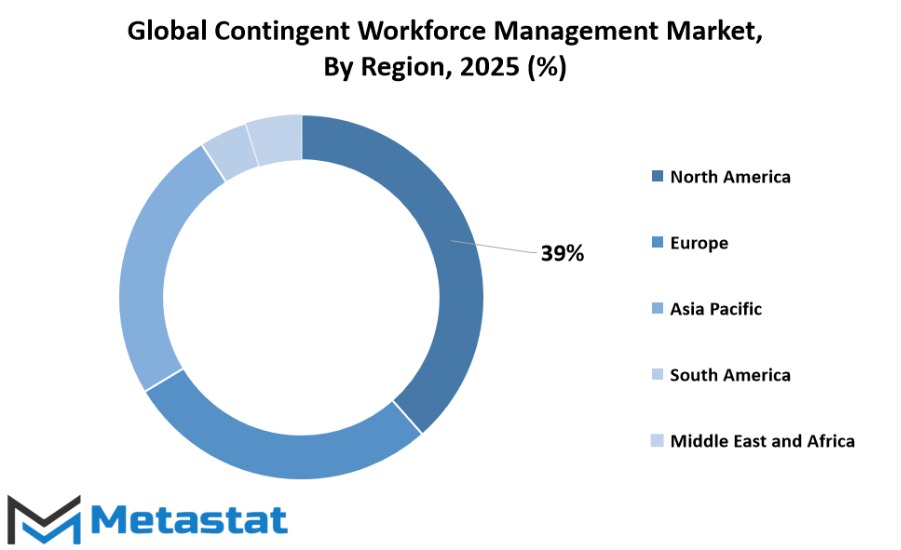
The global contingent workforce management market is steadily gaining importance as businesses across the world adapt to changing labor trends and increasing reliance on flexible work arrangements. As companies seek efficiency, scalability, and specialized skills, contingent workforce solutions will play a central role in future employment strategies. The market, when analyzed geographically, shows distinct patterns and opportunities for growth across different regions.
North America remains one of the most advanced regions in terms of adoption. The United States, Canada, and Mexico are increasingly using technology-driven platforms to streamline contingent hiring, compliance, and workforce analytics. The U.S., in particular, will likely maintain a leadership position due to its mature business infrastructure and emphasis on innovation. Canada is also expected to experience steady growth, driven by the rising demand for specialized contractors, while Mexico is attracting interest for cost-effective talent solutions that appeal to multinational companies.
In Europe, countries such as the UK, Germany, France, and Italy are witnessing growing acceptance of contingent workforce solutions, particularly in technology, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors. The UK’s flexible labor regulations and Germany’s engineering expertise will likely make them significant players, while France and Italy are showing increased interest in remote and project-based work models. The rest of Europe is gradually catching up, with smaller markets adopting these solutions to remain competitive in a globalized economy.
Asia-Pacific, with its vast and diverse workforce, presents a major growth opportunity. India, China, Japan, and South Korea are experiencing rapid expansion in contingent workforce usage, driven by digital transformation, outsourcing trends, and the need for industry-specific expertise. India’s large talent pool in IT and customer support will continue to attract global demand, while China’s manufacturing and technology sectors will push for more agile workforce strategies. Japan and South Korea, facing demographic shifts and evolving labor needs, are turning to flexible staffing models to maintain productivity. The rest of Asia-Pacific is showing promising signs as emerging economies embrace more adaptable work arrangements.
South America, led by Brazil and Argentina, is integrating contingent workforce solutions into industries like energy, agriculture, and finance. While economic challenges may affect adoption rates, the region’s growing digital infrastructure will open new opportunities for managed workforce services.
In the Middle East & Africa, GCC countries, Egypt, and South Africa are investing in modern workforce management tools to support large-scale projects and diversification efforts. As governments push for economic transformation, contingent workforce models will become vital in meeting shifting labor demands. This global shift signals a future where adaptability and technology will define workforce strategies worldwide.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The global contingent workforce management market is shaping the future of how organizations hire, manage, and retain talent. This market is not just responding to immediate business needs but is also creating systems that will redefine workforce planning in the years ahead. With the growth of project-based roles, freelance professionals, and flexible staffing models, companies are seeking solutions that combine efficiency, transparency, and adaptability. This shift is encouraging competitive players to develop more advanced platforms and services, aiming to give businesses better control over their contingent talent while offering workers more flexible opportunities.
Among the major players, SAP SE continues to expand its technological solutions, providing tools that integrate with broader enterprise systems. Magnit is driving innovation with data-driven insights, helping organizations optimize performance and spending. Coupa Software Inc focuses on procurement and expense management, extending its reach into workforce solutions. IMPARTX and KellyOCG bring expertise in connecting global talent pools with companies that require specialized skills. Randstad Sourceright and Beeline offer end-to-end management solutions, while ManpowerGroup Solutions and Pontoon Solutions emphasize matching the right talent with the right projects efficiently. Allegis Global Solutions combines recruitment strategy with operational excellence, and Upwork has built a platform that empowers freelancers and employers to connect seamlessly.
Ramco Systems Ltd is leveraging automation and AI to streamline workforce administration, while Avature offers highly customizable recruitment technology. CXC Global focuses on compliance and contractor engagement, ensuring smooth cross-border operations. Hays Talent Solutions and PeopleScout are enhancing their capabilities to meet rising demand for scalable hiring models. AMS (Alexander Mann Solutions) is using its expertise to create tailored workforce programs, while Guidant Global focuses on delivering flexible staffing strategies. FlexTrack is developing solutions to track and manage contingent workers effectively, and SIA (Staffing Industry Analysts) plays a vital role in research and insights that guide the market.
Looking ahead, these competitive players are expected to push the boundaries of automation, predictive analytics, and AI integration. Future systems will likely provide real-time workforce visibility, predictive hiring needs, and advanced compliance management for multinational operations. This evolution will make contingent workforce strategies more proactive, allowing companies to secure skilled professionals faster and with greater accuracy. The global contingent workforce management market will not only influence how talent is sourced and managed but will also shape the balance between flexibility and stability in modern employment. As organizations embrace this future, the leading players will keep refining solutions that bridge business goals with the growing preference for flexible and remote work arrangements.
Contingent Workforce Management Market Key Segments:
By Type
- Permanent Staffing
- Flexible Staffing
By Organization Size
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Large Enterprises
By End-user Industry
- Information Technology (IT) and Telecom
- BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance)
- Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Manufacturing
- Retail and E-commerce
- Others
Key Global Contingent Workforce Management Industry Players
- SAP SE
- Magnit
- Coupa Software Inc
- IMPARTX
- KellyOCG
- Randstad Sourceright
- Beeline
- ManpowerGroup Solutions
- Pontoon Solutions
- Allegis Global Solutions
- Upwork
- Ramco Systems Ltd
- Avature
- CXC Global
- Hays Talent Solutions
- PeopleScout
- AMS (Alexander Mann Solutions)
- Guidant Global
- FlexTrack
- SIA (Staffing Industry Analysts)
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential







 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






