MARKET OVERVIEW
The Global Ship Leasing market plays a crucial role in the international trade and transportation landscape. It involves the practice of leasing ships, primarily to carry goods and commodities across the world's seas and oceans. This market has witnessed significant growth and transformation over the years, becoming an integral part of the global trade infrastructure.
The Global Ship Leasing market caters to a diverse set of clients, ranging from multinational corporations to small businesses involved in the import and export of various products. The market encompasses various types of vessels, such as container ships, bulk carriers, and oil tankers, each designed to transport specific types of cargo efficiently. The demand for these vessels is closely linked to global trade patterns, and it fluctuates with economic conditions, geopolitical factors, and shifts in supply chains.
Ship leasing offers a flexible and cost-effective solution for companies that need to transport goods by sea without the significant capital investment required to purchase a vessel. It allows businesses to access a wide range of vessels tailored to their cargo requirements. This flexibility is particularly valuable in an ever-changing global market where shipping needs can vary considerably from one region or season to another.
The dynamics of the Global Ship Leasing market are influenced by factors like the global economic situation, international trade agreements, and environmental regulations. Additionally, geopolitical tensions and disruptions, such as the closure of key trade routes, can have a profound impact on the demand and supply of vessels for lease. This makes the market highly responsive to both short-term and long-term global trends.
Moreover, the industry has witnessed notable developments in recent years, particularly concerning environmental sustainability. With increasing awareness of the ecological impact of maritime transportation, many ship leasing companies have started adopting eco-friendly technologies and practices. They are exploring the use of alternative fuels and optimizing vessel designs to reduce emissions, aligning with international efforts to combat climate change.
In conclusion, the Global Ship Leasing market is an integral component of the modern global trade landscape, offering flexibility and accessibility to businesses that require maritime transportation. It is a dynamic and responsive sector that reflects the ever-changing nature of international trade, economics, and environmental concerns. As global trade continues to evolve, the ship leasing industry will remain a critical player in facilitating the movement of goods across the world's oceans.
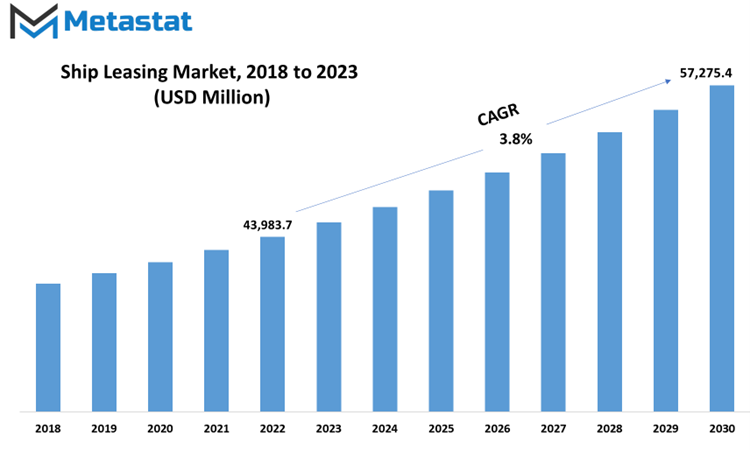
Global Ship Leasing market is estimated to reach $57,275.4 Million by 2030; growing at a CAGR of 3.8% from 2023 to 2030.
GROWTH FACTORS
The Ship Leasing market is experiencing robust growth, primarily driven by its cost-efficiency and flexibility. This modern approach to acquiring vessels has supplanted the traditional practice of outright vessel purchase, offering a more resourceful means for companies within the maritime sector to manage their financial assets. The transition to leasing over ownership eliminates the substantial upfront investment, thereby freeing capital for strategic deployment elsewhere. This newfound financial flexibility empowers companies to navigate economic uncertainties more adeptly. Furthermore, ship leasing's hallmark feature is its ability to cater to the ever-fluctuating market conditions, allowing for the seamless scaling of fleets according to the demands of the shipping market, thus optimizing operational efficiency.
The Ship Leasing industry is further stimulated by the expansion of global trade. International trade has become a pivotal driver of economic growth, underlining the heightened requirement for maritime transportation. As global trade volumes swell, the need for efficient cargo movement escalates. Ship leasing is ideally positioned to offer a responsive solution to the continually shifting cargo requirements. Businesses can efficiently and swiftly adjust their fleet sizes to accommodate cargo demands, ensuring a streamlined operation that culminates in customer satisfaction.
However, alongside these opportunities, there are restraints that impact on the Ship Leasing market. The inherent dynamism of global trade engenders challenges for maritime transport companies. The fluctuations in cargo volumes necessitate a level of flexibility that traditional vessel ownership struggles to provide. Ship leasing offers an effective solution through its capacity for dynamic fleet adjustments. Nevertheless, this solution entails vigilance and adaptability from both lessors and lessees to effectively manage these oscillating demands.
In addition to market fluctuations, regulatory compliance looms as a substantial restraint in the Ship Leasing market. The maritime industry operates under a complex web of regulations aimed at safeguarding safety, security, and environmental responsibility. The relentless evolution of global environmental standards mandates that ships conform to stringent emission, fuel usage, and waste disposal requirements. These ever-changing regulations can impact operational procedures and leasing terms. Both lessors and lessees are confronted with the intricate task of navigating these mandates, necessitating the integration of green technologies, which, in turn, can bring about complexities in cost allocation and technological adaptation.
Despite these challenges, the Ship Leasing market presents promising opportunities. Sustainable Shipping Initiatives have emerged as a compelling prospect. The heightened global environmental consciousness, evolving regulations, and evolving consumer preferences have stimulated increased demand for eco-friendly vessels that not only adhere to environmental standards but surpass them. Companies that invest in modernizing their fleets with environmentally conscious technologies are well-positioned to emerge as pioneers in this burgeoning segment. Offering energy-efficient, low-emission, and eco-friendly vessels is not just in alignment with sustainability objectives but also appeals to environmentally conscious customers. Embracing sustainability can lead to enhanced brand reputation and a competitive edge in a market that increasingly values responsible consumption.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Vessel Type
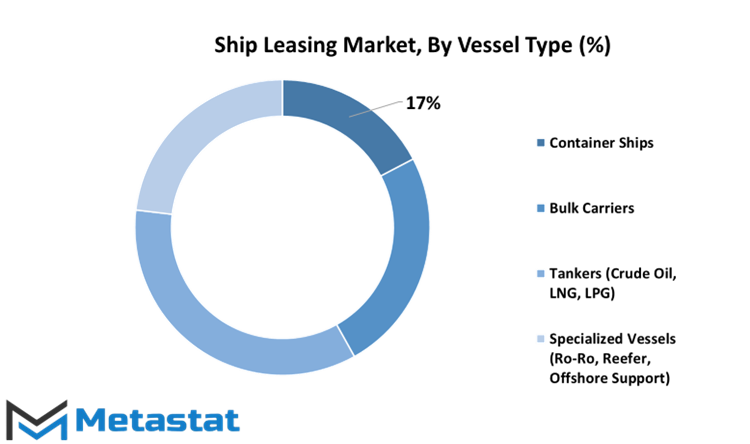
The Ship Leasing Market is a dynamic arena where various vessel types play a significant role. In 2022, the market exhibited varying values across different segments, reflecting the diverse nature of this industry.
The Container Ships segment stood at a value of 7581.7 USD Million in 2022. These vessels, designed for efficiently transporting standardized cargo containers, have a substantial presence in the global shipping landscape. Their value in the market is a testament to their importance in facilitating global trade.
Bulk Carriers, another vital category in the Ship Leasing Market, accounted for a value of 10315.2 USD Million in 2022. These ships specialize in transporting bulk cargo such as coal, grain, and minerals. Their significant market value emphasizes their role in the transportation of essential raw materials and goods.
Tankers, encompassing Crude Oil, LNG, and LPG carriers, comprised a segment valued at 15474.8 USD Million in 2022. These vessels are crucial for the global energy supply chain, transporting various forms of liquid energy resources. Their substantial market value highlights their role in ensuring a steady flow of these resources worldwide.
The Specialized Vessels segment, which includes Ro-Ro (Roll-on/Roll-off), Reefer (Refrigerated), and Offshore Support vessels, was valued at 9075.5 USD Million in 2022. These specialized vessels cater to specific cargo and operational requirements, reflecting the diverse needs of industries and regions.
In conclusion, the Ship Leasing Market is a complex and multifaceted industry with distinct segments, each contributing significantly to global trade, resource transportation, and specialized cargo needs. The varying values within these segments underscore their individual importance in the broader context of the maritime transportation sector.
By Lease Duration
The Ship Leasing Market encompasses a variety of lease durations that play a significant role in the maritime industry. These lease durations include Short-Term Lease (less than 1 year), Medium-Term Lease (1-5 years), and Long-Term Lease (more than 5 years).
In 2022, the Short-Term Lease (less than 1 year) segment of the Ship Leasing Market held a value of 13,688.6 USD Million. This segment is characterized by its brief lease duration, making it suitable for businesses and industries that require ships for short, immediate needs. It offers flexibility to adapt to changing demands without a long-term commitment.
On the other hand, the Medium-Term Lease (1-5 years) segment was valued at 15,377.2 USD Million in 2022. This category provides a middle-ground option for businesses that anticipate the need for ships over a more extended period but prefer not to commit to a long-term lease. It strikes a balance between flexibility and stability.
The Long-Term Lease (more than 5 years) segment, with a value of 13,381.3 USD Million in 2022, is designed for businesses with consistent, long-term shipping requirements. It offers stability and cost-efficiency, as long-term leases often come with lower rates and the assurance of having the required vessels available for an extended duration.
These segments reflect the diverse needs and preferences of businesses in the maritime sector. Whether a company requires ships for short, medium, or long durations, the Ship Leasing Market offers tailored solutions to meet their specific demands. This diversity in lease durations is a testament to the adaptability and customer-centric nature of the maritime industry, ensuring that businesses can access the vessels they need, precisely when they need them
By Lease Type
The Ship Leasing Market is a dynamic and multifaceted domain where various lease types play a pivotal role. These lease types cater to distinct needs and circumstances, shaping the landscape of the market. Bareboat Charter, Time Charter, Financial Lease, and Others represent the four primary segments of the Ship Leasing Market, each with its unique characteristics and market values.
The Bareboat Charter segment, valued at 13,845.9 USD million in 2022, is a lease arrangement where the lessee gains full control and possession of the ship. In this scenario, the lessee effectively becomes the temporary owner and assumes responsibility for the ship's operation and maintenance. This lease type provides a high degree of flexibility and autonomy to the lessee, allowing them to use the ship as if it were their own.
The Time Charter segment, on the other hand, was valued at 6,867 USD million in 2022. In a Time Charter, the lessee gains possession of the ship for a specific period, typically a set number of months or years. However, the ship's owner retains ownership, and maintenance and operation responsibilities usually rest with them. Time charters offer lessees a fixed period of use, allowing them to employ the ship for their needs during this defined timeframe.
The Financial Lease segment is valued at 17,019.4 USD million in 2022, making it one of the prominent segments in the Ship Leasing Market. In a financial lease, the lessee effectively enjoys many of the benefits and responsibilities of ship ownership. However, ownership technically remains with the lessor until the lease agreement's end when the lessee often has the option to purchase the ship at a predetermined price. This lease type is especially popular for lessees who intend to possess the ship eventually but prefer to spread the financial burden over time.
The others segment, valued at 4,714.9 USD million in 2022, encompasses various alternative leasing arrangements that do not fit neatly into the categories of Bareboat Charter, Time Charter, or Financial Lease. These "others" may include niche or hybrid lease types, which are tailored to specific requirements and circumstances.
Each of these segments caters to distinct needs within the ship leasing market, offering lessees a range of options to acquire and utilize vessels. This segmentation allows businesses to select the lease type that aligns with their operational and financial objectives, providing flexibility and diversity within the broader Ship Leasing Market. The market's overall health and vitality are influenced by the interplay and performance of these segments, reflecting the diverse demands and strategies of companies involved in ship leasing.
By End-User
The global Ship Leasing market is a diverse landscape with a range of end-user industries steering its course. These industries play a pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of the ship leasing market. Among the leading contenders in this market, the Oil and Gas sector is a heavyweight, having been valued at a substantial 8501.2 USD Million in the year 2022. The demand for shipping vessels in this industry is driven by the need for the transportation of oil, gas, and related products across vast distances.
The Manufacturing and Industrial sector, valued at 6983.5 USD Million in 2022, follows closely. It relies heavily on ship leasing services for the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products. This sector's reliance on efficient and cost-effective shipping is evident in its significant market presence.
The Automotive industry, which was valued at 5670.4 USD Million in 2022, also finds its footing in the ship leasing market. It leverages vessel transportation for the export and import of vehicles, parts, and components, making it an indispensable end-user industry. The Agriculture and Food sector, valued at 6813.9 USD Million in 2022, significantly contributes to the ship leasing market. It depends on shipping for the import and export of various food products, ensuring a steady supply chain in a globalized food market.
At the forefront, the Retail and Consumer Goods sector towers with a valuation of 10185 USD Million in 2022. The retail industry relies heavily on efficient logistics and supply chain management, making ship leasing an integral part of its operations.
The Others segment, valued at 4293.1 USD Million in 2022, encapsulates a variety of end-user industries that are not limited to the categories. It is a diverse category that includes various sectors with unique shipping requirements.
In essence, the global Ship Leasing market thrives on its symbiotic relationship with these end-user industries. Their diverse needs, spanning from raw material transportation to consumer goods distribution, fuel the growth and vitality of the ship leasing market. The varying demands and dependencies of these sectors highlight the dynamic nature of the ship leasing market, making it a critical component of the global economy..
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The global Ship Leasing market, concerning geography, is segregated into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World. This geographical division offers a comprehensive outlook on the dynamics of the market.
North America, as one of the key players in the Ship Leasing market, exhibits robust growth. This region's maritime industry is a vital contributor to its economic prosperity. With a strategic location, advanced infrastructure, and a well-established shipping network, North America attracts significant leasing activity in the ship industry.
In Europe, the Ship Leasing market maintains a prominent presence. The continent's extensive coastline, bustling ports, and a strong maritime tradition make it an ideal hub for ship leasing. European countries, including Greece and the United Kingdom, play pivotal roles in the global ship leasing landscape. The European market experiences consistent demand for various types of vessels, from container ships to oil tankers.
Asia Pacific, a region known for its rapid economic expansion and burgeoning international trade, offers a lucrative platform for ship leasing. China, in particular, is a frontrunner in the global ship leasing market. With its colossal demand for imported goods and commodities, China relies on an extensive fleet of leased ships to facilitate its trade operations. This robust maritime activity propels the growth of the ship leasing market in the region.
In the Rest of the World, which encompasses regions outside North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific, the ship leasing market displays a diverse landscape. Various countries with coastal access and active maritime industries engage in ship leasing activities. South America and the Middle East, in particular, have witnessed substantial growth in this sector. They cater to unique demands, such as offshore drilling and oil exploration, contributing to the global ship leasing market's vibrancy.
In summary, the geographical distribution of the global Ship Leasing market offers a profound insight into its vitality and adaptability. Each region, North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World, contributes to the market's resilience and diversity, reflecting the global significance of ship leasing across different parts of the world.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The Global Ship Leasing market is a dynamic and competitive sector where the movement of vessels on the world's waters intersects with the financial intricacies of leasing. This market entails companies and individuals renting ships for various purposes, including transporting goods, commodities, and people across the world's oceans and seas.
Key players operating in the Ship Leasing industry include A.P. Moller - Maersk Group, Mitsui O.S.K., and several other major companies. These industry giants have significant market influence and are deeply involved in the leasing of various types of vessels, from container ships to oil tankers. They cater to the global demand for efficient and reliable means of maritime transport.
A.P. Moller - Maersk Group, a Danish conglomerate, is a prominent player in the Ship Leasing market. With a history dating back to the early 20th century, it has established a global presence and offers a wide range of shipping services. They own and lease container ships, providing crucial support to global trade by facilitating the transportation of goods across the seas.
Mitsui O.S.K., a Japanese corporation, is another significant player in the industry. This company is involved in various aspects of shipping, including ship leasing. Mitsui O.S.K. manages a diverse fleet of vessels, ensuring the smooth flow of goods and resources across international waters.
Both of these key players, along with others in the Ship Leasing industry, play a vital role in global trade and commerce. They provide the vessels that underpin the global supply chain, moving goods from one part of the world to another efficiently and effectively.
The Ship Leasing market's significance cannot be overstated. It is an integral part of the global economy, supporting trade, commerce, and the movement of goods on a massive scale. The key players in this market are the backbone of this industry, enabling the transportation of everything from consumer products to natural resources and energy supplies across the seas. Their role in facilitating global trade makes them essential to the world's economic systems.
Ship Leasing Market Key Segments:
By Vessel Type
- Container Ships
- Bulk Carriers
- Tankers (Crude Oil, LNG, LPG)
- Specialized Vessels (Ro-Ro, Reefer, Offshore Support)
By Lease Duration
- Short-Term Lease (Less than 1 year)
- Medium-Term Lease (1-5 years)
- Long-Term Lease (More than 5 years)
By Lease Type
- Bareboat Charter
- Time Charter
- Financial Lease
- Others
By End-User Industry
- Oil and Gas
- Manufacturing and Industrial
- Automotive
- Agriculture and Food
- Retail and Consumer Goods
- Others
Key Global Ship Leasing Industry Players
- P. Moller - Maersk Group
- Mitsui O.S.K. Lines (MOL)
- COSCO Shipping Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Ocean Yield AS
- Global Ship Lease, Inc.
- Seaspan Corporation
- SFL Corporation Ltd
- Navigator Holdings Ltd.
- Costamare Inc.
- CCB Financial Leasing
- ICBC Leasing
- First Ship Lease Hoiding
- CMB Financial Leasing
- Minsheng Financial Leasing
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential






 US: +1-(714)-364-8383
US: +1-(714)-364-8383






