MARKET OVERVIEW
The global rocket and missile market is growing, there are some issues that may hinder its growth. One of their biggest challenges is the high investment for rocket and missile development and production. These projects cost a lot of research, cutting-edge materials, and skilled labor that could be hard to find. The countries might have budget limitations, hence finding it difficult for smaller countries and private companies to keep up. Along with it, strict government rules related to the export and use of these technologies may develop blocks. Such laws are usually on export to check misuse and control proliferation of hazardous weapons; however, these rules also create roadblocks in establishing a new market and working with international partners.
A well-established sector finds itself undergoing unprecedented transformation amid governments' changing views of global security and defense priorities. This very precision in speed and modernization will no longer apply solely to military applications. In time to come, the art of rocket and missile technology would find uses beyond conventionally established uses wherein it held no operational relevance.
However, while threats and defense contracts have greatly influenced procurement trends in this sector, it is anticipated that the demand for space defense and anti-satellite capabilities along with suborbital launches, by both government and commercial entities, will create new avenues of activity. Thus, with satellite constellations now rapidly increasing in low Earth orbit, this sector must prepare to counter unexpected threats in orbit. Those same rockets that were originally designed for land combat will be modified to counter or dissuade in space, thus shifting the entire technical paradigm and posing demands on new international regimes.
Civil applications will, however, get introduced in due course. Governments and specialized entities will look at missile-grade propulsion technologies for climate monitoring, disaster management, and high-speed cargo delivery. Where infrastructure is inadequate, rapid-response logistics using missile-derived technologies may factor in. While this may seem inapt, implementation will ultimately be possible due to ongoing work, combined with the transfer of technology from defense to civil use. Gradually, research and development outcomes will blur the boundary between offensive application and peaceful utility.
Technologies for simulating battlefield scenarios will increasingly find applications in emergency response and aerospace training. These systems, developed for missile guidance and targeting, would further the development of precision AI models for education, healthcare, and atmospheric sciences. Although purely defense will still be the main driver, non-defense applications will quietly grow and change the perception of this sector away from strategic discussion realms.
In the near future, advancements would also spring not just from government-funded projects or large aerospace firms. Smaller start-ups and independent laboratories will stake their claims in the new competition, bringing new materials, lightweight structures, and reusable means of delivery that defy traditional operating procedures. Their nimbleness and voracious appetite for risk will permit rapid prototyping and experimentation, therefore, respond to shifts in technology and political atmosphere faster than traditional primes.
In time, onlookers standing on the sidelines will see fresh legal, ethical, and environmental issues come to the fore, causing regulatory bodies to reconsider long-standing frameworks. Questions about debris generation, autonomous targeting systems, and jurisdiction within contested airspaces must be addressed.
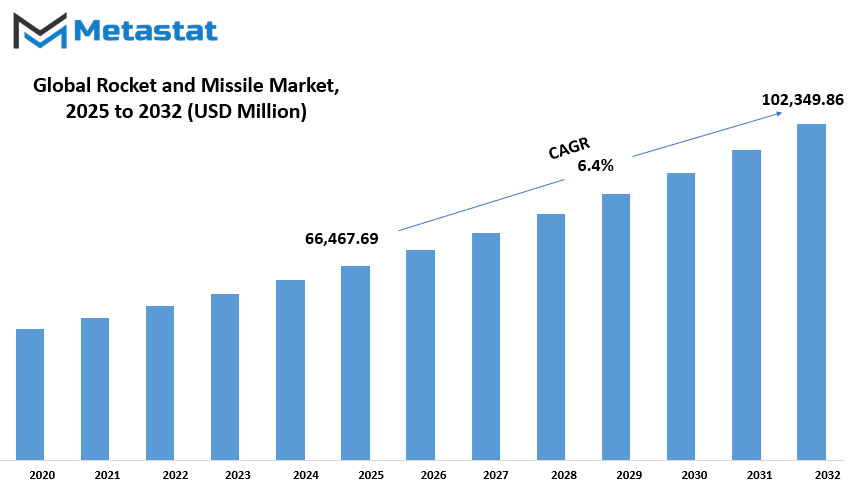
Global Rocket and Missile market is estimated to reach $102,349.86 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The global rocket and missile market has embarked upon a growth trajectory fueled by two very significant reasons. The first one, countries are putting their efforts to modernize military systems and are thus increasing their defense budgets, which cause the nations to invest in advanced missile and rocket technologies. Countries are getting concerned about strengthening their defensive capabilities-the upgradation of old missile systems and design of newer ones that are faster and increasingly reliable. Primarily, it is one of the increasing military power for countries-with also a touch of keeping up with international standards and ensuring security within countries.
Secondly, the first factor which boosts the market is the increasing interest in the exploration of space and then increased commercial satellite launching. Nowadays, private companies and even space agencies of the government come together more often for the development of strong demand rockets that they carry into space with satellites and other cargo. More countries are joining the space race while private firms are working on an ambitious goal of offering commercial space travel in future. This leads to an increase in demand for reliable and reusable rocket systems.
But that does not mean there aren't some very thrilling developments. Breakthroughs in hypersonic technology are poised to revolutionize defense systems-for example, the new missiles that could in theory fly at speeds greater than 5 times that of sound. Besides, on the same line, the introduction of artificial intelligence in missile guidance systems will make these weapons smarter and more efficient. Such developments open up new horizons, creating opportunities for the rocket and missile market in the future. As technology is advancing and interest among counties is up in space and defense, the market shall grow with military needs and commercial aspirations.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Product
With the continuing increase in defense budgets and the need for advanced weapons systems, the worldwide missile and rocket market has begun to find its strength. Countries all across the world have been pouring money into enhancing their national defense capabilities using modern technology. This has resulted in astonishing developments in the different types of missile and rocket systems: cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, artillery rockets, multiple launch rocket systems (MLRS), torpedoes, etc. Each of these plays a different role in the defense strategy and may be used for short-range or long-range targets. Cruise missiles, for example, could see at least an investment of $25,583.41 million, which shows the importance of these missiles in military operations.
Cruise missiles promise a very high degree of accuracy and a flying behavior that is extremely low to the ground, making it very difficult to detect and intercept these systems. Most of the nations make use of cruise missiles to achieve target specific strikes and thus are considered a credible strike option for the modern armed forces. Ballistic missiles, however, follow a parabolic trajectory and cover vast distances for strategic purposes. Ballistic missiles are based in the air and finally race down in towards their targets at extraordinary speed. These tactical munitions are generally used with a short range for immediate firing and in large numbers, offering the possibility to maximize rapid-fire capacity. They end up providing fire support to ground troops in combat.
Multiple Launch Rocket Systems (MLRS) allow to fire several rockets simultaneously. Thus, they can potentially spend a lot of enemy defenses in one go and inflict serious damage. Such systems are used very often as mobile devices for applications across the battleground. Torpedoes are types of underwater constructs that are chiefly used by naval forces. They are engineered to create hits on submarines or ships, usually launched from submarines or warships. The "Others" segment includes developing or limited-use technologies and specific equipment.
The expanding market has a lot to do with increasing conflicts, border tensions, and national security concerns. Countries want to make sure that they will be able to act rapidly and effectively at any moment, and this can happen only via advanced weapons. Technological advancements combined with strong governmental support will continue to deliver boosting prospects for the rocket and missile market. Induction of new systems or modernization of the old systems will keep the demand for efficient, reliable, and advanced weapon systems alive for long years to come.
By Propulsion Type
The international rocket and missile market is proliferating steadily as a result of increased military spending, rising geopolitical tensions, and defense technology advancements. All countries are focusing on strengthening their military power to ensure security, thus creating a huge demand for advanced missile systems and rockets. These systems fulfill the key role of providing not only defense but also deterrence. With the increasing unpredictability of threats, countries are investing greater resources in developing and acquiring systems for rapid and accurate response capability. Government policies, international relations, and technological improvements all influence the market. Many governments are financing research and development programs to improve the range, speed, and accuracy of missiles, thereby enhancing the effective and dependable nature of these weapons.
There are several types of propulsion systems, namely solid, liquid, hybrid, ramjet, turbojet, and scramjet. Each has a role for specific applications. The solid type is the most widely used propulsion system. This is due to reliability as well as simple design. It facilitates quick launch and low maintenance. Liquid propulsion entails higher control and power over missile systems but is associated with complex systems requiring a lot of preparation. Hybrid propulsion systems are designed to create a mix of both solid and liquid propulsion advantages, having the flexibility and a higher degree of safety. Ramjet and turbojet engines are intended for tasks that require high-speed conditions where speed and performance become key factors. Ramjets are very efficient in the supersonic range; turbojets are based on subsonic and supersonic conditions. Although scramjets are currently in the testing and early stages of development, the promising technology operated at hypersonic speeds will most likely feature in future missile systems.
Moreover, the focus on precision strike weapons is really fuelling this market. More importantly, modern warfare strategies are relying more on targeted operations as opposed to large-scale engagements. Essentially, this has created a demand for missiles that can hit tightly-defined targets with minimal collateral damage. Furthermore, nations are enhancing their present missile systems rather than developing new missiles. Upgrades include better navigation, increased range, and smart guidance technologies. Private companies are entering the defense space with innovative solutions that challenge the established manufacturers; this processes competition and propels quicker innovation. The evolving requirements in defense will continue to cause the rocket and missile industry to transform and grow into offering newer and better capabilities to the states that are interested in enhancing their security.
By Launch Mode
Rocket-Missile Market, Defense technologic advancement and security concerns significantly shape a global rocket and missile market. The launch mode is the attribute that organizes the market. These modes translate to how and from where the missile or rocket is launched. The market is further divided into surface-to-surface, surface-to-air, air-to-air, air-to-surface, and subsea-to-surface. Each of these launch modes serves a specific purpose in modern military operations.
Surface-to-surface missiles typically have fixed platforms and are mainly employed for long-range strikes against surface targets. Such missiles are usually counted in both offensive and defensive tactical arsenals, as states build strategic capabilities around them to protect borders. Other than attacking enemy fighter aircraft or incoming missiles, surface-to-surface missiles are extensively associated with defending airspace areas perceived to be under a high threat of aerial attack. These systems also tend to have a quicker response option and are often stationed around critical military bases or cities.
Air-to-air missiles target other aircraft and are fired from an aircraft. Their main function is to assure air superiority in combat. Air-to-air missiles are fast and accurate and meant to hit a moving target while airborne. Most air forces around the world spend their budget on upgrading these missiles so that they can have a prominent edge in aerial warfare. Air-to-surface missiles are also launched from an aircraft to hit ground targets. Generally used for precision strikes, these missiles target very specific enemy positions with as little damage as possible to surrounding areas. These missions are often credible for rapid, controlled attacks.
Subsea-to-surface missiles can be fired from underwater platforms like submarines for the purpose of targeting threats anywhere on land or at sea. These missiles lend themselves to stealth and surprise, making them a key part of naval strategy. Because the launch points are obscured, they are difficult to detect, giving the military a powerful advantage when engaged in conflict.
In the end, the different launch modes in the rocket and missile market capture the wide spectrum of requirements that modern defense systems should cater to. Considering that global tensions keep rising and enlargements of the defense budgets are so prevalent worldwide, the demand for these technologies would, in all likelihood, be continuously generated. Each mode presents its unique strength and together forms a sturdy foundation for national and international security endeavors.
By Guidance Mechanism
Conceptually, the world rocket and missile market is bifurcated by guidance mechanism into guided systems and unguided systems. Guided rockets and missiles are fitted with systems that keep changing their flight patterns in order to strike certain positions on the earth. These guiding systems operate on technologies such as GPS, laser, radar, or infrared sensors. Their precision ranks guided weapons highly for missions where accuracy matters. They help prevent excess damage to unintended areas by having low collateral damage. Over the years, the advancements made have made guided systems reliable and generally accepted in modern military operations.
On the contrary, unguided rockets and missiles will not change their path after being propelled. They are set on a course and do generally rely on parameters set at launch, such as the angle and the thrust. Therefore, production is quite easy and inexpensive. In cases when precision is not so pertinent, unguided systems do find utility, like saturation offerings or during excessive bombing raids. However, because of accuracy-related issues, unguided systems have secondary preference when preciseness in hitting is called for.
Based on mission requirements, both systems carry varying relevance. While guided systems are accurate and allow for control of operations in the field, unguided systems can be valuable when speed and numbers become important. The commitment to develop both the guided and unguided varieties continues by countries across the world, as laid down by their military strategy and the resources at their disposal.
Growth in the missile and rocket market with respect to the latest developments will continue to be strategically driven in increasing concern for security, regional disturbances, and war-like situations in many parts of the world. The quest for developing the defense industry, equipping old systems, and acquiring advanced missiles technologies is really primarily in focus in the nations around the globe. As a consequence, the demand for guided and unguided systems has also increased. With the result, governments have begun investing greater amounts of money into R&D, attempting to optimize the performance while at the same time finding cheaper methods.
Therefore, we see that the global market of the rocket and missile in terms of the guidance mechanism has been clearly bifurcated into guided systems and unguided systems. Both possess unique strengths for their battlefield niches. As long as new defense needs continue to occur, both will remain significant, and as the industry continues to advance all in an effort to meet modern day challenges.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$66,467.69 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$102,349.86 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
6.4% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
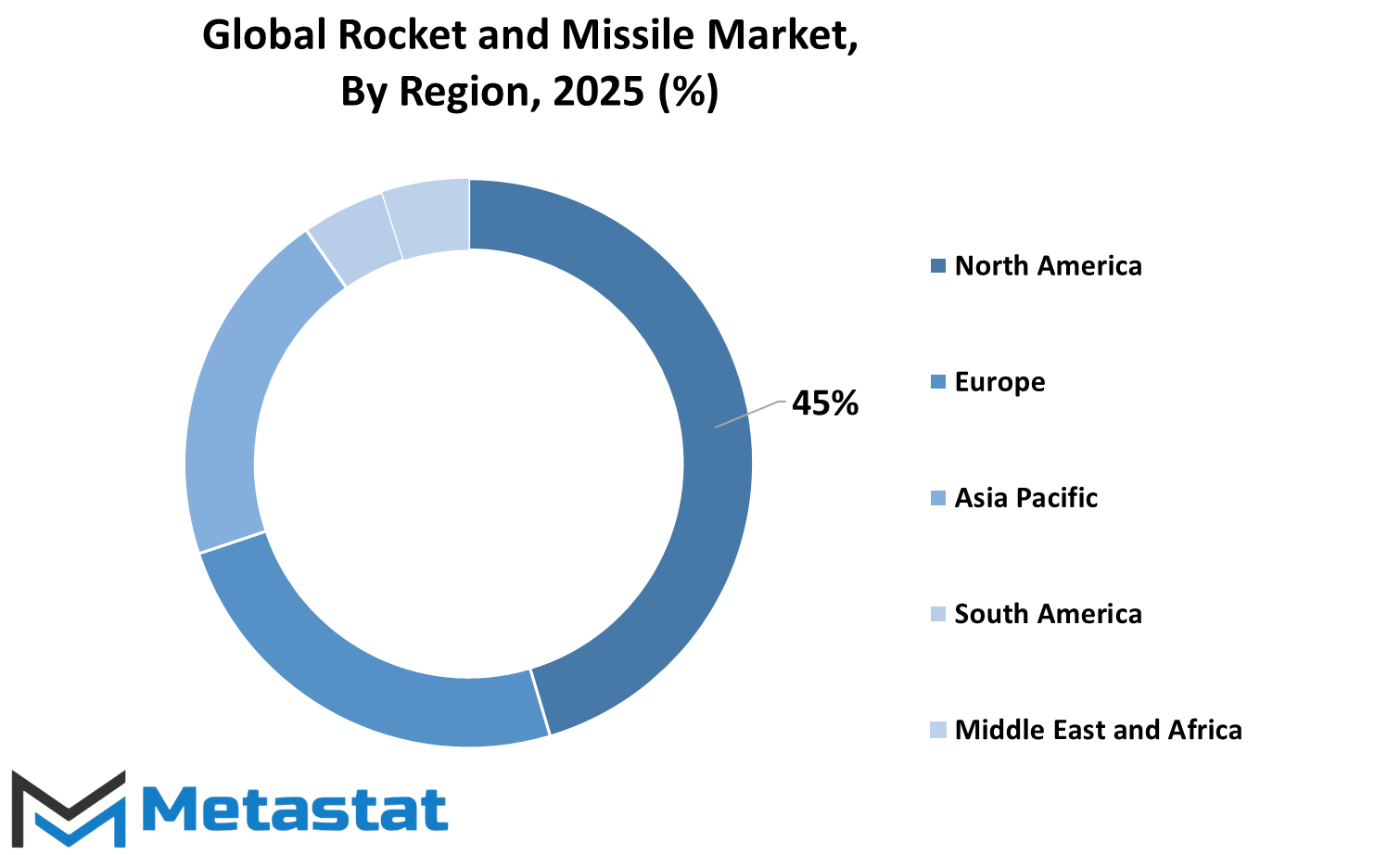
The global rockets and missiles market is diversified through a massive number of key regions, of which some belong to the global market development power. This region includes areas like North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and Africa. This region's North American portion covers the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Demand for advanced weapons systems has been constant due to military upgrades and modernization of defense programs to provide government investments, especially from the United States. The U.S. has a very dominant role in production or R&D.
European countries have been classified into locations as the U.K., Germany, France, Italy, and Rest of Europe. Increased regional tension along with the growing concerns for national security have compelled countries in this region to fortify their defense capabilities. The cooperation between European countries and defense contractors has facilitated technological advances and joint missile development programs. Furthermore, a shift in governmental policies toward long-term defense planning among countries in Europe is expected to nourish market growth in the foreseeable future.
Asia-Pacific contains India, China, Japan, Korea, and the Rest of Asia-Pacific. Personnel in the area, border security issues, and strategic rivalries have made the region increasingly important for the rocket and missile industry. India and China, in particular, are investing significantly in missile systems to keep their respective militaries alert. Japan and South Korea are also developing their defense sector by joint partnerships, capable of procuring advanced missile systems mainly because of regional threats and the need for upgrading existing equipment.
South America refers to such nations as Brazil, Argentina, and the Rest of South America. Although countries in this region do not dominate the industry, they are making efforts to expand and modernize their defense systems. Defense investments in missile technology and national security improvement are led by Brazil in this region.
The regions mentioned under Middle East & Africa comprise the GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and the Rest of the Middle East & Africa. This region is never found to contain an iota of reluctance in pursuing the advancement of defense technologies owing to the incessant rumbles and indispensable sound structures within national defense. With the increase in defense budget allocation by countries like Saudi Arabia and UAE, there are more opportunities for resurrection in the market.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The rocket and missile market across the world has seen tremendous growth in the recent years because of geopolitical tensions and increasingly aggressive defense budgets. A country increases the demand for advanced weapons like rockets and missiles when it builds its military capability, which in turn increases their consumption in indigenously produced weapons. However, apart from national security, they are also crucial and vital for peace and deterrence. Most countries in the world are now investing a considerable amount of money to upgrade their missile technology, ensuring that such missiles are more accurate, long-ranged, and difficult to detect. Therefore, the sector now has a moderately progressive attitude toward such an innovation and development.
Missiles and rockets are made for many applications, from air defence to land strike; and others would belong to naval warfare. As threats become more complex, it really becomes imperative for the defence forces to have systems that are designed for rapid or efficient response. Now it calls for missiles equipped with smarter guidance systems, better speed, and superior targeting capabilities. In recent times, both developed and developing countries, are really keen to either boast a stronger independent missiles capabilities or tie- up to leading defence firms for modernised solutions.
Key players in the rocket and missile industry include BAE Systems Plc, Bharat Dynamics Limited, Denel Dynamics, Elbit Systems Ltd, Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd, Kongsberg Gruppen, LIG Nex1, Lockheed Martin Corporation, MBDA Inc., Northrop Grumman Corporation, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, Saab AB, and Thales Group. They continuously indulge themselves into research and development in order to get a notch higher than the rest in the competition and also in fulfilling the ever-increasing requirements from the defense forces. Many of them have also cycled into nations to assure that their equipment is customized to fit the needs of different nations.
With military demand, this market is equally driven by space exploration programs, albeit, to a much smaller extent. However, the primary driving force still remains the need for capable defense systems. Countries are looking beyond the traditional threats to mechanisms that might, in the future, engage advanced technologies like hypersonic weapons and autonomous systems. This transition will define the trajectory for the rocket and missile market.
The sector does not show any signs of slowdown. The sheer rivalry among the major players together with the sustained need for an improved arsenal will continue nurturing the market. As long as the world continues to grapple with security issues, investments in rockets and missiles will remain uppermost on the list of priorities for most nations.
Rocket and Missile Market Key Segments:
By Product
- Cruise Missiles
- Ballistic Missiles
- Artillery Rockets
- Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS)
- Torpedoes
- Others
By Propulsion Type
- Solid
- Liquid
- Hybrid
- Ramjet
- Turbojet
- Scramjet
By Launch Mode
- Surface-to-surface
- Surface-to-air
- Air-to-air
- Air-to-surface
- Subsea-to-surface
By Guidance Mechanism
- Guided
- Unguided
Key Global Rocket and Missile Industry Players
- BAE Systems plc
- Bharat Dynamics Limited
- Denel Dynamics
- Elbit Systems Ltd
- Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd
- Kongsberg Gruppen
- LIG Nex1
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- MBDA Inc.
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- Saab AB
- Thales Group
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential












 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






