MARKET OVERVIEW
The global private cloud market, falling under the enterprise IT infrastructure and cloud computing sector, will be a niche segment catering to organizations that require dedicated and secure clouds. In contrast to public cloud networks operating on shared resources, private cloud networks will be designed to deliver sole data management services for one organization or a closed community of users. This market will focus on a combination of control, customization, and compliance, reflecting the operations requirements of large businesses that value data sovereignty and enterprise governance models. The global private cloud market will include platforms that can sustain a broad variety of enterprise workloads, from internal applications to sophisticated analytics and storage arrays.
Vendors operating within this space will develop solutions that allow full integration with existing on-premise systems, while also enabling migration to virtualized infrastructure without compromising data visibility or security parameters. These systems will often run behind the firewall of a business or be hosted externally in a way that mimics in-house resource control, thereby maintaining performance expectations specific to each enterprise's workflow. In the Global Private Cloud space, tech architecture will be established around virtualization, software-defined networking, and autonomic service orchestration. Organizations will look to these configurations in order to standardize business operations and automate IT services across diverse departments.
While the public cloud will provide scale and accessibility, the private alternative will meet the need for regulated performance, high availability, and direct supervision. The capability of on-demand configuration of network, compute, and storage will differentiate the private cloud model, particularly in data-driven industries like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. Scope will span multiple models like on-premise private clouds, hosted private clouds, and managed private cloud services. Both will serve a distinct level of enterprise need, with the decision based on the desire for operational flexibility, hardware investment, and in-house technical expertise. Businesses with high compliance needs will prefer models that enable them to have physical control over hardware, while some might outsource infrastructure management to third-party experts, instead concentrating on delivering applications and customer experience.
The global private cloud market will involve participants such as software vendors, infrastructure firms, security experts, and system integrators. These parties will concentrate on interoperability, with private cloud environments being integrated effortlessly with public cloud or legacy infrastructures through hybrid or multi-cloud deployments. With companies becoming more focused on customization and strong control over digital resources, the market will move in the direction of modular platforms with quick deployment support without sacrificing regulatory conformance. Geographies in North America, Europe, and Asia will take the lead in adoption because of the presence of industries with sensitive data and regulation requirements. Businesses in these geographies will force vendors to innovate security, compliance, and network latency control. In contrast to public services of a one-size-fits-all nature, the global private cloud market will require a flexible structure that suits business-critical applications and industry-specific compliance requirements.
In the future, this marketplace will serve as the cornerstone upon which organizations construct secure and scalable digital solutions, supporting operational resilience through focused cloud offerings.
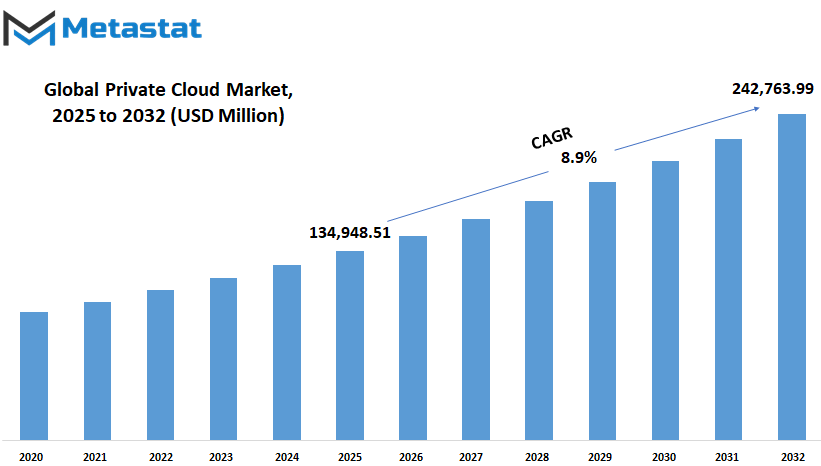
Global private cloud market is estimated to reach $242,763.99 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 8.9% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The global private cloud market is gradually defining the future of how companies manage data and computational requirements. With more attention being paid to keeping information safe and confidential, private cloud services are increasingly attracting attention. These cloud platforms enable firms to maintain their own space for data storage and hosting applications independent of the public networks available to many others. Among the most compelling reasons for this transition is the increasing need for data privacy and obeying stringent regulations. Sectors such as finance and healthcare, which are closely monitored because of the nature of information handled by them, are gravitating toward private cloud options since they provide enhanced control and more robust security features. Private cloud infrastructure provides organizations with dedicated resources, and hence they enjoy better performance and lower risk of sharing information or space with others.
This is particularly critical for companies that have no room to spare in the event of even the smallest data leak or service delay. Though this arrangement has very strong advantages, it also has some disadvantages. The major disadvantage is the high price involved. Establishment and upkeep of a personal cloud environment may demand substantial financial investment in hardware as well as skilled personnel. These are greater compared to a shared or public cloud, which is less expensive owing to shared resources and economies of scale. Another consideration is that private clouds are not as flexible and have fewer growth possibilities as public cloud services. Companies operating with a private cloud may struggle more to adapt quickly when their needs shift or when they expand swiftly. This restricted scalability could put the brakes on in high-growth industries. But the future is bright as more businesses are starting to employ hybrid cloud methodologies. Hybrid gives companies the opportunity to leverage both private and public clouds in a harmonized manner. This is an opportunity for them to maintain their confidential operations safe in a private environment and utilize public cloud capabilities for less urgent activities. This is a more intelligent and economic means of driving data and services.
With increasing organizations venturing into these adaptable solutions, the global private cloud market is bound to continue advancing steadily. With better technology and advanced tools emerging in order to minimize costs and enhance performance, more sectors could tread in the footsteps of embracing private cloud solutions. The emphasis on privacy, dependability, and performance will continue to propel this market forward in the future.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Services
The global private cloud market is likely to expand gradually, buoyed by increasing needs from enterprises seeking greater control of data and operations. As enterprises seek solutions that are more secure, flexible, and responsive, private cloud solutions remain highly competitive. In contrast with public cloud resources, private cloud facilities are reserved for one organization, where businesses can customize them according to their specific requirements. This emphasis on customized infrastructure is one of the reasons why several organizations will find private cloud services more attractive in the years to come. In the future, the global private cloud market will grow in the direction of more sophisticated service models.
It is already migrating away from simple storage and computing capabilities. The services are now classified into Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service. They all play distinct roles in how companies organize their workload. Infrastructure as a Service provides companies with access to virtualized computer resources, eliminating the necessity for physical hardware in-house. This ensures costs are cut and they remain flexible when they need to organize their systems. Platform as a Service will allow developers to create and test programs more easily without concerns about the foundation setup. It saves time, reduces errors, and enables firms to get their products to market sooner. Software as a Service, by contrast, provides preconfigured software tools available from any location. Such tools assist groups in working together more effectively, particularly when located in remote areas. Increasingly in the future, firms will turn towards hybrid approaches, combining public and private models of cloud. The private aspect will still be necessary for dealing with sensitive information and mission-critical functions.
With ongoing advances in technology, we can expect to witness more intelligent systems that automatically adapt based on use patterns. This will minimize downtime and enhance performance. Security will also be a top priority. Businesses will require private cloud systems to include more robust inherent security and compliance mechanisms that meet global standards. The global private cloud market will not just cater to big businesses but also become increasingly viable for small and medium-sized enterprises. With simpler interfaces and pay-as-you-go models, private cloud offerings will provide new avenues of opportunity for those who were deterred by their earlier complexity or expense. Gradually, the market will continue to expand as it evolves to suit business requirements and evolving technology, and it will be an integral component of digital operations for most industries.
By Deployment Model
The global private cloud market will keep expanding as companies look for more secure and personalized means of handling their information. As companies progress toward digital configurations that require privacy and dependability, private clouds will gain even more significance. In contrast to public cloud services shared with many users, private clouds provide companies total control over their information. The control permits improved personalization and enhanced security features. Companies that deal with sensitive or valuable information will most probably opt for private cloud environments due to their assurance of peace of mind and added control over operations. In the future, the market will trend towards flexible solutions that suit varying business requirements.
And it is here that the deployment choice is vital. The Managed Private Cloud approach provides organizations with the means to outsource the technical burden of maintaining the cloud. Providers take care of updates, monitoring, and day-to-day performance. This option is useful for businesses that want a dedicated environment but may not have the resources or skills to manage it themselves. It allows them to stay focused on their work while still benefiting from the strength of a secure cloud setting. Conversely, the Hosted Private Cloud model provides organizations with greater control over how their cloud is managed, without ever depending on external hosting. It is a compromise that provides control without having to construct everything from the ground up. This deployment option will benefit those companies that wish to grow without the full expense of infrastructure construction. As technology advances further, these options for deployment are bound to become more specialized and effective. As data security concerns increase and remote work becomes increasingly prevalent, private cloud configurations will attract a lot of attention.
As cloud technology simplifies and becomes more cost-effective, more organizations of all sizes will seek the advantages of private cloud solutions. Such systems will be required to evolve not only to existing needs but also to emerging trends like AI software and machine learning platforms which need high-speed and secure computation. The global private cloud market in the future will serve to ensure balance is achieved for companies providing robust security, reliability, and freedom to control resources based on individual requirements. Through intelligent deployment models and consistent innovation, this arena will dictate how businesses secure and operate their systems.
By Organization Size
The global private cloud market is predicted to increase steadily in the future, driven by the increasing requirement for safer and more customizable digital environments. As more companies search for enhanced data and system control, private cloud solutions are proving to be an appealing choice. Such platforms enable organizations to have control over their infrastructure while enjoying cloud flexibility and access. In contrast to public cloud models, private implementations provide greater privacy, which is paramount for a majority of companies that focus on data security and regulatory compliance. One of the principal reasons for this transformation is how various business sizes are responding to digital transformation.
Small and medium-sized enterprises, or SMEs, are increasingly turning to private cloud systems in order to achieve greater reliability and minimize long-term operational risk. These businesses usually operate within limited budgets and do not have the luxury of constant technical interruptions. With private cloud, they enjoy more consistent performance and greater control over their technology operations. While implementation of a private cloud might initially appear to be challenging for SMEs, the long-term advantages like cost management, security, and stability of service are making it a rational move. Large businesses, however, have more sophisticated requirements and larger operations. They need cloud environments with high data volumes while observing rigid internal and external standards.
Private cloud solutions for them are not merely security issues, but also ensure business continuity, enhance speed, and remain competitive. These businesses typically already have a type of cloud infrastructure already established but are now trending toward having completely private systems in order to better handle future needs. As automation, AI, and data management continue to improve, private cloud technology becomes increasingly scalable, which makes it more appealing to larger businesses. In the coming years, the global private cloud market will likely be helped by future developments in edge computing and smart infrastructure. As businesses seek new ways to remain competitive, the need for secure, flexible platforms will increase. SMEs and large corporations will continue to seek means of utilizing these technologies not only for storing data, but also for real-time processing and decision-making.
With the increasing number of organizations aware of the long-term benefits of personalizing their digital spaces, the adoption of private cloud systems will increase in various industries. This continued transformation is a testament to just how crucial secure, effective, and governed online environments will be to the future of business.
By Industry Vertical
The global private cloud market is poised to expand gradually with companies from various industries ongoing to move towards more secure and customizable virtual environments. As companies pay greater emphasis on data privacy as well as control, private cloud offerings are gaining popularity. These provide companies with the control to manage their own resources with less dependence on public cloud offerings, which frequently involve shared infrastructure and security issues.
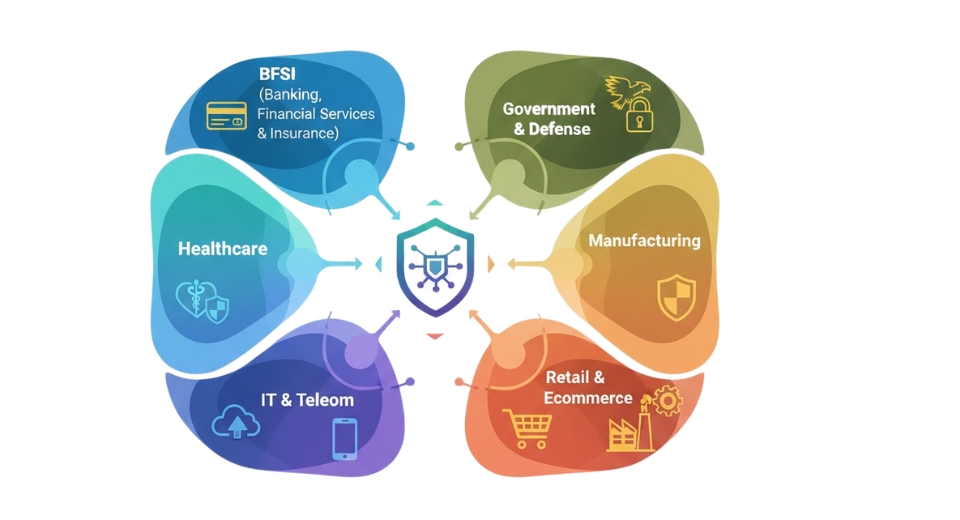
Industries like Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance are at the forefront of the transition. These industries handle sensitive data and require maximum security and compliance. A private cloud infrastructure provides the security they need, along with flexibility and speed. IT & Telecom businesses also shift to private cloud environments in order to handle peak demands and continuous connectivity. As these businesses tend to function as service providers, they require systems that are dependable and able to be customized. Government and Education are also areas with high interest. Governments handle national security, citizen information, and other sensitive information. Having a private cloud enables them to handle and store data with more control. Educational institutions are also using these technologies to handle vast amounts of student and employee data, research material, and web-based learning systems. With learning becoming increasingly digital, there is a demand for robust and secure platforms.
Healthcare is one sector where private cloud usage is increasing. Hospitals and clinics handle patient records, medical images, and sensitive health information. A private cloud ensures this information is secured while providing quick access to doctors and other healthcare professionals. In the Retail industry, businesses employ private cloud systems to store customer information, product stock, and sales patterns. With the growth of online shopping, it becomes crucial to have a secure and responsive system. Manufacturing companies are looking towards private cloud offerings for the management of production data, logistics, and quality testing.
These platforms are able to enable automation and enhance overall efficiency. For Media & Entertainment, private cloud is necessary due to scale-level content creation, storage, and streaming. These companies require platforms that are fast, secure, and reliable. Energy & Utilities industries are also considering private cloud systems to allocate resources, track infrastructure, and act quickly to problems. In the future, the global private cloud market will remain in the spotlight among many industries. As technology is developing and digital requirements are expanding, more companies will invest in private cloud systems to assist their operations securely and efficiently.
|
Report Coverage |
Details |
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$134,948.51 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$242,763.99 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
8.9% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
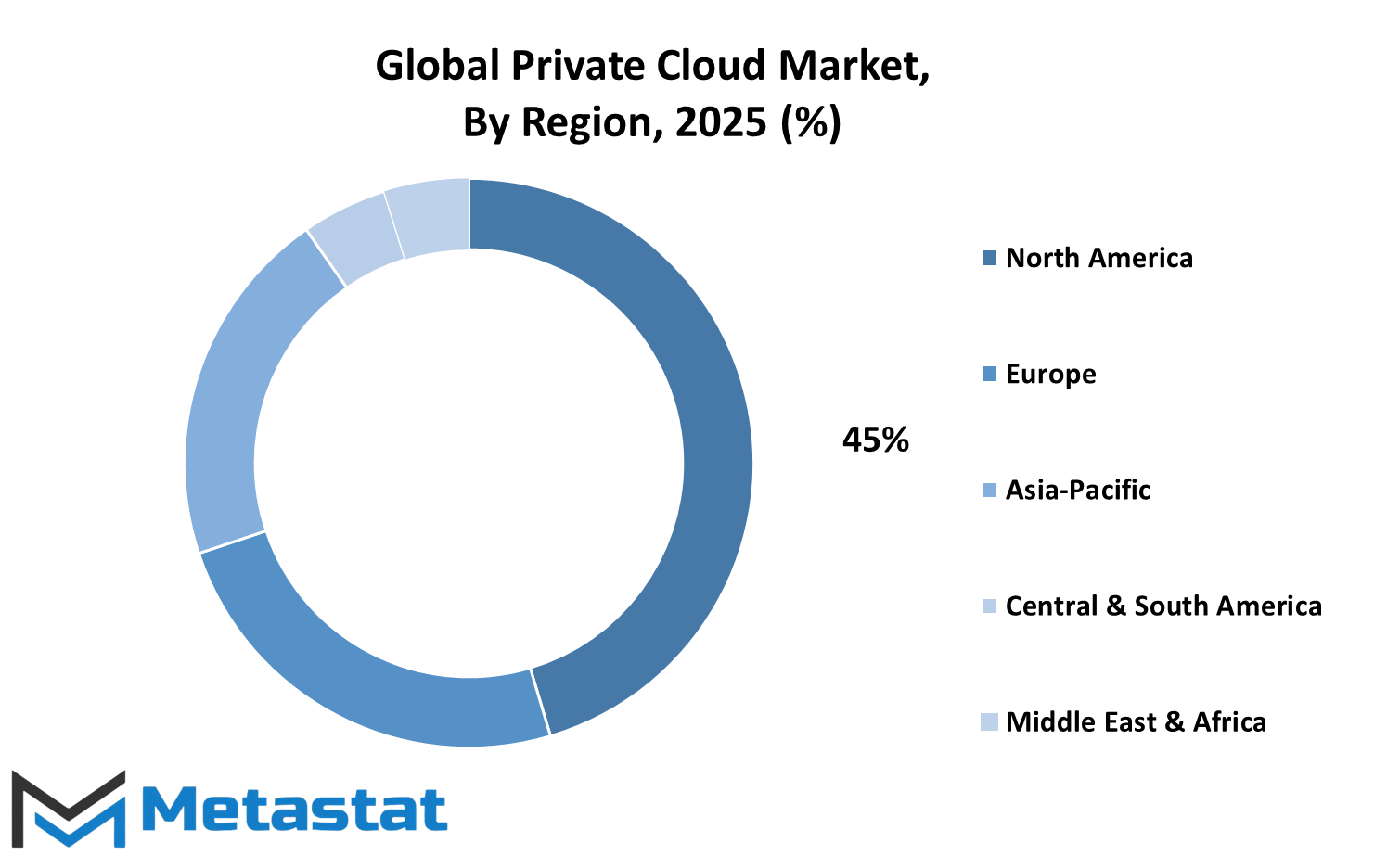
The global private cloud market is driven by regional factors mirroring divergence in technology adoption, readiness of infrastructure, and digital transformation strategies. With regions shifting towards creating more robust digital foundations, private cloud services are on the radar for their ability to deliver security, control, and scalability. It's not just about today, but also about future readiness, with data contributing ever more to decision-making and growth across industries.
In North America, the presence of mature tech firms and emphasis on security through cybersecurity has contributed to huge demand for private cloud models. The U.S. remains at the forefront of innovation when it comes to cloud technologies, followed by Canada and Mexico. They are investing in platforms that can securely manage sensitive data without using public systems. Companies here are searching for long-term solutions that will be capable of evolving future modifications without sacrificing safety or performance. Europe too is moving forward in an incremental manner, with nations like the UK, Germany, France, and Italy making strides in cloud adoption owing to governmental encouragement and data protection regulatory frameworks. As data residency and compliances are what many organizations give high importance to, private cloud services are finding their way as a necessity. The desire for digital sovereignty in sections of Europe indicates that the trend is expected to grow further, particularly as industries move towards increased automation and interconnectedness.
Asia-Pacific also gives a contradictory image, with the likes of China, India, Japan, and South Korea promising high growth. Their momentum is driven by fast digitalization, increasing internet penetration, and increasing demand for secure infrastructure. Their governments are also backing technology-based initiatives, making private cloud adoption even more attractive. As local businesses look to compete globally, they will be required with agile and secure solutions in order to maintain and store important information.
South America is slowly gaining momentum, especially in Brazil and Argentina. With companies looking to transform their IT infrastructure, private cloud solutions are being considered for their ability to provide secure, flexible, and future-proofed environments. These advancements might not be as rapid as other parts of the world, but the trend is unmistakable.
In the Middle East and Africa, particularly in GCC nations, Egypt, and South Africa, cloud technologies are components of broader economic diversification and digital capability-building plans. With continuous infrastructure development and increased tech investments, private cloud services will become increasingly prevalent. These markets might contribute more significantly to future trends since they are in the process of catching up with more advanced market.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The global private cloud market is poised for consistent growth as more companies look for secure and customized digital platforms. With data security and privacy issues on the rise, most companies are moving away from public options and instead looking at customized systems that provide greater control and flexibility. Trust is of paramount importance in this field. Businesses are not only investing in infrastructure but also in long-term digital stability. This path has led organizations to look for private cloud environments where they can handle sensitive data more confidently and satisfy specific regulatory requirements without compromise. This market will be even more inclined towards platforms that balance personalization with efficiency in the future.
Companies will no longer accept a one-size-fits-all model. Rather, they will require services that cater to their distinct business models and workloads. As such, the emphasis will shift towards developing flexible systems that scale without compromising on performance or adding risk. The secret to success here will depend on the extent to which providers are able to secure systems, but also keep them usable and easy to modify when necessary. IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) are some of the key players in this market with strong reputation and cutting-edge technology. Their capability to design secure systems that are simple to manage provides them a distinct advantage.
Meanwhile, Oracle Corporation and VMware, Inc. are also working on improving their services to entice organizations seeking dependable and personalized solutions. These players realize that future business requirements will keep evolving to be even more specific and that their success will be a function of how effectively they are able to fulfill these requirements without introducing superfluous complexity. Some other players whose role in determining the direction of the global private cloud market is significant include Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Dell Technologies Inc., and Cisco Systems, Inc., which bring innovations making cloud adoption easier. Fujitsu Limited, Atos SE, and Rackspace Technology, Inc. are also growing their presence by concentrating on security, performance, and support. NetApp, Inc., Citrix Systems, Inc., and T-Systems International GmbH are likely to lead the charge in creating systems that align business objectives without imposing change on the way teams work.
Hitachi Vantara Corporation, SAP SE, and OVHcloud are leading the way with solutions for industries of high value where control and compliance are not merely available choices but are anticipated.
Private Cloud Market Key Segments:
By Services
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
By Deployment Model
- Managed Private Cloud
- Hosted Private Cloud
By Organization Size
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Large Enterprises
By Industry Vertical
- Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance
- IT & Telecom
- Government & Education
- Healthcare
- Retail
- Manufacturing
- Media & Entertainment
- Energy & Utilities
- Others
Key Global Private Cloud Industry Players
- IBM Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- NTT Communications Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- VMware, Inc.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Fujitsu Limited
- Atos SE
- Rackspace Technology, Inc.
- NetApp, Inc.
- Citrix Systems, Inc.
- T-Systems International GmbH
- Hitachi Vantara Corporation
- SAP SE
- OVHcloud
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential






 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






