MARKET OVERVIEW
The global precision machining market over the next several years will likely experience the application of cutting-edge tools and equipment that can provide micro-level precision with negligible tolerance levels. As manufacturing processes get more automated, reliance on cutting-edge CNC machines will increase. The CNC machines will assist manufacturers in making complex parts repeatedly, improve repeatability, and reduce the impact of human error. Precision machining will also embrace additive manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing that will supplement subtractive techniques that have been conventionally applied to make parts.
The industry will also see emphasis placed on specially machined materials like advanced composites, ceramics, and elusive alloys. These are increasingly going to be used in weight-saving while strengthening and making components tougher industries like aerospace and motor vehicle manufacturing. Precision machining operations will be forced to change to accommodate the new materials using new tooling solutions and state-of-the-art cooling and lubricating techniques to guarantee efficiency and component integrity.
Environmental issues will dictate the course of the global precision machining market, with more emphasis on sustainable manufacturing. Waste and energy-saving operations will take center stage, both because of regulatory needs and consumer calls for clean manufacturing. Technologies that allow dry machining or recycling of cutting fluid and scrap metal will become increasingly sought after, and the industry will be greener.
Furthermore, deployment of digital twin technology and real-time monitoring will define the future precision machining environment. Through creation of virtual representations of real machining processes, manufacturers will optimize and simulate procedures before actual production. This predictive aspect will reduce downtime and increase productivity. Machine learning algorithms will analyze data generated by machining equipment to predict maintenance needs, prevent breakdowns, and extend tool life.
The labor pool for the global precision machining market will also shift. While automation will reduce the need for direct human intervention in standard tasks, there will be greater demand for skilled operators and engineers to program, monitor, and maintain high-tech equipment. Training programs will integrate interdisciplinary skills, bridging mechanical expertise with data analysis and computer programming capabilities.
In addition, the global nature of the market will imply that regional centers will have their own functions. New economies with growing manufacturing hubs will increase their participation in precision machining, providing competitive alternatives for the established strongholds. Supply chains will be more integrated and good logistics and quality control procedures will be required to enable smooth operations.
The use of Industry 4.0 ideas will drive the development of the global precision machining market into more connected, intelligent, and responsive manufacturing plants. Precision machining shops will communicate with other manufacturing plants effortlessly, allowing rapid real-time adjustments and customization to meet shifting product designs and customer demands.
With manufacturing evolving toward smaller production runs and specialty products, the precision machining industry will be challenged to deliver highly adaptable manufacturing solutions. It will optimize processes on a continuous basis to balance speed, accuracy, and cost savings, consistent with requirements in tomorrow's manufacturing environment.
Briefly, then, the global precision machining market will remain an integral element of industrial manufacture, shaped by technological advance, materials development, environmental concerns, and shifting marketplace forces. Its role in providing precise and reliable components for production will only escalate as the business grapples with the complexities and challenges ahead
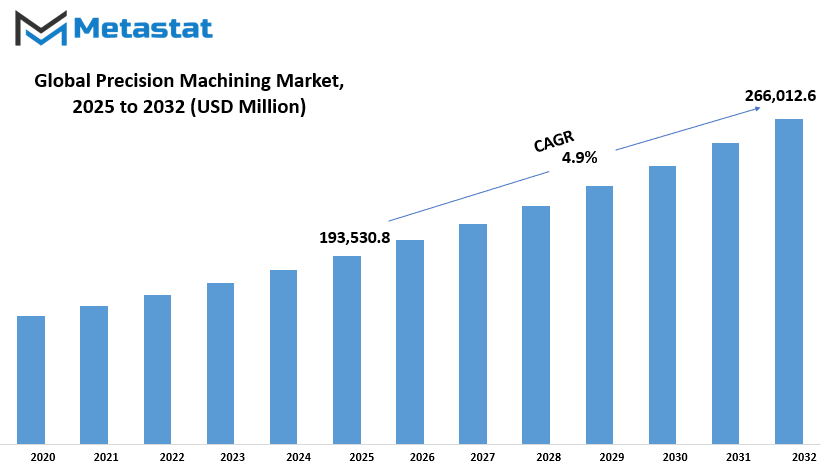
Global precision machining market is estimated to reach $266,012.6 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 4.9% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The global precision machining market is increasing on a daily basis due to the rising need for extremely precise components in the aerospace and automotive industries. The components must be of extremely high quality, as these industries need components that operate consistently under harsh conditions. Precision machining provides the accuracy and quality required to satisfy their demands. For that reason, greater numbers of firms are turning towards precision machining for manufacturing parts which can operate at all times within harsh environments. This increasing trend is one of the most vital factors that propel the market further to grow.
The other major force of the expansion of the precision machining market is advances in technology, particularly automation and CNC machines. Despite such encouraging trends, there are some problems that the industry is facing. One of the primary problems is the extremely high initial investment needed to invest in sophisticated machinery. The machinery itself may be costly, and small producers may lack the funds needed to afford it. This financial limitation may retard the uptake of the newest technology in some sectors of the industry. Another factor that could restrain development is the lack of trained labor. Precision machining is done by skilled and experienced operators, and an insufficiency of sufficient numbers of such proficient workers can hinder the capacity of manufacturers to keep up with increased demand for precision parts.
On the positive side, increased application of precision machining in the medical device sector has a vast potential for future growth. Medical equipment needs accurate and dependable parts, and the medical industry increasing means that such high-value components are in even greater demand. The segment will offer lucrative possibilities for precision machine companies in years to come. There are a few problems that need to be addressed, but growing demand across multiple industries along with technological advances will keep the market on an upward track.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Type
The global Precision Machining Market is seeing fast growth as companies invest in better technology to improve their manufacturing process and meet the needs of the customer. The global precision machining market – type is further segmented into Manual Operation and CNC Operation. Manual operation is a traditional practice wherein the machinists use hand tools and rely on their skills to shape the material. Though this method is flexible and appropriate for low-volume work, it is experience-based and labor-intensive. On the other hand, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) operation uses automated technologies that carry out programmed instructions. CNC machines are capable of churning out high volumes of parts with repeatable accuracy, thus they are appropriate for mass production.
CNC operation is quickly becoming the preference of the numerous industries. It facilitates production at a quicker rate, lesser errors, and reduced labor. Manually machining certainly finds its place in specific activities requiring the touch of hand, but CNC machines are the undisputed leaders in terms of precision, speed, and magnitude. The greater use of automation in production is further supportive of the drift toward CNC operation.
There are certain reasons for the growth of the market. Technological advances are making CNCs more accessible and user-friendly. In addition, companies are being forced to cut waste and increase production efficiency, and precision machining is just the thing for that. Growing demand for top-quality parts for healthcare and electronic industries is also fueling market growth.
In short, precision machining is gaining prominence with industries needing greater efficiency and performance. As the market remains divided between manual and CNC operations, the focus is decisively shifting towards automation. With technology continuing to rise and industries looking for solutions based on intelligence, CNC precision machining will likely lead the way.
By Machine Types
The global precision machining market is picking up pace as manufacturing sectors of all kinds are more and more demanding precision and accuracy. Segmented according to the kinds of machines, the market can be classified into electric discharge machines, milling machines, and turning machines. Among these, the highest market share of $76,772.1 million belongs to the milling machine segment.
Turning machines are also essential in precision machining. They produce material by rotating the workpiece with a cutting tool that removes it. They are most often used for the production of cylindrical parts and are heavily relied on in mass production as they are fast and precise. As demand for specialized and precise parts continues to grow, turning machines are becoming ever more important to various industries. Electric discharge machines, or EDMs, also figure in the increasing market. EDM machines have a reputation for cutting hard metals with fine and precise cuts. EDM is especially convenient for tools and die-making applications where close tolerances are a necessity.
The development of the precision machining business is a direct result of technological advancement and demand for higher-performance parts. Automation and computer numerical control (CNC) have improved machines to be more efficient and easier to operate. They reduce errors and consume less time, hence increasing productivity. CNC milling and turning machines, in particular, are being widely accepted because they accommodate rapid change of design and higher output without sacrificing accuracy.
The second reason for rising demand in this sector is the expansion of industries like defense, electronics, and healthcare. These sectors require parts that must adhere to exact standards of quality. Producers thus are investing more in high-technology precision equipment in order to stay competitive. Additionally, with the shift towards light and durable materials in manufacturing, precision machining was even more important as these materials are more difficult to shape without the aid of accurate machinery.
Overall, the global precision machining market is slowly expanding, with milling machines leading the pack in terms of value. The turning machines and electric discharge machines are also crucial. As industries require greater performance and reliability, the demand for advanced precision machines will continue to grow.
By Material Type
The global precision machining market is always growing as businesses keep needing highly detailed and accurate parts. The material type used is among the major factors driving the market. Different materials are chosen based on what the end product demands, and each material has its advantage in precision machining. These resources include plastic, steel, bronze, glass, brass, and other metals, each having a specific role to play in shaping and shaping the market direction and growth.
Plastic is used most frequently whenever light components are needed, especially in industries like electronics and transportation. It is easier to cut and shape, and therefore it is a convenient one if speed and efficiency are of concern. Although not as tough as metal, plastic parts are generally strong enough for most applications and less expensive to produce. Steel is more appealing because of its durability and wear resistance. Steel is widely used in construction, aviation, and heavy industry, where parts must withstand pressure at both ends and extreme conditions. Strength of steel and resistance to wear and tear are the reasons why steel is the most common material used within the precision machining process.
Bronze and its resistance to corrosion along with the low surface finish is another common material used in the event of movement and friction applications. It is useful in bearings, valves, and other such components where the part must be flexible as well as strong. Glass, while less common, nonetheless is used in high-purity and chemical-resistant markets such as medical or laboratory machinery. It is to be used with care, but it is helpful in certain uses. Brass, as it is simple to machine and polish, is extensively utilized in ornamentation, plumbing, and electrical accessories. It offers strength coupled with a bright, shiny finish, so it can be utilized for function as well as form.
By End-use Industries
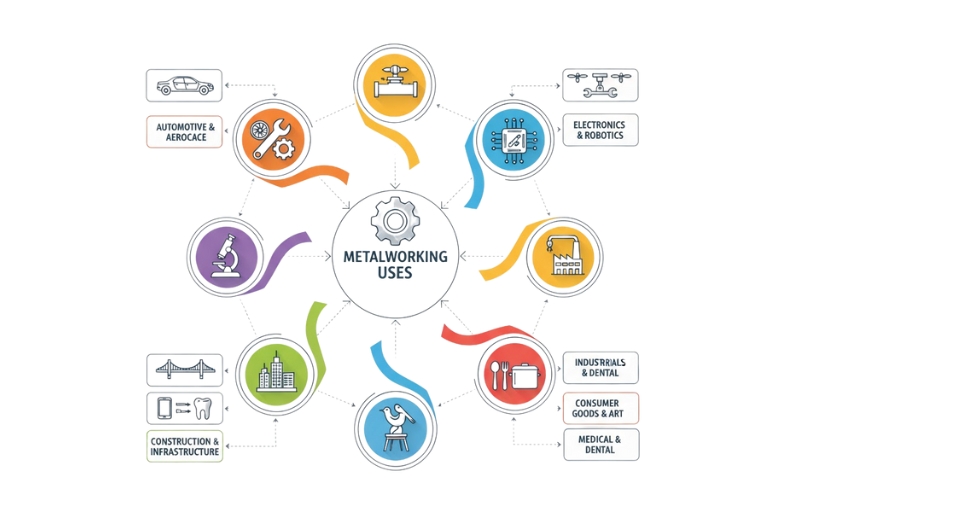
The global precision machining market continues to grow steadily, driven mainly by growing demand in several key industries. One of the principal industries utilizing precision machining is the automotive industry. The requirement for parts with high precision and consistency becomes more necessary as auto designs become more sophisticated. From transmission systems to engine parts, precision machining is what ensures each piece meets strict measurements, so vehicles can travel smoothly and safely. Businesses in this sector rely heavily on this process to provide quality and performance in product output.
The aerospace sector is another huge user of precision machining. Making aircraft has to be extremely precise because a small imperfection in a part can lead to drastic issues. Precision machining helps to make parts that meet strict safety and performance standards. These include turbine blades, landing gear components, and structural frames, all of which need to fit perfectly and function without a hitch. The safety standards in this sector are non-negotiable, and therefore precision machining is a critical factor to consider.
The medical sector is also the leading cause of the demand for precision machining. Devices utilized in operations, implants, and diagnostic tools need to be manufactured with high accuracy in order to function appropriately. Whether a knee implant or an operation tool, these devices need to be of the same size in order to access effective utilization and not injure patients. The pursuit of better healthcare tools and devices keeps boosting the demand for consistent machining solutions.
Precision machining in the semiconductor industry helps in the building of the complex equipment required to produce chips and microprocessors. The machines have to operate at extremely close tolerances, and even a slight variation can result in defects in the final product. As the technology is changing day by day, this industry requires machines and components that can keep pace with smaller, faster, and more efficient chips, and hence precision machining is a must.
Lastly, the "others" category includes sectors like defense, energy, and industrial machinery, also relying on high-precision parts for performance and longevity. For each of these sectors, precision machining is used to increase efficiency, reduce waste, and maintain innovation.
Overall, the global precision machining industry is shaped by the distinct needs of its end-use markets. For safer automobiles, better medical devices, or faster chips, this technology remains a foundation of modern manufacturing.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$193,530.8 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$266,012.6 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
4.9% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
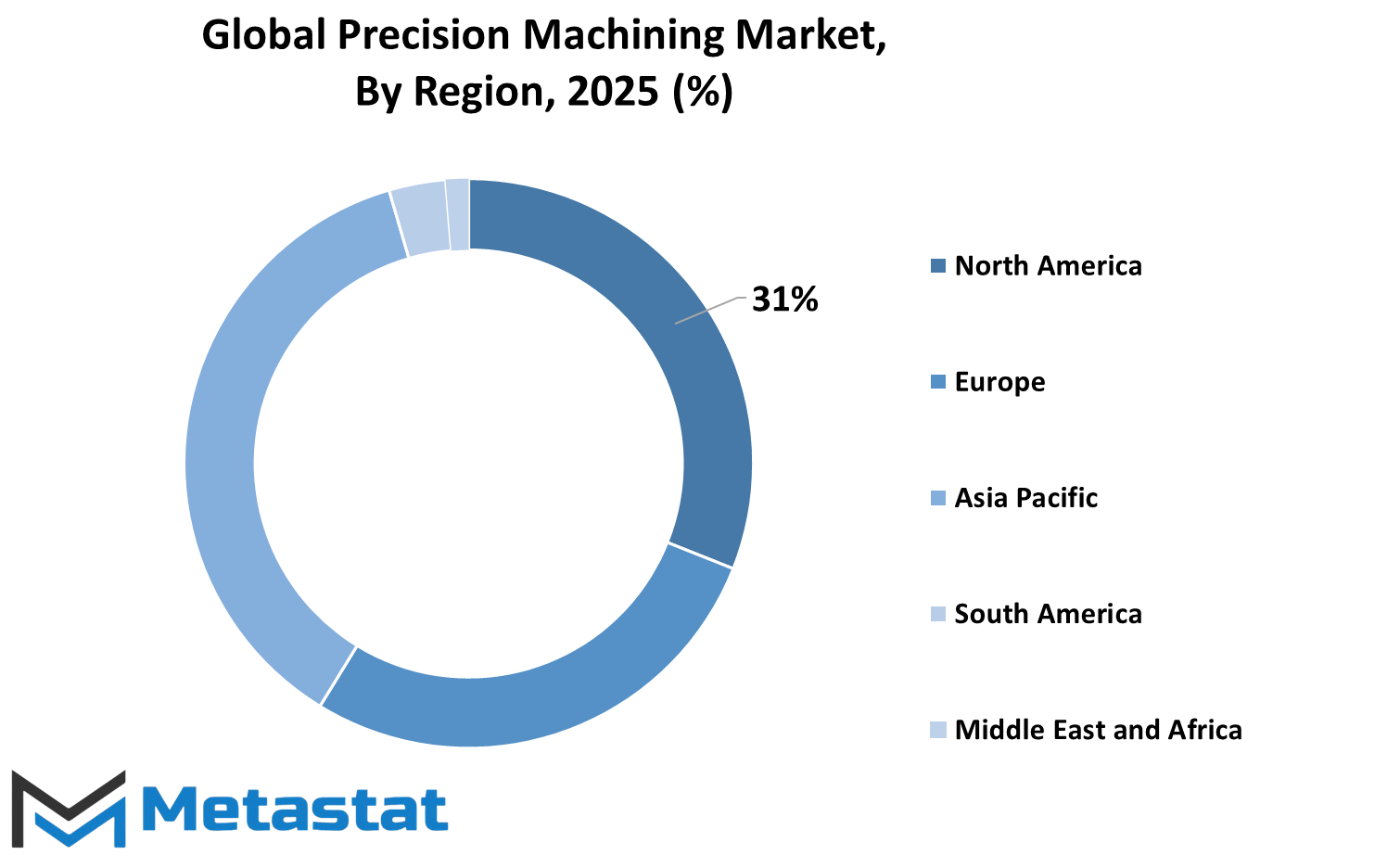
The global Precision Machining industry is distributed across various regions, and each of them has its own contribution towards the sector. The industry is segregated geographically into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East & Africa. Each region consists of certain countries that are included in the comprehensive analysis. North America is divided into the United States, Canada, and Mexico. These nations possess well-established industries and a high demand for precision parts, particularly in markets such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. The United States, more than any other country, still stands at the top with its superior manufacturing systems and high automation and innovation investment.
Europe comprises the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, and the Rest of Europe. These nations are recognized for their established manufacturing heritage and remain important participants in this market. Germany contributes a significant role with its solid engineering core and automotive industry. So does the UK and France with consistent growth through emphasis on high-value machining and exports. Italy contributes to the region's dominance with its production of machinery and tools. The Rest of Europe consists of the remaining countries that are smaller in size but contribute to the overall demand and capacity of the market.
Asia-Pacific comprises India, China, Japan, South Korea, and the Rest of Asia-Pacific. The fastest expansion in precision machining is being witnessed in this region because of expanding industrial activity and growing investments in manufacturing infrastructure. China and Japan are particularly significant, with China dominating in terms of production capacity and Japan in terms of high-precision technology. India and South Korea are also witnessing robust development, backed by government support and an expanding need for industrial components.
In South America, the key contributors are Brazil and Argentina, followed by the Rest of South America. Although the market size of this region is small compared to others, it contributes to some extent because of its expanding industries and regional manufacturing bases. Finally, the Middle East & Africa consist of the GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and the Rest of the region. Even though this region is yet to develop in terms of industry, it is slowly building its role in the international market, particularly through investments in industrialization and technology.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The global precision machining industry is continuously expanding due to increasing demand from industries such as automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and electronics. Precision machining is the process of manufacturing parts with very tight tolerances with the aid of machines that execute step-by-step instructions. This process is used to produce consistent and high-quality parts incorporated into products we use daily. As companies strive for greater efficiency and performance, demands for precise and reliable parts increase, forcing businesses to implement new machining technology.
Manufacturers are also making investments in sophisticated machinery like CNC machines, which increase productivity and ensure accuracy even on intricate operations. Computer programs manage these machines, and this lessens human error as well as saves time. They are extensively utilized by industry leaders in the precision machining industry, such as Amada Machine Tools Co., Ltd., Amera-Seiki, Dalian Machine Tool Group (DMTG) Corporation, Datron Dynamics Inc., DMG Mori Co., Ltd., Fanuc Corporation, Haas Automation, Inc., Hardinge, Hurco, Kent USA, Lagun, Okuma Corporation, Shenyang Machine Tool Co., Ltd., and Yamazaki Mazak Corporation. These organizations emphasize innovation and enhancing product offerings to cater to international demand.
Skilled workers are also a significant component of this market. Although machines perform the majority of the labor, operators and engineers contribute significantly by programming, maintaining, and inspecting the products. The synergy of human expertise and machine accuracy enables industries to produce parts that are highly accurate to specifications. Consequently, most companies are providing training programs to reskill workers and keep pace with technological advancements.
Furthermore, the demand for energy-efficient machines and green production practices has affected the way manufacturers do business. There is increased interest in waste reduction, material reuse, and creating machines that use less energy without compromising performance. Not only do these efforts benefit the environment, but they also save money in the long term.
Despite economic downturns and supply chain disruptions around the world, the precision machining industry has good prospects. Ongoing research and development enable businesses to design improved solutions, remain competitive, and serve customers with changing needs. The emphasis continues to be on providing precision, speed, and flexibility while keeping pace with contemporary manufacturing trends. As the major players continuously upgrade their technologies and reach out further, the precision machining business is poised to remain relevant and significant in numerous industries for the years ahead.
Precision Machining Market Key Segments:
By Type
- Manual Operation
- CNC Operation
By Machine Types
- Milling Machine
- Turning Machine
- Electric Discharge Machine
By Material Type
- Plastic
- Steel
- Bronze
- Glass
- Brass
- Other Metals
By End-use Industries
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Medical
- Semiconductor
- Others
Key Global Precision Machining Industry Players
- Amada Machine Tools Co., Ltd.
- Amera-Seiki
- Dalian Machine Tool Group (DMTG) Corporation
- Datron Dynamics Inc.
- DMG Mori Co., Ltd.
- Fanuc Corporation
- Haas Automation, Inc.
- Hardinge
- Hurco
- Kent USA
- Lagun
- Okuma Corporation
- Shenyang Machine Tool Co., Ltd.
- Yamazaki Mazak Corporation
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential




 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






