MARKET OVERVIEW
The Global Microfinance market has been expanding in practice, offering the kind of financial services which an individual may not have easily accessed through existing banking system modes. This sector is based on the premise of providing small loans and other financial products to economically backward sections to promote their participation in the economy, most of which are neglected by mainstream financial institutions. Though mostly seen as a financial-inclusion model, it actually has ties with social development, digital transformation, and policy development or reform.
Enabling self-sufficiency is what microfinance really means - giving the tools that allow small-scale businesspersons and marginalized communities to become self-sufficient in developing micro-income-generating activities. Over a period of time, it has included lines such as insurance, savings plans, and financial literacy training along with credit. The industry has reoriented from a short-term credit service towards long-term economic stability. Technology-inaugurated changes in the financial landscape would, in the near future, be set to change the service delivery process, under the same with provisions such as digital lending platforms and AI-powered credit assessments, to reduce dependence on traditional means. Mobile banking is the next big step in ensuring faster access to such funds in areas that lack a proper banking infrastructure.
Apart from these financial services that microfinance has for populations, they also bring wider socio-economic changes to such countries. Empowerment of women is an area affected because microloans can help a woman start her own business, thus making her financially independent. Educational outreach through microfinance programs will continue to gain traction since the idea would be making the populace well informed about financial choices. The tie between microfinance and sustainable development will strengthen in line with global endeavors that support inclusive economic growth.
The regulatory regime will continuously keep changing with authorities balancing access to the financial services against consumer protection. Thus, compliance with the regulations would become stricter as well as closely monitored operation frameworks that would ensure responsible lending practices. The influence of international organizations and policy-makers will determine under where microfinance regulations are heading particularly in poor yet growing economies. The association of blockchain technology may even add that degree of transparency to minimize fraud instances and ease record-keeping.
It will also experience an increase in partnership arrangements between established banks and microfinance institutions. While microfinance institutions will benefit from the resources and know-how of traditional banks, banks will enjoy accessing untapped populations using the networks of microfinance institutions. Public-private partnerships will be another avenue of major strategic importance in enhancing financial inclusion initiatives.
Like most developments, microfinance has its own hindrances when it comes to continuity popularization. There are issues of over-indebtedness, repayment difficulties, and market saturation, which will need novel solutions.
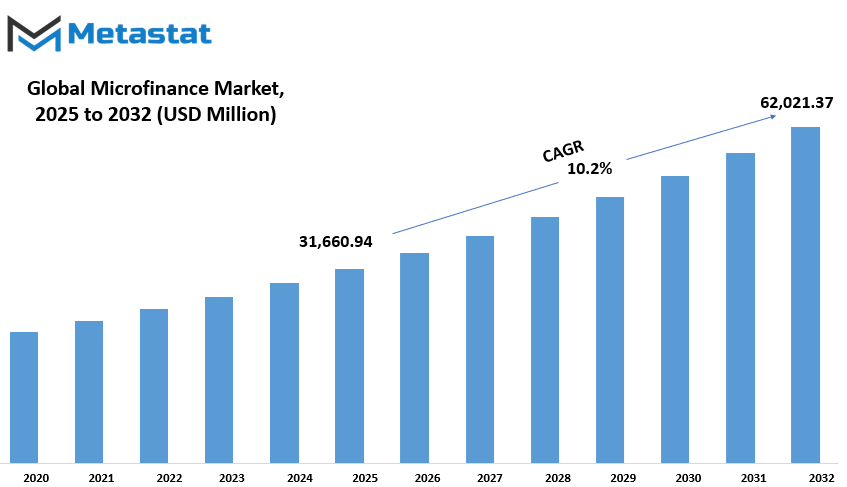
Global Microfinance market is estimated to reach $62,021.37 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 10.2% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
Gaining momentum for the global microfinance market is the rising financial inclusion schemes initiated by both governments and NGOs. These programs aim to provide financial services for persons excluded from obtaining them through traditional banking channels. Many microloans assist low-income earners and small enterprises to better their living conditions and improve the economy. These days, microfinance policies are being adopted in many countries with interventions to encourage more people to access credit, insurance, and savings products. Among NGOs, emphasis is also being placed on enhancing borrowers' understanding of microfinance, especially through the offering of financial literacy programs to equip borrowers in managing their loans.
Digital lending platforms have also contributed to the growth of the market significantly. Technologically, microfinance services are being rendered in a more accessible manner, with applicants enjoying speed in the loan application stage. In rural areas, mobile banking and digital payment services promote the accessibility of financial transactions. With the user-friendly apps and automated systems provided by fintech players, loan processing becomes very efficient, bringing timely disbursement of funds for borrowers. Compared to these undergoing the traditional route, digitalization affords greater scalability and comfort of accessing microfinance products for the lenders and the borrowers.
Although growth is positive, there are a variety of constraints present for the market, one being the very high risk of loan defaults and credit fraud. Microfinance institutions take up such areas as poor-risk borrowers in making most of their loans. So repayment falls within borrowers with unstable income sources, and defaults become ever so likely. Defaults directly affect the lenders proving financial stability. Then some borrowers may give false information to secure loans they cannot repay, which truly indicates credit fraud. These risks make it imperative for microfinance institutions to have a good risk assessment and risk management program in place to shield their enterprises and yet serve the underserved sector.
Another constraint is the stiff regulatory and compliance requirements imposed on microfinance institutions. There are governments imposing strict norms for financial stability and consumer protection, but in doing that, these regulations place an extra burden of complexity on lenders' operations. Often, compliance with such rules involves additional administrative work and costs, thereby hampering growth for the smaller institutions. While the regulation is welcome at keeping the business transparent and preventing people from being exploited, it is indeed a challenge to find a balance between stringent rules and free access.
There remain, however, great opportunities for growth in emerging markets, where access to financial service continues to remain limited. Most developing countries house large populations that depend on informal lending, hence posing strong market demands for microfinance solutions.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Provider Type
The microfinance global reach is growing at breakneck speed because of the significantly increasing number of people who want economic empowerment, thus turning to financial products. It is in place to provide such access, like loans, savings, or other financial instruments, which may go a long way to improving incomes for small-scale enterprises as well as low-income communities. Microfinance itself does the provision of financial services to persons who are alien to traditional banking. With greater demand, other providers have emerged to serve the needs of marginalized segments.
Microfinance providers comprise banks, non-banking finance companies (NBFCs), microfinance companies (MFIs), non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and cooperatives. Banks provide the highest amount in this category with a total of $10,850.18 million. Banks have resources to offer microfinance services, but they operate in collaboration with specialized institutions for a larger population. NBFCs and MFIs also assist by catering to those who may be outside the reach of traditional banking. NGOs and cooperatives, however, are more interested in bottom-up approaches, such that even the most excluded members of society are able to gain access to financial inclusion.
Microfinance lends money to people more than just that. Microfinance empowers the individual to own business, educate, and increase living standard as a whole. Microloans are many times depended upon by small business owners to expand their business further, purchase the goods to sell, or upgrade equipment. By providing individuals with the option to participate in these undertakings, microfinance facilitates economic growth and also combats poverty in underdeveloped regions of countries.
Technology has also greatly helped in increasing microfinance services. Mobile money and online platforms have made the provision of financial services possible without the need for individuals to move to branch offices. Many microfinance institutions also have mobile applications through which individuals can apply for loans, pay money, and check their accounts easily. The technology advancement has streamlined things, reduced the operation costs, and allowed banks to reach a greater number of customers.
Although microfinance has benefits, there are challenges. High interest rates, repayment complications, and regulatory issues can be pitfalls for borrowers and lenders. The failure of some borrowers to repay their loans can result in financial distress. Therefore, microfinance institutions typically provide money management and responsible borrowing education to its borrowers. Governments and regulators must also ensure sound lending practices and protection from abuse for the customers.
With the microfinance sector expanding, lenders must innovate in order to keep up with changing needs and tap into new technologies to make access more available. With continued initiatives towards financial inclusion, microfinance will remain a significant vehicle in helping people achieve economic stability and independence.
By Service Type
Currently, there exists a huge demand for people and businesses to finance themselves well, improving their economic conditions. Microfinance market has made various essential services available to low-income individuals so that they can obtain credit, insurance, and investment opportunities to build businesses and manage daily expenses while planning for the future. It is certainly very helpful, particularly relevant when it comes to financial inclusion, in developing countries where conventional banking services are absent or limited.
Microfinance is categorized based on the financial services it delivers. It includes group and individual microcredit, leasing, micro investment funds, micro insurance, savings and checking accounts, and others. Group and individual microcredit offer small loans to start or expand a business for individuals or groups. The company provides a medium through which an entrepreneur can get a piece of equipment or an asset without having to pay a large upfront payment. Micro investment funds were set up so that individuals could invest small amounts into businesses as an opportunity for many to benefit economically. A service that protects borrowers from unforeseen risks of a financial nature so that, should a set-back occur, they are not significantly affected, ensuring that their activities can continue. Secure ways through savings and checking accounts for managing money and building financial fortification.
One key driver in the microfinance market is the growing demand for financial services from less privileged sections of society. For example, in rural areas, people can be found to have very little or no access at all to banks and other financial institutions. They fill this void by providing controlled financial solutions that can meet specific needs. It's also digitalization that has contributed greatly to strengthening the reach of microfinance services. People are able to access money, repay loans and manage their finances without having to visit the bank through mobile banking or by using digital payment platforms. Such improvements in technology have greatly enlarged the net within which microfinance institutions operate so that they can serve more customers.
Microfinance has an edge but it is riddled with problems. For instance, most borrowers often find microloans to be very expensive to take, and that makes repayment a burden. Some microfinance institutions unlike their peers are never sustainable mostly due to the high operational costs that they incur while trying to provide small loan products. Risk to the industry also arises out of fraud and the lack of financial literacy among borrowers. Continued investment in improving financial education as well as through good regulations would help the industry overcome these hurdles.
It will continue to remain important in an evolving global economy. It gives people the required tools for financial liberation to help bring improvement in their lives. With constant advances and support from the governments and financial institutions, microfinance will continue to be a very strong force in economic development.
By End User
Global microfinance markets are very important in providing financial services to those with no access to conventional banking. They provide tiny loans, deposits, insurance, and other financial products to individuals or small enterprises needing quick capital to grow or sustain their living activities. Not only has this sector gathered momentum over the years, but it has also seen improved economic conditions in a large part of the world, especially developing countries. The burgeoning demand for microfinance products springs from the need for more individuals to achieve financial independence and stability. The other major aspect driving the market is growing demand for financial inclusion.
Small businesses and entrepreneurs often turn to microfinance institutions to provide funds where mainstream banks will give no approval because of lack of credit history or collateral. These microenterprises, conversely, generate jobs and help kick-start the economic growth of their local communities. Microfinance services enable people and families to afford immediate needs, allow them to acquire education, and improve their standard of living. For most, these services provide a dignified means of escaping the poverty cycle and into a bright future. Agriculture is another sector relying heavily on microfinance. Farmers and agricultural workers often deal with cash constraints arising from variable income across seasons and unpredictable climatic conditions.
Microloans enable them to acquire seeds, fertilizers, and farming equipment, hence leading to improved crop yields and productivity. In rural areas, where banking infrastructure is largely absent, microfinance is a vital source of funding for the sustenance of agriculture. Women business owners have also gained hugely from microfinance. A majority of financial organizations have formulated initiatives aimed at promoting women entrepreneurs as they see potential in their contributions to economic growth. Through extending credit facilities to women, microfinance assists them in building and growing enterprises, generating jobs, and financing households. Financial inclusion of women and the provision of financial services has demonstrated beneficial impacts on communities with women ploughing back income into education, health, and the economy at the grassroots.
Self-employed professionals are another significant group of the microfinance market. Independent workers like artisans, tailors, and service providers need small loans to buy tools, raw materials, or increase their business. Conventional banking organizations might not be able to serve their purposes, and hence microfinance is a safe option for them to receive financial assistance. Microfinance helps create economic stability and self-reliance by allowing self-employed people to increase their income.
As the microfinance market for the world grows, technology innovations and online platforms are increasing accessibility to financial services. Digital lending and mobile banking have made the process easier for borrowers to gain access to money in a short and efficient time. With increasing support and innovations, microfinance will continue to be a fundamental driver of financial empowerment and economic growth for vulnerable groups across the globe.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$31,660.94 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$62,021.37 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
10.2% |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The main role of the global microfinance market is to deliver financial products and services to small enterprises and individuals who are not served by traditional banking schemes. While small loans, insurance, and savings receive partial credit for promoting economic growth, poverty reduction, and business empowerment, microfinance institutions have expanded in numerous areas over recent years with a striving to serve the financial requirements of the poor from different locations.
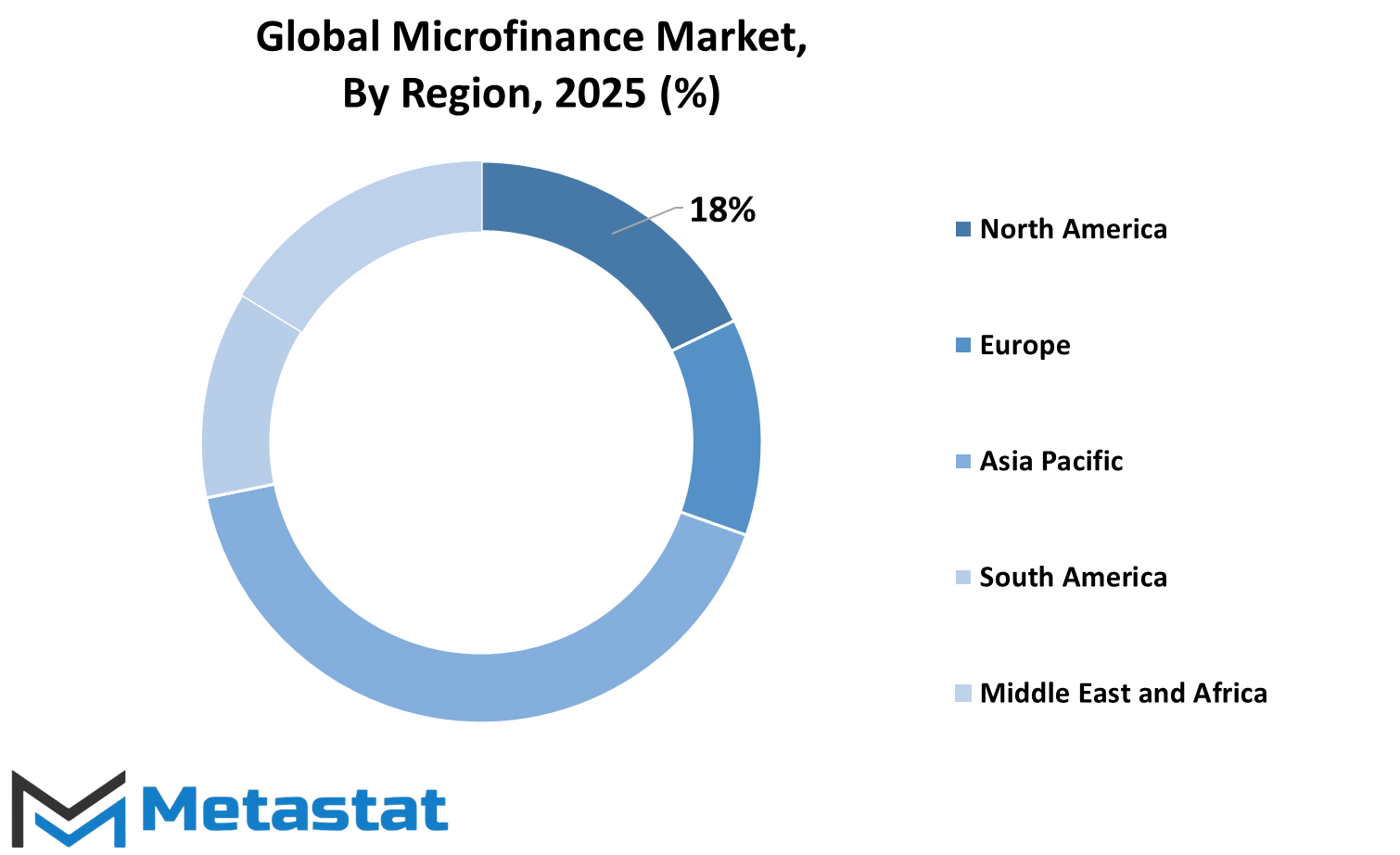
The global microfinance industry has been divided geographically in terms of North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East & Africa. The countries that are included under North America are the U.S., Canada, and Mexico, which are all developed hubs with the financial system that facilitates the development of the industry. Microfinance is a top client with the UK, Germany, France, Italy, and Rest of Europe to finance poor individuals and small businesses. Asia-Pacific includes India, China, Japan, and South Korea, and nations such as India and China have witnessed strong growth in microfinance because they are densely populated and need financial inclusion.
The South American market is Brazil, Argentina, and Rest of South America, in which microfinance has played an effective role for entrepreneurship and economic stability. Geographical area comprises Middle East & Africa, which are GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and Rest of Middle East & Africa. Demand for microfinance services in these areas is gradually increasing, particularly in rural villages and low-income urban communities. To achieve this, government policies and foreign aid have encouraged the development of microfinance institutions in these areas.
Technology has been one of the major new areas in microfinance. Mobile banking and electronic channels have facilitated access to financial services, lowered costs, and improved efficiencies. All but a few of the institutions utilize data analytics in order to assess the creditworthiness of customers, thereby opening up more space for customer outreach. Technology thus has a central role in propelling financial inclusion in remote areas where traditional banking may not be feasible.
Successful as it has been, the microfinance sector is faced with a multitude of challenges. Sometimes, excessively high markup rates, repayment challenges, and regulatory hurdles are in the way of the lenders and borrowers. While some of the institutions are fighting to survive, others are working towards doing some social good while achieving commercial viability. These problems will be solved through innovation, regulatory frameworks, and investment in financial literacy programs to empower the borrowers to utilize their money wisely.
Thus, the global microfinance sector is developing and growing because there is increasing demand for available financial services. By fostering enterprise and creating possibilities for the poor, microfinance largely plays a key role in livelihood improvement and poverty reduction.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The microfinance industry has an eminent place in offering financial services to an individual and small enterprises without access to the conventional banking system. Providing small loans, savings, and insurance empower low-income communities, thereby fostering economic development and reducing poverty. This industry expanded widely in the preceding years due to the necessity of increasing the flow of funds and fostering financial inclusion.
Several key players work in the industry with a view to strengthening the productivity of the microfinance sector. Grameen Bank, SKS Microfinance (Bharat Financial Inclusion), Bandhan Bank, and FINCA International have all greatly influenced this sector. These institutions lend credit to individuals without a regular bank loan qualification, granting them the opportunity to set up their businesses or improve their living conditions. Among other significant names in the industry are ASA International, Asirvad Microfinance Limited, BRAC, and Equitas Small Finance Bank, all working to enhance access to financial services for marginalized communities.
Microfinance institutions are not just giving out loans but are also teaching their borrowers how best to manage their finances. Many microloan recipients have no history with the formal banking system. Financial literacy is a key element of this process. With financial education programs attached to their roles, the likes of Ujjivan Small Finance Bank, CreditAccess Grameen, and Spandana Sphoorty Financial Limited are helping their borrowers establish sustainable financial habits. Thus, providing capital and empowering individuals with the knowledge to effectively manage their finances.
Microfinance in the last few decades has also attracted lots of attention for its role in women empowerment. By and large, a good amount of the microloans is given to women entrepreneurs so that they can establish small enterprises to sustain their families and obtain financial independence. Organizations such as Annapurna Finance, Satin Creditcare Network, and Fusion Microfinance lend out mainly to women since they are seen as contributors to local economies. The same focus has raised women's economic participation, thus creating a more inclusive financial system.
Blessings come hand in hand with challenges for the microfinance sector, including high operational costs, loan defaults, and the burden of regulations. Some organizations such as LOLC Holdings and VisionFund International are continuously searching for innovations to bring new methods with which to improve their respective service deliveries, ensuring that their work continues to be sustainable. The growth of the microfinance sector will depend on the adaptability of this industry to the changes imposed by the outside world in an economic sense. Microfinance institutions, by further honing their instruments and expanding their operational reach, will hold the key to advocating economic stability and development.
Microfinance Market Key Segments:
By Provider Type
- Banks
- Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFCs)
- Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
- NGOs and Cooperatives
By Service Type
- Group And Individual Micro Credit
- Leasing
- Micro Investment Funds
- Insurance
- Savings And Checking Accounts
- Others
By End User
- Small Businesses and Entrepreneurs
- Individuals and Households
- Farmers and Agricultural Workers
- Women Entrepreneurs
- Self-Employed Professionals
Key Global Microfinance Industry Players
- Grameen Bank
- SKS Microfinance (Bharat Financial Inclusion)
- Bandhan Bank
- FINCA International
- ASA International
- Asirvad Microfinance Limited
- BRAC
- Equitas Small Finance Bank
- Ujjivan Small Finance Bank
- CreditAccess Grameen
- Spandana Sphoorty Financial Limited
- Annapurna Finance
- Satin Creditcare Network
- Fusion Microfinance
- LOLC Holdings
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential






 US: +1-(714)-364-8383
US: +1-(714)-364-8383






