MARKET OVERVIEW
The Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing and Transportation market stretches far beyond the conventional aspect of satellite deployment and orbital logistics. This market will transform how materials, structures, and spacecraft are built, serviced, and transported in space, fostering a future in which off-earth operations become sustainable and autonomous. Though primarily discussed with respect to satellite servicing and debris management, the wider repercussions of this market will expand into areas that challenge long-standing assumptions regarding space operations.
Over the coming years, in-space manufacturing will facilitate the making of structures and materials that have been impossible to construct on Earth. Microgravity will provide the avenue for the processing of ultra-pure pharmaceuticals and stronger composite materials and next-generation fiber optics that cannot be manufactured on human terms. Such advances will change industrial practices on Earth while also laying the foundation for self-sustaining habitats in space. Assembling and repairing spacecraft directly in orbit will extend their mission life while also reducing reliance on expensive Earth launches.
And it will be outside the field of maintenance and assembly where extra developments in space transportation will sweep in interplanetary logistics. Instead of sending ready-made spacecraft from Earth, modular components will be manufactured in space, transported efficiently, and assembled on-demand. This will result in a more flexible approach to space exploration in which the missions themselves can be modified and optimized on the basis of actual requirements and real-time information rather than being constrained by prelaunch designs. Additionally, such gradual shifting of materials between Earth orbit, the Moon, and beyond would herald the dawn of a space-based economic system in which mining asteroids for rare metals or habitat construction in Mars would seem no longer a theoretical ambition.
The servicing dimension of this market would also witness a shift. From the current focus on satellite refueling and repairs, an era will come when futuristic applications will deploy autonomous robotic systems capable of performing complex mechanical tasks. These machines will be engaged in high-precision repairs, upgrades, and assembly without any human intervention, thereby greatly reducing the risks associated with human-led extravehicular activities. AI-powered diagnostics will allow one to do truthful failure predictions and address those with corrective actions much before they arise, ensuring the space assets' sustainability over time. This will massively reduce operational costs while increasing viability for long duration missions.
Moreover, the fallout of this market will go beyond the aerospace sector. Supply chains that until now were dependent entirely on terrestrial production will see a drastic shift, in which very high-value materials will get sourced and processed in orbit, instead of just being mined from the ever-diminishing resources of Earth. This will not only alleviate pressure on global supply chains but, in turn, will also further drive developments in material sciences, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Infrastructure for continuous production in space will emerge as a result of sustained cooperation by governments, private enterprises, and research institutions, opening the way to completely new industries.
With the Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing, and Transportation market growing larger, the nature of legislation will have to change to cope with ownership rights, environment, and ethical matters involved with space operations. Aspects of the transition from Earth-based logistics toward in-space autonomy will harbor issues that go beyond technical ones and call for international collaboration and proactive policies. What was once thought to be a field of government-handled projects is changing into a competitive arena where commercial actors will soon become major players determining the future prospects of space applications.
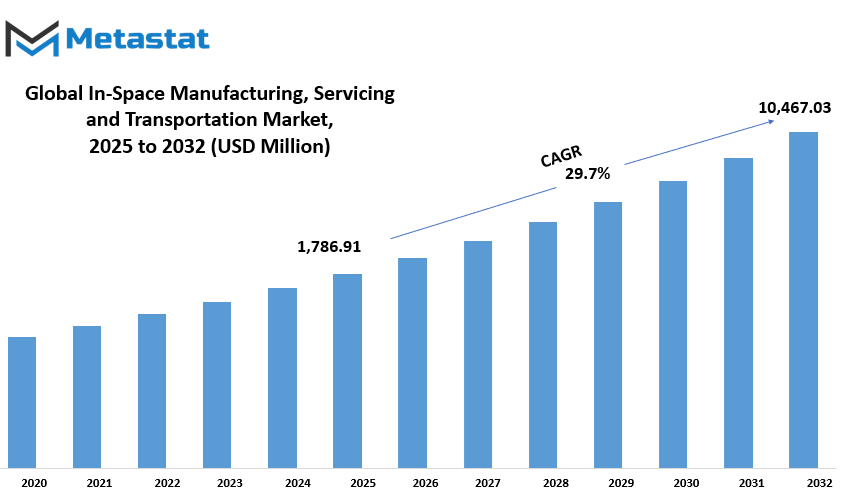
Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing and Transportation market is estimated to reach $10,467.03 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 29.7% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing and Transportation market is buoyed because of some significant reasons, which are causing the moderate growth of markets. Development in investment for space exploration and satellite sustainment is one of the foremost reasons behind this growth because both governments and private entities spend a fortune in developing technology to augment space operations. Satellite sustainment demand soars because of satellite life extension and higher operational efficiency. The whole focus is on satellite servicing activities aimed mostly at in-orbit repair and refueling, thereby reducing costly replacements and maximizing sustainability.
The development of 3D printing and robotic servicing must expedite greater efficiency, thereby enabling the mitigation of risks involved with space operations. For instance, 3D printing permits the construction of components in space and thus reduces dependency on terrestrial supply routes. Robotic servicing, on the other hand, ensures accurate repair and maintenance without human intervention; hence, it renders missions in space safer and more executable in a cost-effective manner. Maintaining and building spacecraft using these technologies greatly increases the flexibility for mission design.
However, some challenges may slow down the market growth. One of these major issues is expenses involved and the technical hindrances arising in the construction of space-based infrastructure. This requires a capital-intensive investment in the development and launch of the equipment capable of operating efficiently in space, and many companies find themselves constrained in finance and engineering. In such situations, regulatory and safety concerns slow down rapid commercialization. Governments and space agencies impose strict measures to ensure safety and reliability, with the result that project time is extended and operational costs are increased.
Yet the market also affords vast potential for further growth. The increasing volumes of tourism in space and deep-space missions would create a demand for in-orbit services. As commercial space travel becomes feasible for more companies, there will be a need for maintenance, transportation, and manufacturing solutions to support missions of long duration. Such developments could signal new opportunities for emerging businesses looking to maximize the present interest in space exploration.
In conclusion, start-up investment and technology innovations propel the Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing, and Transportation market. Although relatively high costs and regulatory issues hinder development, opportunities are growing with space tourism and long-duration missions. This market is one of the industries that promise to influence the future of space operations in the days ahead as technology matures and investments grow.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Type
The emerging global market for In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing and Transportation has an upward trend due to evolving space technology and a quest beyond the Earth for sustainability. The market is grouped into three categories, In-Space Manufacturing worth USD 302.88 million, In-Space Servicing, and Finally, In-Space Transportation. These segments are at the forefront of redefining space exploration, thereby opening avenues up to future research, commercial initiatives, or even long-term missions into space.
In-Space Manufacturing aims to develop materials, tools, and parts directly using space resources. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods on Earth, which often have limits regarding size for launch into orbit, space-based manufacturing makes it possible to produce lighter, stronger, and functionally superior materials that would be difficult or impossible to produce under Earth's gravity conditions. This technology is supposed to benefit a greater number of industries NHS, telecommunications, medicine, and construction. Building and assembling in microgravity cuts down on expensive resupply missions, making deep-space exploration more practical.
In-Space Servicing constitutes other important part of this market. Satellites are important for communications, navigation, and Earth observation, and many satellites get obsolete due to some coding failure or another from fuel depletion. These servicing technologies are helping satellite repair, fueling, and giving upgrades in orbit: thus, substantially increasing the life of satellites. This further helps to reduce space debris and is cost-effective for satellite operators. Moreover, service capabilities would also facilitate the infrastructure on growing demands of space maintenance, thereby keeping critical systems operable for longer periods.
In-Space Transportation relates to conveying freight, equipment, and even astronauts from point to point in actual space. As missions go beyond low Earth orbit, so do the necessary efficient transportation solutions. For example, such advances are helping to develop vehicles that will bring supplies to and from space stations, move payloads to distant destinations, and help explore planetary bodies. These advances will facilitate long-term travel in space in the future for missions to the moon and Mars.
Fueling the growth of the market is government investment and private initiatives, as well as cooperation between the space agencies and the corporate world. Companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and others are busy working on technologies that improve space logistics. As costs come down and technology improves, more businesses and nations will join the ranks participating in space-related activities, which would otherwise continue to fuel the industry.
Much as there are still challenges with high development costs, regulatory issues, and technical complexities, the potential benefits far outweigh the obstacles. The progress of this particular market will be a game-changer in the revolution of human operations in space, but it will be made accessible and sustainable for future generations. With continuous innovation, the Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing, and Transportation market is all set to transform the way space is used for science and commercial purposes.
By Service
Satellite Servicing is a lead area covering refueling, repairing, and upgrading satellites that are already in orbit. SATELLITE SERVICING means ensuring that those satellites will be operational for an extended period. Since a satellite is expensive to build and launch, the longer functioning of these satellites is secured through servicing, thus making their operations in space more cost-effective. Many companies and agencies invest in robotic technologies and autonomous systems to improve servicing capability, requiring less human intervention. This, in turn, caters to the maintenance of indispensable space-based services: communication, navigation, and Earth observation.
Orbital Assembly brings construction and assembly of structures into space, rather than launching them fully built from Earth. This helps make room for building larger and more complex structures, such as space stations, telescopes, and even habitats for long-duration missions. Robotics improvements and introducing modular components have made this far more efficient in terms of bringing these structures together. This service is going to be important for the coming deep-space explorations and even in commercial undertakings outside of Earth's orbit.
Resupply Missions sustain existing activities in space by bringing goods for consumption, mostly food and fueling for recharging, and such equipment to space stations and other habitats. These activities guarantee that astronauts and automated systems never run short of supplies required to continue operations. Governments and private companies are working on reusable spacecraft to increase efficiency and cost-effectiveness concerning resupply missions. This could also contribute to self-sufficiency in space exploration with materials less dependent on Earth.
Space Tourism Transportation is a developing field catering to private sector involvement in human space travel. Most of the investigation is preliminary, but with limited success, some companies have launched suborbital flights, giving short jumps beyond the atmosphere. Future developments in the space tourism sector will reduce the cost of space travel, opening huge avenues for research and leisure at a smaller cost, thus possibly making it available for a larger population.
The Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing, and Transportation market is going to grow as long as innovations in technology continue improving the efficiency and bring down costs. With such investment from companies and governments into these services, space activities will be more affordable, sustainable, and economically viable, paving the way for new horizons in space exploration and development.
By Application
The Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing, and Transportation market is assuming importance because technological developments and the demand for space-based solutions are on the rise. In the sector of satellite maintenance in space service, in-space resource manufacturing, and efficient gravitational systems, these fields are being increasingly invested in by companies and governments. While the market divides its sectors into commercial applications and military & government applications, the commercial sector boasts a huge number of private companies engaged in experiments in the manufacture of products in space.
Working on these products makes use of microgravity conditions that permit processes which are either impossible or very complex in terrestrial settings. Pharmaceuticals, fiber optics, and semiconductor production are favorable examples of industries that have adopted an off-planet approach to production. Such companies are also currently studying and developing service offerings for most satellite servicing.
Currently considering examples for space-based production are mostly pharmaceuticals, fiber optics as well as semiconductor manufacturing. Also, there are many companies that are looking into the satellite servicing business, which would extend the life of satellites by resupplying them when their fuel runs low or by repairing parts damaged by space debris. Transportation forms a large aspect, where private entities are developing reusable launch systems and in-orbit transfer services to render space access affordable and viable.
Satellite capabilities are imperative to national security, intelligence gathering, and global communications from the perspective of military and government sectors. Governments are engaged in these satellite servicing and refueling projects to maintain strong presence in space. Military applications need more advanced spacecraft that are repairable and upgradeable in orbit to reduce and delay the frequency of replacement. Governments also retain a keen focus on space transportation to deploy defense systems or support missions involving planetary exploration and deep-space travel.
In-space manufacturing, servicing, and transportation are rather popular; hence, technology development begins. Companies are investing in technologies such as robotic arms, automated assembly systems, and 3D printing systems to improve the efficiency of in-space manufacturability. The generally accepted fact is that the existence of in-orbit repair and maintenance activities reduces costs and curtails wastage. Progression of transportation services has entered a new path...with the improved propulsion systems capable of shortening travel time and lowering costs.
Investment and research will continue to defeat any challenges, such as cost, technology, and regulations. Government search partnerships with private companies will prove very important in the future. Manufacturing, servicing, and transportation orbiting advantages will leave a deep imprint on industry, scientific research, and space in sociocultural and economic terms as space activities become so common within societies.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$1,786.91 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$10,467.03 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
29.7% |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
All these had led to that amazing growth that marks the age of technological improvements necessitated by increased ownspace businesses. In actual fact, many governments and companies financially invest in the development of the newer capabilities that complement space infrastructure or satellite maintenance and transport services. These transformations would play up how industries would develop beyond Earth and open further opportunities for new innovation and collaborative efforts.
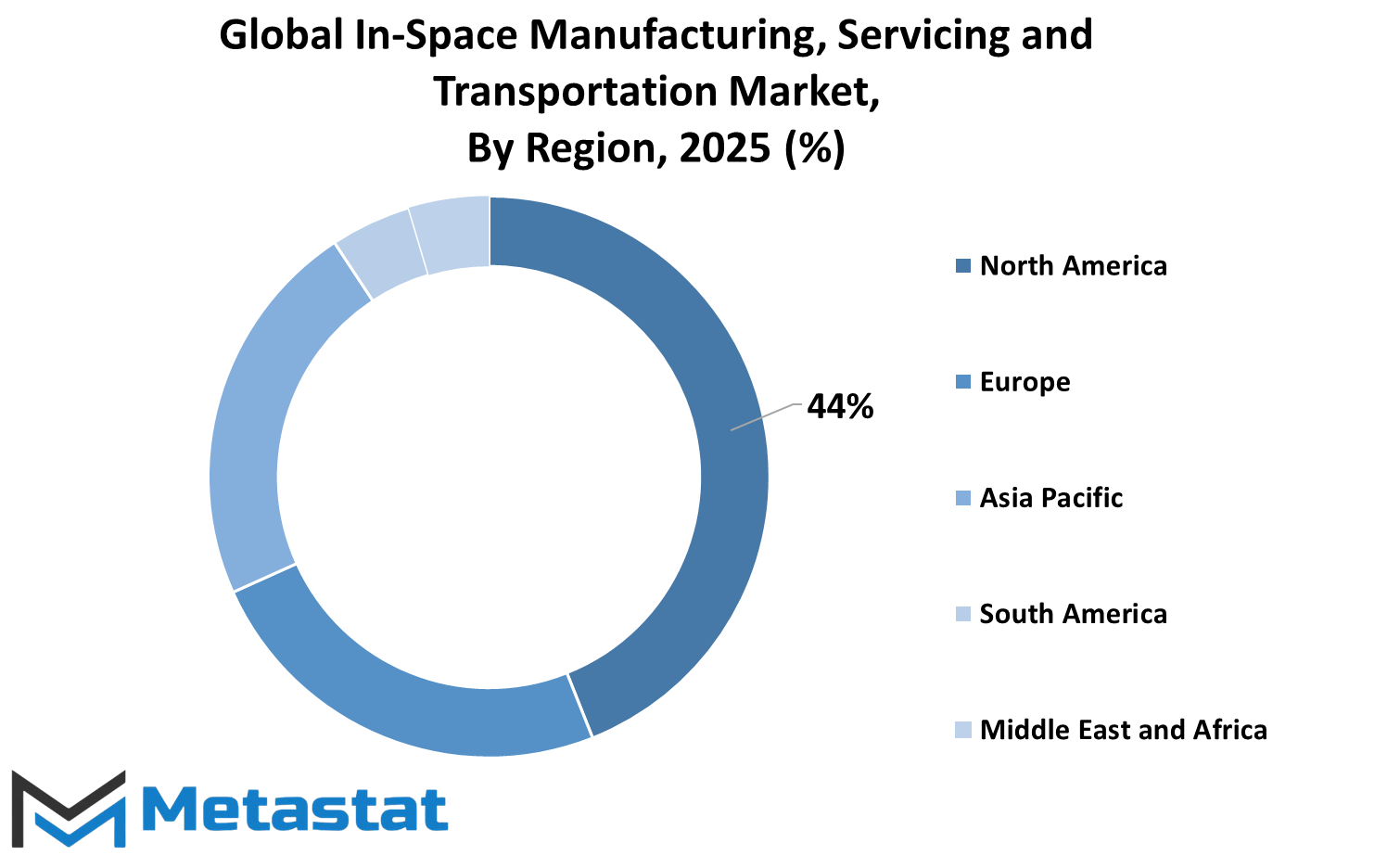
The analysis of this market is based on geography, which includes North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, and the Middle East and Africa. North America includes the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. Most of the very active national and private space agencies have interests in satellite servicing, space-based manufacturing, or orbital transportation. Thus, the role the U.S. plays in the commercial growth of established space programs is quite significant.
Major European countries, such as the UK, Germany, France, and Italy, have been actively involved in technology development in this market. Quite a number of initiatives have been undertaken with the focus of such activities being improved satellite servicing and in-orbit manufacturing, to possibly attain the capability of bringing such regions to space capability. Various combined efforts among nations in Europe lead to increased research and development and make Europe a major competitor in the global market.
Asia-Pacific is another vital area and includes countries like India, China, Japan, and South Korea, along with the rest of Asia-Pacific. The quick establishment and launching of such space programs have caused investments in satellite deployments and in-orbit servicing and transportation to surge in this region. A critical achievement in this sense will therefore be delivered soon by ongoing projects in China and India, which are meant to boost their influence in space operations. Technological innovations and strategic partnerships are also expanding the contributions by countries like Japan and South Korea.
South America, including Brazil and Argentina, and the Rest of South America is gradually coming up to participate in space activities. Not quite the leading region compared to others, but investments in satellite programs and emerging partnerships with already established space agencies can provide room for future growth. The region thus seeks to enhance its infrastructure and capabilities so that it can compete with the ongoing worldwide initiatives behind space.
The Middle East & Africa region, further categorized as GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and the Rest of the Middle East & Africa, is also making histrides in space exploration and related technologies. Some countries are investing a great deal in satellite technology and conducting space research to place themselves in the market. Such efforts are anticipated to promote a significant growth rate in the area of space-based manufacturing, servicing, and transportation operations in future years.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The In-Space Manufacture, Service, and Transportation Global Market are increasing because space technology is developing more and more new possibilities. Companies in our field develop solutions that create more efficient, sustainable space operations--manufacturing materials and equipment in orbit, servicing satellites to give them again, and transportation systems that allow moving between various different locations in space. This market opportunity grows with investment from increasing numbers of nations and private organizations in space exploration and infrastructure.
One of the main sectors in this industry has turned toward in-space manufacturing. It involves launching a space-built structure instead of a complete one built here on Earth. It enables lowering the cost and making bigger and more complex systems that will be difficult or impossible to bring from the ground. It also opens the possibility of using materials from outer space, which further reduces reliance on terrestrial resources. Companies such as Airbus S.A.S. and Honeybee Robotics are leading this charge by developing technology to allow on-orbit construction and production.
This market also revolves around its much-important aspect, which is servicing. They are expensive to build and launch, and primarily due to the very few operational years, they need to be replaced. In-space servicing would extend the time operationally for a satellite, for instance, by refueling it, repairing parts, or upgrading old technology systems. Costs could also be reduced since less space debris has otherwise accumulated. Astroscale Holdings Inc. and Northrop Grumman Corporation work to create solutions that will enable servicing of satellites rather than discarding them once they have malfunctioned.
Space transportation is yet another important engine of growth for this industry. Efficient and reliable transportation systems will help move cargo, equipment, and even people between different points in space. Companies like Momentus Space, D-Orbit SpA, and Firefly Aerospace are coming up with new propulsion and transfer technologies, making space travel much more feasible. These advancements will support missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, while also improving the efficiency of moving satellites and other assets in orbit.
Investment in space activities is expected to continue growing with time, and so is the development of the In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing, and Transportation market. An increase in private and government activities is creating competition and innovation that will make space operations more sustainable and cost-effective. Some of the companies contributing to this sector's growth are Orbit Fab, Atomos Space, Infinite Orbits, and Thales Group. All these companies ensure that space exploration and development are moving forward.
In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing and Transportation Market Key Segments:
By Type
- In-Space Manufacturing
- In-Space Servicing
- In-Space Transportation
By Service
- Satellite Servicing
- Orbital Assembly
- Resupply Missions
- Space Tourism Transportation
By Application
- Commercial
- Military & Government
Key Global In-Space Manufacturing, Servicing and Transportation Industry Players
- Airbus S.A.S.
- Honeybee Robotics
- Momentus Space
- Astrobotic Technology
- D-Orbit SpA
- Astroscale Holdings Inc.
- Orbit Fab
- Atomos Space
- Infinite Orbits
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Thales Group
- Firefly Aerospace
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential





 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






