MARKET OVERVIEW
The Global Power Generation market will not be limited to old, centralized generation systems but will also integrate developing decentralized grids and the increased use of modular generation units. This transformation will be critical for any interface set up to ensure that where demand peaks depend on supply, overreliance on single streams of energy is avoided, and any transmission constraints in far-off areas are tackled. New and diverse generation strategies, with hybrid models that integrate different generation technologies becoming strategically important, will be seen.
Conceptually, power generation is part of the larger energy industry. Power generation is still the primary way in which electricity is generated and supplied to different areas. It encompasses a host of technologies and fuel sources, ranging from fossil fuels, nuclear, hydro, solar, and wind. While adapting their approaches to energy security, reliability, and sustainability, nations will find regional infrastructure development, technology employments, and economic prioritization unavoidable in the context of the Global Power Generation market. Electricity supply sustains all industrial processes and life itself and will call for innovations at every level of the power generation process.
Advanced control systems and data-driven monitoring tools will redefine the functioning of generation facilities in this industry. Efficiency will become a core parameter with maximum energy output from each energy input to be the goal of the operators. The Global Power Generation market will respond to a changing consumption pattern with residential, commercial, and industrial users increasingly electrifying their solutions for heating, transport, and products. These new demands, imposed on the generation operators, will require a careful balancing act between production capacity and consumption forecasting whereby predictive analytics and responsive infrastructure will come to the fore.
Technology development in fuel processing and thermal efficiency will continue determining the layout of the new generation plants and the refurbishment of the existing ones. Driven by this market, Global Power Generation will consist of newly commissioned plants and retrofitted legacy systems, thus creating an arena for the coexistence of several generations of technologies. Such infrastructural diversity will pose challenges for operations, such as the integration and standardization of various platforms. However, it will create opportunities for research institutes and engineering companies to work together on solutions aimed at these hybrid contexts.
Further, the operational framework of the Global Power Generation market will be shaped by international policies and national energy strategies. Governments will set performance standards, emissions limits, and technological road maps that generation facilities must satisfy. Meeting these conditions will thus be a fundamental requirement for companies wishing to function in regulated environments.
The Global Power Generation market shall see active investor participation in terms of all kinds because it is a capital-intensive market. Investment would not only go to the physical infrastructure but also to software platforms that run forecasting, asset management, and cyber security. Market players considered these intangible assets as the first requirement for long-term operational success.
Moving forward, the Global Power Generation market would provide operational infrastructure for numerous downstream applications. Its structure, strategy, and innovation path will have to be defined by the demand for a mechanism that meets electricity needs globally, with efficiency, flexibility, and accountability. As the consumption dynamics change, the market will realign its technology and regulatory approaches to ensure the integrity of supply and maintain economic feasibility.
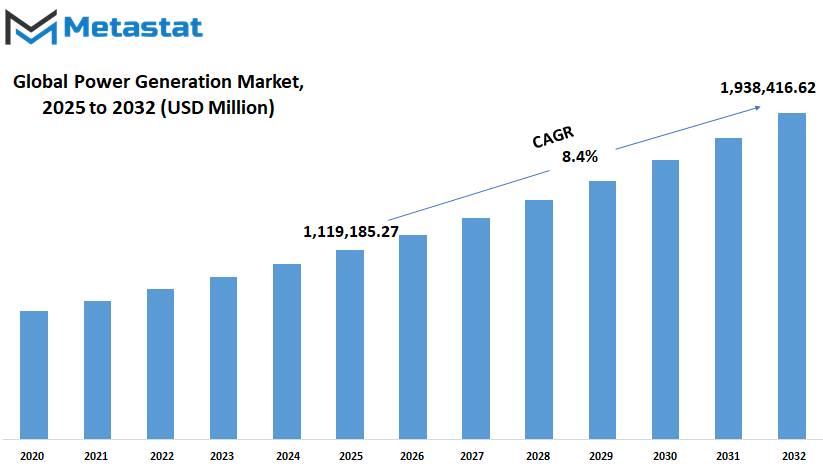
Global Power Generation market is estimated to reach $1,938,416.62 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 8.4% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The Global Power Generation market is expected to grow significantly owing to an infinite capacity of electricity consumption requirements worldwide. With this expanding population and growing industries, the demand for reliable power will steadily increase. An increasing number of homes, offices, and digital infrastructure will require constant energy, thereby putting a strain on the existing power infrastructure. Governments and private enterprises are investing heavily in renewable energy sources-solar, wind, and hydropower-to satisfy this ever-increasing demand. These sources are sustainable; as technology develops, they are becoming more efficient and economical. With this gradually evolving trend, the power generation market will gradually phase away from fossil fuels towards a greener and more reliable energy future.
However, there are quite a few hurdles along this transition. One of the larger ones pertains to the setting up of new power generation plants in a cost-effective manner using newer clean technologies. Their initial capital costs for solar farms or wind turbine construction and management are heavy, albeit with low operating costs in the long term. This would deter indigenous developers or areas with a limited budget from taking up these cleaner measures. Environmental issues and regulations play a key role in shaping the course of development in the industry. Governments are tightening the noose on emissions and pollution, therefore leaving power companies with a lot of obligations to adhere to. While those laws help save the world, they can also halt a project in its tracks or balloon expenses.
Nevertheless, the fast-paced changes in energy storage have created interesting opportunities. Probably the time when storing renewable energy for use when the sun is not shining, or the wind is not blowing has been an eternal hitch. Well, with the recent development of battery technology and other storage systems, that problem is coming close to being tackled. In the coming days, advanced storage solutions will manage to save power generated from clean sources and utilize it at a later stage that will add to the flexible and reliable energy systems.
Looking into the future, this Global Power Generation market is expected to turn out smarter and adaptable energy solutions. If better infrastructure and investment and supportive policies keep pouring into the market, then the conditions will give further rise to economic growth along with environmental responsibility. Energy generated and used based on today's decisions will have a major impact on shaping the world and its future for many years to come.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Technology
The Global Power Generation market gradually moves towards future developments that will be forged through innovation, sustainability, and their demands. The drastic reforms which changes have been taking place in the way electricity is produced over the last decade as countries try to reconcile economic development with environmental care move to the next level. For instance, fossil fuels, nuclear, solar, hydro, and others as current topics reflect where one is at present and potentials of the future market: the different types of technology play different roles on supporting world needs; and what they do or do not do depends on investment, interest, efficiency, environmental impact, and long-term viability.
Electricity from fossil fuels, backbone for power supply across the world till today, still enjoys much market share. It will probably be of little less than 661735.83 million USD in 2025 and is still very important for those areas where the alternatives were either too costly or have not yet been developed. However, one could visibly sense the increasing pressure to decrease reliance on the same given concerns regarding emissions and the world now increasingly becoming cleaner energy oriented. Although still large, its growth might gradually decelerate owing to new policies and public proclivities being skewed toward greener solutions.
Also, nuclear electricity is going to hold its position, with a projected value at USD million 129,036.19 in 2025. It assures stable and large-scale power generation at lowered carbon emissions making it an attraction for those countries intending to sustain their output without harming the environment. Safety issues and long-term waste storage remain controversial, which may limit it from being extended in certain areas. Nonetheless, with the new technology and safety improvements in the modern era, nuclear energy probably has a more optimistic future ahead.
One of the fastest developing technologies, solar electricity is forecast to be valued at USD million 132,174.08 by 2025. Really a component part of the whole energy planning across the world, it is being encouraged by lower costs of installation and government incentives together with peoples' support. It is also practical and inspirational because sunlight alone will be able to light homes, even entire communities. As it stands, with the development of storage technology, solar might one day overcome its deficiencies based on time of day and weather.
Another renewable source of energy that will value USD million 119,862.18 in 2025, hydroelectricity stands as significant to millions of dependability sources. It gives one reliability and scale, especially in countries with wonderful water resources. Environmental concerns, such as affecting aquatic life, are there, but innovations are being brought forth to make the developments eco-friendlier.
Other methods of electricity generation wind and geothermal collectively lay a value of USD million 76,376.99 in 2025. These technologies are gaining popularity, with their emissions and complementary roles toward energy diversity making them attractive.
By Grid
The Global Power Generation market is evolving slowly, being somewhat restructuring in terms of priority according to the energy needs changing and mostly by the growing interest in clean stable energy sources. Most visibly, the change would be towards the connection and distribution of electricity. It divides the market on-grid into Off Grid and On Grid: two major sections. This distinction is beyond a technical detail since it reflects a larger movement toward redefinition about the way of obtaining electricity by communities and nations. While On Grid systems continue to serve most urban and industrial areas, Off Grid systems are becoming ever more important in those regions which are difficult to access or where traditional infrastructure simply cannot keep pace with rising demand.
On Grid systems connect to central electric sources usually through old grid lines for the sake of electric distribution. These systems commonly rely on steady generation and broad-reaching connections either controlled by utilities or government agencies. The Global Power Generation market is heading towards the trend of modernizing On Grids with smarter technology and better control systems as it develops. Balancing the demand and supply can minimize emissions and waste, allowing the integration of renewable energy resources such as solar and wind. The importance of this kind of change is enor-more to maintaining cities and industries powered without putting undue pressure on the environment.
At the same time, Off Grid systems will be blazing a trial, especially in areas where it would be resource-intensive or time-consuming to bring in a full-fledged connection to the grid. They are self-contained systems that are generally smaller, but they can allow an easy way for bringing power to people who otherwise fall power-less. With technology becoming cheaper and more user friendly, Off Grid settings will in the future probably be the most common. It will sustain households, farms, and even small factories without having to plug into a centralized power source-an opportunity to broaden future possibilities in person local economies and have a better life.
In the course of time, both types of grid systems will continue growing and changing. The Global Power Generation market will be conditioned to satisfy the demand for effectively balancing huge power demands with the emerging demand for local, flexible options. While On Grid system will carry a considerable part of the global energy use, the Off Grid system is intended to play a critical role in 'plugging' areas that have historically lagged behind. They will create a future wherein access to electricity is more equitable as well as more applicable to the changing needs of people around the world.
By Source
The Global Power Generation market is poised for a big shift, as in the current world, there is a transition from traditional sources of energy to sustainable cleaner ones. This transition is being pushed not only due to a concern for the environment but also out of technological development, rising energy demand, and the increasing need for reliable affordable electricity. This has compelled people and industries alike to take notice of the origins of their electricity, and that awareness is making market waves.
For generations, coal, oil, and natural gas remained the mainstays of power generation. Non-renewable sources have offered economies a constant and heavy supply of full justification for electricity in the past decades. However, the future Global Power Generation market will not be dependent solely on these sources. These may still be useful for some time in distant areas where renewable alternatives are still a work in progress, but the trend is evidently somewhere else: towards renewable sources. Momentum is building for solar, wind, hydro, and other clean energy alternatives, not just on their green merits but also on their maturing price competitiveness.
The major face of energy generation will continue to change with many newer and better technologies. Improving efficiency of renewable power generation systems and developing energy storage solutions are essential to ensuring an uninterrupted supply when the sun isn't shining or wind isn't blowing. This transition is also favoring decentralized energy systems, where energy systems are generated closer to energy demand centers. Smaller plants are distributed with installation near the power end-user.
The interest from supportive governments, investors, and businesses continues. Policies are being developed to promote cleaner energy generation, while investment in renewable energy infrastructure is on the increase. This will be sustained and with acceleration now that both local and global efforts are being made to reduce emissions and tackle climate issues. The future of the Global Power Generation market is more likely to see a balanced approach where it coexists with cleaner technologies before fully transferring leadership in the long run.
In such a scenario, attention is given to energy efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and increased energy access. As more countries invest in renewable technologies and develop better systems for storing and managing energy, the Global Power Generation market will continue to evolve and create new opportunities for growth, innovation, and sustainability far into the future.
By End-Use Sector
The Global Power Generation market is in a gradual transition toward a future that will be shaped by increas-ing energy needs, transforming consumer demands, and foremostly, increasing sustainability concerns. The shift is already underway across various end-use sectors, namely industrial, commercial, and residential. Industries have graduated from purely chasing energy supply solutions to also looking into more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions in their exertion to fulfil increasing operational demands. For smart grid industrial areas, the future should be more automated and increasingly cleaner in power sources to allow production to carry on smoothly with minimum waste and carbon emissions. This transition is, rather than a trend, a mode of existence rapidly being adopted by any industry that needs high productivity and competitiveness on a global scale.
In commercial settings, energy costs and reliable energy supply are becoming the center of attention. The aim now is to keep interruptions to daily functions to an absolute minimum, particularly as technology becomes more embedded in daily business operations. Offices, retail spaces, and service organizations will prefer systems that not only minimize energy costs but also provide for reliability. This will, in turn, lay soil for backup systems, decentralized power generation, and energy-efficient design specially catered for modern workspace. In an overall sense, energy use in this sector will become increasingly targeted in its precision, data-based in its calculation, and automatically controlled in responsiveness to demand.
Residents focus heavily on comfort and convenience; future homes will have energy-saving appliances, smart meters, and solar panels. Control of energy use will be desired without accompanying technical complexities. This shift will, in turn, affect new construction designs and retrofits to existing homes. The government and utilities might be offering incentives, tools, and programs targeting energy-reducing measures and cost savings for homeowners. As technical realities favor the movement, then and there begins the entry of more people into the movement, making energy-smart homes a norm and not a luxury.
In conclusion, the aforementioned three sectors shape the Global Power Generation market. Although needs differ from group to group, efficiency, sustainability, and control is the common point and direction. Energy production and delivery will become more personalized and responsive over the coming innovations. What lies ahead is not just a system fit for use today but designed for tomorrow's expectations, where every end-user-from factory to families-will be connected and empowered in smarter ways.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$1,119,185.27 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$1,938,416.62 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
8.4% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
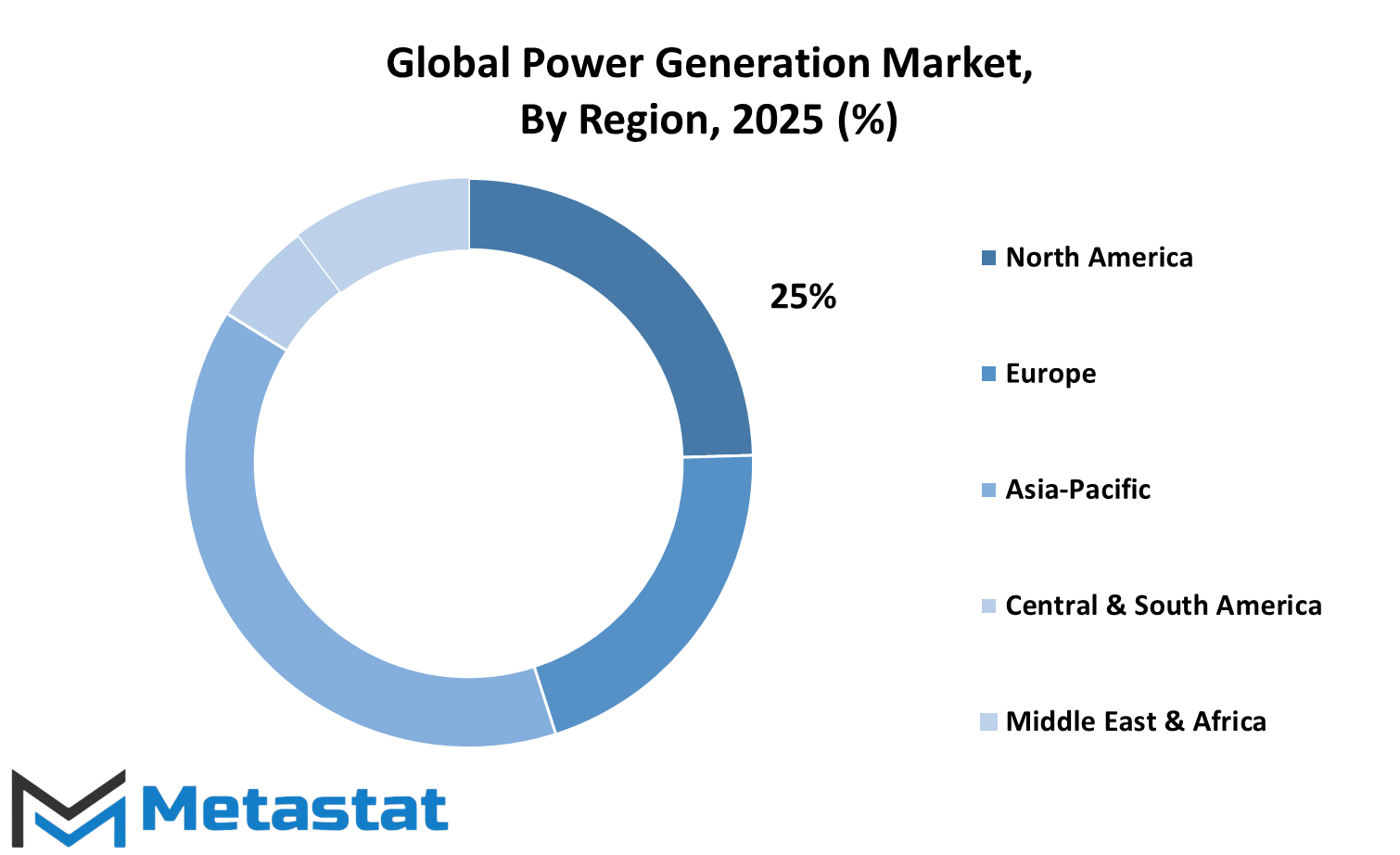
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The Global Power Generation market will likely have some divergent growth paths all over the regions, depending on local conditions like policies, economic developments, natural resources, and investments in energy technologies. Each region has its distinct profile of energy consumption and development speed for the next few decades likely to affect market evolution and transformation. In North America, relatively stable demand will be witnessed, especially where countries like the U.S. and Canada are investing heavily in upgrades of older power systems. Clean energy opportunities will still be prevalent in this region so as to ensure enough capacity is available for industries and residential uses. Over the next few years, limited gradual improvements will be expected in Mexico's infrastructure, leading to more opportunities in the market.
In Europe, energy transition goals are being pursued by countries such as Germany, the UK, and France. Increasingly, this seems to be a shift away from conventional energy to new ones, which are less harmful to the environment. These changes will likely attract more investments in wind, solar, and renewable sources. Southern and Eastern parts of Europe may take a while to catch up, but in any case, this pathway is toward cleaner and more flexible power systems, which will condition the performance of the Global Power Generation market across the region.
The Asia-Pacific region should see the fastest transformation. Power demand is quickly growing in countries such as China and India due to a growing population and industry. These nations are struggling to achieve a more balanced dependence between reliable energy sources and greener solutions. Japan and South Korea, though relatively smaller, are technologically quite advanced and should continue with the research for new and improved means of producing and storing energy. All these efforts are going to play a huge part in deciding how the market is progressing in this part of the world.
South America's development will depend on better energy access and political backing for large-scale energy projects. Since Brazil is one of the biggest players in the region, it will actively push the development of traditional and new energy projects. Argentina, among others, may seek foreign aid and partnerships to assist in building their capacities.
Mixed progress is witnessed in the Middle East and Africa. Some countries are capable of investing in future-ready power systems, strongly those from the GCC. Others will grow cautiously, depending on external support and internal stability. Generally, the Global Power Generation market will evolve differently for every region based on local needs, resources, and future aspirations and goals.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
A steady transition is being experienced by the global power generation market wherein companies, countries, and communities search for more efficient and cleaner methods to generate energy. Keeping in mind the environmental impact, energy security, and long-term sustainability, the very nature of this business will keep evolving toward the new technologies and renewable sources while, for quite some time, the traditional power systems will remain operational in several regions. This gradual yet clear transformation defines how leading players lie awake at night contemplating the future of energy production regarding various company designs.
Major players in the Global Power Generation industry like General Electric (GE), Siemens AG, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and ABB Ltd. are already reshaping their strategies to stay with the times. Not only are these companies working to improve their current systems, but they are also investing in research and innovation to develop smarter, adaptable technologies. Schneider Electric SE and China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC) are also focusing on advanced solutions that will help cater to the rising demand for reliable and cleaner power. These together could strengthen energy networks that fit both old-fashioned power demands and those of newer green solutions.
Meanwhile, the companies Exelon Corporation, NextEra Energy, Inc. and EDF Group have become strongly focused on renewables. Public and private grants are extending the reach of wind and solar power projects, and this trend is likely to strengthen. As these cleaner sources gain cost-competitiveness and become common, other major energy suppliers such as Engie SA, Enel Group, and Duke Energy have started to look for ways to make their systems more flexible. They are investigating improved energy-storage technologies, using artificial intelligence for supply-demand matching, and more efficient grid interconnection.
Companies such as Tata Power, Orsted, and E. ON SE are also preparing themselves for a future where energy is local. This is to support communities that generate their own electricity and share it through small and smart grids. Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), NTPC, and Adani Green are similarly upgrading infrastructure, minimizing wastage, and experimenting with new energy storage models. Even larger transmission operations like Power Grid Corpn are beginning to upgrade their networks to transport cleaner energy across greater distances.
In the future, Global Power Generation will keep on evolving at a high rate with technological advancement and ever-changing public perceptions. The companies that are spearheading this transition are not only responding to the present day but are also actually building for a future where energy is more efficiently, more accessible, and more environmentally balanced.
Power Generation Market Key Segments:
By Technology
- Fossil Fuel Electricity
- Nuclear Electricity
- Solar Electricity
- Hydroelectricity
- Other
By Grid
- Off Grid
- On Grid
By Source
- Non-Renewable Source
- Renewable Source
By End-Use Sector
- Industrial
- Commercial
- Residential
Key Global Power Generation Industry Players
- General Electric (GE)
- Siemens AG
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- ABB Ltd.
- Schneider Electric SE
- China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC)
- Exelon Corporation
- NextEra Energy, Inc.
- EDF Group
- Engie SA
- Enel Group
- Duke Energy
- Tata Power
- Orsted
- E. ON SE
- Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO)
- NTPC
- Adani Green
- Power Grid Corpn
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential





 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






