MARKET OVERVIEW
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is building an industry that unites sustainable agriculture with clean energy in ways that will extend far beyond its present use. As the farm and renewable energy industries continue to look for intersections, this market will open up prospects that extend beyond food production and power supply. Over the next few years, it will not be only about cultivated crops under solar cell roofs-it would be a change in such a way that the community is attached with land use, climate flexibility and agricultural adaptation.
Whatever the industry raises is not only for the infrastructure with double objective, but also how it can become an interwaovan solution for both environment and socio-economic issues. The buildings that are still in service today for cultivating crops will be redirected to perform more varied functions like water management systems, carbon offset modules, and even community-based technology centers. Rural territories, once reserved for conventional farming practices, will become home to highly efficient areas that combine energy production, food provision, and research innovation.
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market will soon be a learning and technology nexus in impoverished areas, doing more than simply housing sun-powered greenhouses. These buildings will be part of a sustainable system that drives local employment, advanced agriculture techniques, and environmental community living. As stakeholders come to see the multiple levels of value in this model, the future will see collaboration across sectors as never before. Governments, climatologists, agronomists, and technology enterprises will more and more turn toward the goal of combining intelligent design with local requirements.
As city areas increase and weather patterns change, the appeal of the global photovoltaic greenhouse market will increase exponentially. Cities will seek means to manufacture food nearer to points of consumption, decrease transportation emissions, and preserve areas of greenery within urban design. This will open up avenues where greenhouses made of photovoltaics will not only be employed to produce food but also be utilized as vertical farm installations, botanic research stations, or even city sanctuaries providing clean air and educational interaction. These advancements will find impetus in upcoming policies geared towards carbon neutrality and land preservation, yet again increasing the ambit of this sector.
The development of artificial intelligence and intelligent farming technologies will supplement the growth of this industry, as data-based agriculture will flourish in photovoltaic conditions. Predictive systems will oversee anything from humidity to energy yield, with waste minimized and maximum yield achieved. This will also change agricultural investment models, where returns will no longer be valued in terms of harvest but in accumulated returns from energy savings, appreciation of land value, and climate resilience.
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market will not be limited to commercial agriculture. It will pervade architecture, energy policy, curricula in schools, and even social equity designs. As it continues to develop, it will become a vehicle for testing self-reliance, food justice, and distributed energy systems. As the world increasingly focuses on resilience and sustainability, this market will provide solutions it will give us blueprints for living in harmony with innovation and nature.
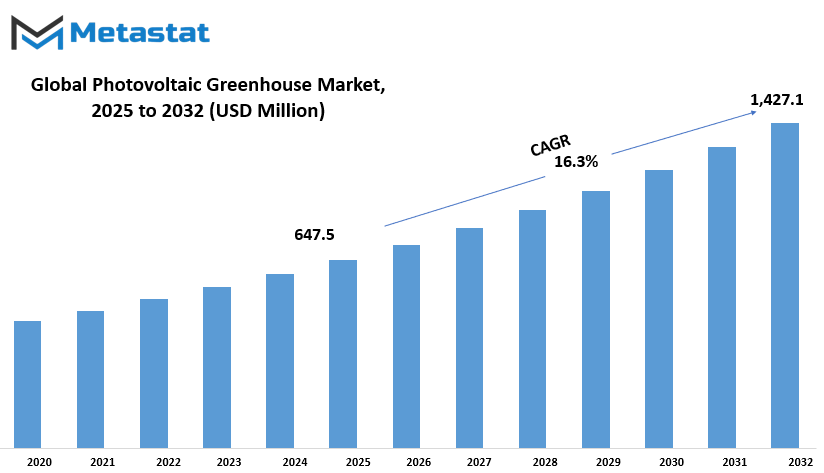
Global photovoltaic greenhouse market is estimated to reach $1,427.1 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 16.3% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is witnessing a significant shift because of the rising attention on sustainable farming techniques and the developing want to combine renewable electricity into agriculture. Across diverse regions, this concept is gaining traction as farmers and agricultural organizations look for ways to lessen dependence on conventional energy sources whilst maximizing land use. By combining solar panels with greenhouse systems, producers are able to generate clean electricity and assist controlled environment agriculture in the identical area, main to progressed aid performance.
One of the principle motives this marketplace is anticipated to develop is the growing push for eco-friendly answers in meals production. The want to deal with climate trade and growing electricity needs has advocated each private and public sectors to guide innovative agricultural models. Financial incentives and subsidies from governments and international organizations have performed a main position in encouraging the adoption of photovoltaic greenhouses. These incentives often help lessen the monetary burden of transitioning to solar-powered structures, making the idea extra realistic for medium and huge-scale producers.
Despite its promising outlook, the global photovoltaic greenhouse market nonetheless faces some vast challenges. A principal issue is the excessive in advance fee worried in putting in solar panels along with constructing or modifying greenhouse systems. For small-scale farmers or agencies with tight budgets, these expenses can be a chief barrier. In addition, using sun panels over greenhouses may also every so often restriction the quantity of natural light plant life obtain, doubtlessly affecting crop yield and excellent. This issue will become mainly crucial for plants that rely heavily on direct daylight for most beneficial growth.
However, ongoing research and technological advancements are helping to lessen these challenges. Developers are working on new transparent and semi-obvious sun panels that permit more light to skip thru at the same time as still producing strength. These innovations are predicted to enhance each power performance and growing situations in the greenhouses. By optimizing the balance between electricity production and plant fitness, these technology will likely make photovoltaic greenhouses a extra attractive alternative in the coming years.
As worldwide consciousness of climate problems maintains to develop and demand for cleaner agricultural practices increases, the future of the global photovoltaic greenhouse market appears promising. With supportive regulations, advancements in solar generation, and an growing willingness among farmers to undertake sustainable techniques, this marketplace is about to make bigger and play a key position in shaping the following generation of agricultural structures.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Type
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is set to experience significant changes as demand for green agricultural solutions keeps on surging. This innovative pairing of sun power technology and greenhouse cultivation will define the way food is cultivated in the years to come. Rather than depending on conventional practices, these facilities will enable growers to harvest crops alongside producing electricity, better utilizing land and energy simultaneously. With growing concerns for the environment and tightening clean energy targets across the globe, the global photovoltaic greenhouse market will continue to attract the interest of governments, individual investors, as well as environmentally friendly farmers.
A unique aspect of the market is the diversity of greenhouse structure types that are offered, each suited for various agricultural purposes and climatic conditions. The type is also categorized into Tunnel Greenhouses, Gable Greenhouses, Even-Span Greenhouses, Lean-to Greenhouses, and Gothic Greenhouses. Each of them provides its own advantages in terms of functionality. Tunnel Greenhouses, for instance, are easy and economical to construct, but suitable only for bigger areas. Gable Greenhouses provide improved ventilation and even light distribution, which can accommodate more types of crops. Even-Span Greenhouses are generally more balanced and can be accommodated with solar panels with more efficiency, whereas Lean-to Greenhouses can be used in small areas. Gothic Greenhouses, with their curved structures, are perfect for snow shedding and minimizing damage from extreme weather. This series of choices will provide for the varied needs of small-scale farmers as well as large-scale agricultural ventures.
In the future, the global photovoltaic greenhouse market will not only dictate the way crops are produced but also the way energy is used and distributed in rural communities. These greenhouses will probably be integrated into larger energy systems, supplying nearby houses or farms by selling excess energy back into the system. The farms will also save on electricity expenses and become more autonomous. The potential gains are both environmental and economic, which only fuels the increasing interest in this field.
As the market evolves further, innovation will be instrumental in increasing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these systems. Advances in solar panel technology, greenhouse material, and climate control systems will drive performance improvement over time. Although the initial cost will still be prohibitive for some customers, policy support and technology collaborations will reduce barriers and promote greater adoption. The balance between energy and food production is no longer an abstract concept it is fast becoming a viable solution more parts of the globe will adopt.
Overall, the global photovoltaic greenhouse market is steering toward a future where farming and renewable energy are not two different objectives but two sides of the same coin. It will address several issues simultaneously, ranging from lowering carbon footprints to enhancing food security. With structural options such as Tunnel, Gable, Even-Span, Lean-to, and Gothic Greenhouses suited to various purposes, this market will provide flexible solutions that aid a cleaner, more sustainable agricultural practice.
By Material
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is transferring closer to a future formed by means of smarter agricultural practices and purifier electricity solutions. One crucial area to recognize in this shift is how materials influence the general layout and efficiency of photovoltaic greenhouses. The type of material used in those structures plays a critical position in determining not most effective how a whole lot daylight reaches the flowers however also how correctly sun power is captured and converted.
By fabric, the marketplace is split into Glass, Plastic, and Polycarbonate. Each of those brings its own set of advantages and is chosen based totally on unique needs along with durability, value, energy performance, and plant type. Glass is a classic desire, often valued for its readability and lengthy lifespan. It permits excessive mild transmission, that is beneficial for crop boom, and works nicely with solar panels in phrases of warmth resistance and balance. However, it could be costly and heavy, making it much less ideal for some installations.
Plastic is every other usually used fabric, specifically in areas in which budgets are tighter or in which common shape modifications are expected. While it may not provide the identical clarity or sturdiness as glass, it’s lightweight, simpler to install, and generally greater flexible. It lets in growers to construct greenhouses quicker and with decrease prematurely fees, even supposing which means replacing the quilt extra regularly. Some plastics are dealt with to block UV rays or to reduce condensation, giving them introduced functionality beyond simply being a cover.
Polycarbonate, a newer and extra technical choice, stands someplace in among glass and plastic in terms of overall performance and price. It is understood for its power and effect resistance while nonetheless being lighter than glass. This fabric additionally offers correct insulation and may be synthetic in layers that help manage both warmness and mild greater efficiently. In environments where temperature control is important and harsh climate is common, polycarbonate tends to be a popular choice.
Over time, as technology improves and environmental rules tighten, the call for for specific materials in photovoltaic greenhouses will shift relying on nearby climates, crop types, and electricity needs. Some growers might also lean toward polycarbonate for its thermal houses, even as others may additionally prioritize the readability of glass or the power of plastic. The destiny of the global photovoltaic greenhouse market will in all likelihood reflect these alternatives, as farmers and energy providers aim to balance sustainability, performance, and affordability via the materials they use.
By Mounting System
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is poised to see a significant change in the way solar integration facilitates contemporary agriculture. By concentrating on functional innovation, this market is gradually aligning energy production with sustainable agriculture. Among the key aspects defining its future is the application of mounting systems, which impact not only the process of installation but also the efficiency and yield of the greenhouse itself.
Under mounting system, the global photovoltaic greenhouse market is further segmented into roof-mounted and ground-mounted. The roof-mounted systems tend to be selected when space is to be maximized, particularly where land is scarce or costly. The systems provide growers with an opportunity to utilize their current greenhouse facility without the requirement for more land. Panels that are mounted directly onto the roof can continue to permit filtered sunlight, thus achieving a balance between power and plant growth.
However, ground-mounted systems offer more flexibility as regards to positioning and orientation. They are regularly set up in big open areas in which the route and attitude of sun panels can be varied to house maximum sunlight input all through the day. This setup is in particular beneficial whilst it's far desired to supply a more amount of sun power or when there is a want for the greenhouse structure to remain clear of greater weight or alteration.
Both mounting systems will play a meaningful position as farmers, agricultural agencies, and generation carriers look for approaches to enhance output whilst preserving sustainability in recognition. Each technique gives distinct advantages relying on the dimensions of the operation, price range, and to be had space. What will set the path of the global photovoltaic greenhouse market over the following few years is not merely the uptake of photovoltaic answers, but their thoughtful implementation within agricultural settings with out compromising the basics of crop production.
As these technologies are further developed, the decision of whether to use roof-mounted or ground-mounted systems will not be a question of one being superior to the other, but of which one is best suited for the particular objectives of the user. The global photovoltaic greenhouse market, spurred on by these mounting technologies, will themselves look like a future where clean energy and agriculture progress hand-in-hand with more balance and direction.
By Application
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is steadily remodeling agricultural practices by merging renewable power with present day farming strategies. This marketplace represents a ahead-thinking method where greenhouse structures are prepared with sun panels to generate power even as supporting plant boom. What sets this technique aside is its twin purpose presenting a controlled environment for crops and simultaneously producing clean electricity. As the sector seeks extra sustainable farming answers, this model offers a realistic answer.
By application, the global photovoltaic greenhouse marketplace is segmented based totally at the varieties of plants cultivated underneath these sun-incorporated systems. Among these, veggies account for a great portion, worth $305.0 million. This determine highlights the growing hobby in the use of photovoltaic greenhouses to grow excessive-call for plants even as maximizing land use. These systems assist hold the temperature and humidity stages critical for vegetables, making them a reliable choice for regular deliver at some stage in the 12 months. Fruits, nursery vegetation, and flowers also make up essential segments inside this marketplace. While they don’t currently suit the cost of the vegetable phase, their adoption is expected to grow as farmers discover various makes use of for photovoltaic era in agriculture.
The gain of this model lies in its adaptability. Whether in rural farms or semi-urban setups, photovoltaic greenhouses may be scaled in keeping with want. Countries with high sun exposure are especially located to take gain of this method. With growing strength costs and growing consciousness of weather issues, extra growers will in all likelihood shift towards this power-green system. Over time, this can inspire similarly funding in crop-unique greenhouse development, tailored to distinctive plant desires without compromising solar electricity output.
As generation advances, the materials used for solar panels are predicted to improve, turning into lighter, extra obvious, and better suited for agricultural use. This will make it less complicated to stability mild penetration for plants with strength generation. The global photovoltaic greenhouse market isn't just a step in the direction of greener electricity; it displays a shift in how farming may be approached with innovation and sustainability working hand in hand.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$647.5 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$1,427.1 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
16.3% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
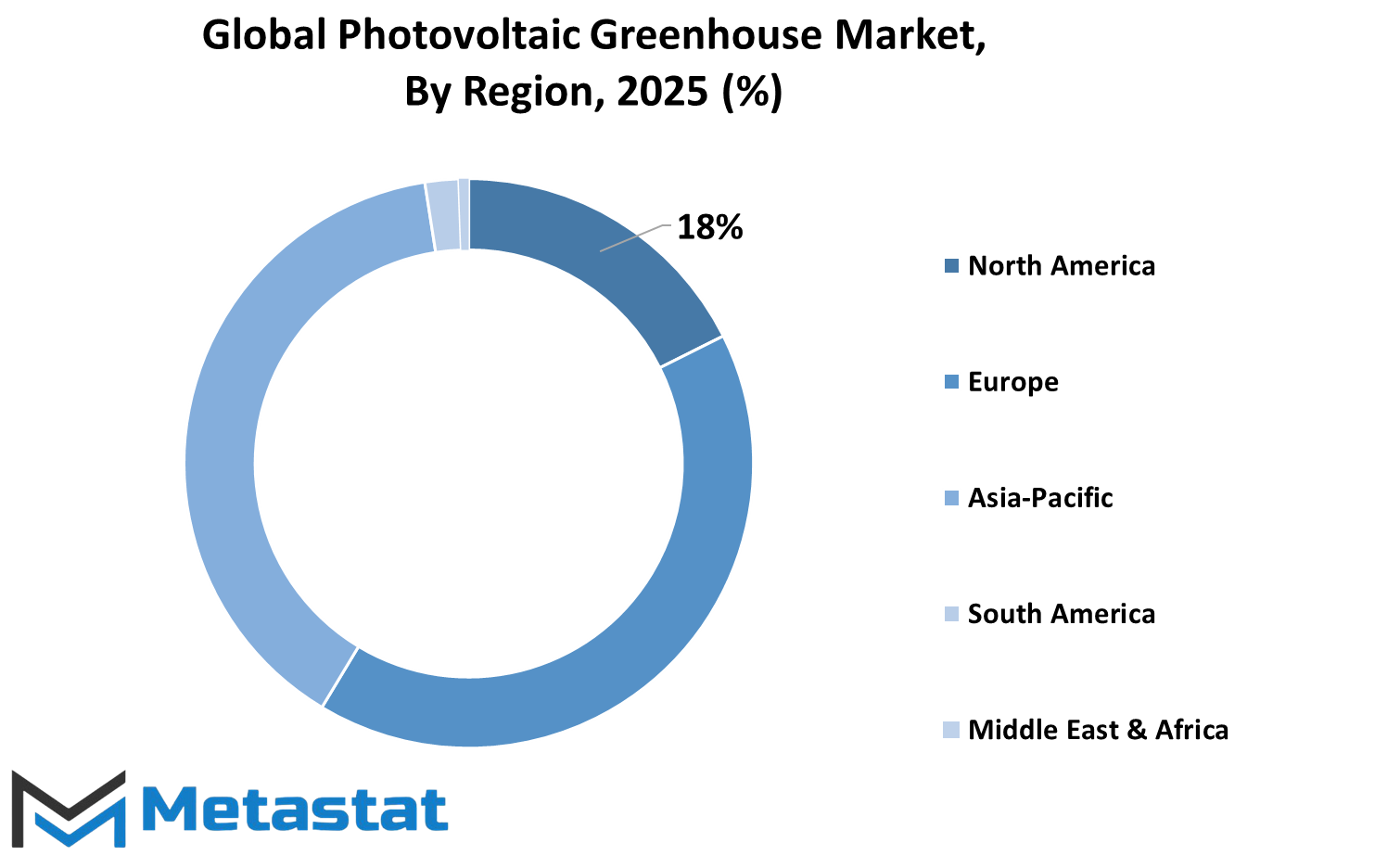
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is gradually gaining interest as a ahead-searching method that blends energy manufacturing with agricultural desires. As demand for sustainable answers rises, those progressive systems are expected to play a larger position in helping meals systems even as contributing to smooth power desires. What makes this market particularly interesting is its unfold throughout numerous areas, each presenting a different backdrop of weather conditions, technological development, and regulatory policies that impact its boom and course.
Based on geography, the global photovoltaic greenhouse market is divided into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East & Africa. North America includes the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. In this region, authorities projects round renewable power and a growing interest in smart farming will possibly assist further adoption. Europe, with key contributors consisting of the UK, Germany, France, and Italy, will continue exploring ways to integrate solar power with agricultural infrastructure, specifically in areas handling electricity transition plans. Asia-Pacific, protecting India, China, Japan, South Korea, and other countries, is expected to see predominant traits due to large-scale agricultural practices and rising energy desires.
Here, technology transfer and regional cooperation will shape future investment and use. Meanwhile, South America, which includes Brazil, Argentina and other neighboring countries, may have to adopt both affected by environmental concerns and energy security. Finally, in the Middle East and Africa, with regions such as GCC countries, Egypt and South Africa, the abundance of sunlight can encourage the development of photovoltaic greenhouses, especially in places facing water scarcity and require food production efficiency.
The future of the global photovoltaic greenhouse market depends not only on technology, but also how well it align with the goals of each region. Whether it is through increased support for solar infrastructure, agricultural modernization, or a change towards more environmentally friendly practices, the global photovoltaic greenhouse market will probably reflect the specific preferences of these geographical segments. This geographical rupture provides a clear attitude of how different parts of the world can affect and benefit from this growing field.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is entering a new era in which energy generation and farming are being intelligently integrated. Rather than either using land for crops or solar panels, this technique has both working together in the same area. It's something that a lot of experts think is going to determine the future of sustainable agriculture and clean energy. The emphasis is not merely on tapping into the power of the sun; it is on doing so in a manner that enhances agriculture, conserves land, and utilizes available resources efficiently.
What is so interesting about the global photovoltaic greenhouse market is how the various technologies are converging. Photovoltaic systems are being engineered these days to allow sufficient sunlight to pass through so that crops can be grown, yet still produce electricity. This compromise between light for plants and power for utilization is being calibrated by engineers and growers both. It is no longer a matter of simply adding panels to the roof of a greenhouse. Increasingly, there is more focus on smart control systems, energy storage systems, and even artificial intelligence for tracking environmental conditions and maximizing performance.
Farm communities and renewable energy developers alike are finding the long-term advantage of this strategy. Through solar panels inside greenhouses, farmers are able to save on energy expenses, become more independent from unreliable electricity grids, and even generate income off excess electricity. Meanwhile, solar businesses appreciate the benefit of dealing with agriculture to access broad, open spaces that allow for both sun access and long-term placement.
A number of companies are helping shape this transformation. Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd., for instance, brings expertise in solar inverters that improve energy efficiency in greenhouses. AgriSolar Solutions is known for its tailored systems designed for dual land use. At the same time, solar panel companies like Aiko Solar Power Inc., Canadian Solar Inc., JA Solar Technology Co., Ltd., and JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd. are further developing their technologies to meet the unique light requirements of greenhouse crops. Heliatek GmbH, for instance, is developing flexible solar films, while Huawei Investment Holding Co., Ltd. makes its contributions by incorporating digital management systems. Green energy industry leaders such as LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd., GCL System Integration Technology Co., Ltd., and Hanwha Q CELLS offer high-performance panels. Sharp Corporation and REC Group also continue to be active players in this arena, providing efficient solutions with years of accumulated knowledge. Solex Greenhouse Solutions, however, facilitates system integration to ensure energy production is synchronized with agricultural yield.
Government incentives and policies also have an influencing role. In most nations, there's increased interest in projects that cater to both energy sustainability and food security. This is already propelling pilot projects and commercial-scale operations in both rural and urban settings. As the climate keeps evolving, such solutions may not be a matter of choice they'll probably become imperative.
As knowledge increases and the advantages come into perspective, more farmers and enterprises will embrace this model. It's not about substituting conventional farming or solar power systems, but enhancing them. As pressure on land increases, energy prices rise, and climate-related issues become a factor, the use of solar power in conjunction with greenhouse farming offers a future prospect. The global photovoltaic greenhouse market is more than a market trend it is a change in the way we conceptualize land use, food, and energy.
Photovoltaic Greenhouse Market Key Segments:
By Type
- Tunnel Greenhouses
- Gable Greenhouses
- Even-Span Greenhouses
- Lean-to Greenhouses
- Gothic Greenhouses
By Material
- Glass
- Plastic
- Polycarbonate
By Mounting System
- Roof-Mounted
- Ground-Mounted
By Application
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Nursery Crops
- Flowers
Key Global Photovoltaic Greenhouse Industry Players
- Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
- AgriSolar Solutions
- Aiko Solar Power Inc.
- Canadian Solar Inc.
- First Solar, Inc.
- GCL System Integration Technology Co., Ltd.
- Hanwha Q CELLS
- Heliatek GmbH
- Huawei Investment Holding Co., Ltd.
- JA Solar Technology Co., Ltd.
- JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd.
- LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
- REC Group
- Sharp Corporation
- Solex Greenhouse Solutions
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential




 US: +1-(714)-364-8383
US: +1-(714)-364-8383






