MARKET OVERVIEW
The Global EV Charging as a Service market has emerged as a dynamic sector within the automotive industry, embodying the transformational shift towards sustainable transportation solutions. This market encapsulates a spectrum of services tailored to meet the charging needs of electric vehicles (EVs), representing a pivotal component in the global transition towards cleaner mobility alternatives.
The industry of EV Charging as a Service revolves around facilitating convenient and accessible charging solutions for electric vehicle owners. Unlike traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, EVs rely on charging stations to replenish their batteries, necessitating a robust infrastructure capable of supporting their widespread adoption. This industry encompasses a diverse array of stakeholders, including charging station operators, technology providers, energy companies, and automotive manufacturers, collaborating to establish an integrated ecosystem that fosters the growth of electric mobility.
One of the defining characteristics of Global EV Charging as a Service market is its emphasis on innovation and technological advancement. As the demand for EVs continues to surge globally, there is a corresponding need for more efficient, reliable, and scalable charging solutions. Consequently, companies within this sector are continually investing in research and development to enhance charging infrastructure, optimize charging protocols, and integrate smart grid technologies. These efforts aim to address key challenges such as charging speed, interoperability, and grid integration, thereby accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles.
Moreover, the landscape of EV Charging as a Service is characterized by a diverse range of business models and service offerings. From public charging networks operated by utilities to private charging solutions deployed by commercial entities, there are many approaches to delivering charging services to consumers. Additionally, advancements in digital platforms and mobile applications have facilitated the emergence of innovative business models such as on-demand charging, subscription based services, and dynamic pricing schemes, catering to the evolving preferences and behaviors of electric vehicle users.
Furthermore, the Global EV Charging as a Service market is closely intertwined with broader trends shaping the future of transportation and energy. As governments around the world enact ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, the electrification of transportation emerges as a cornerstone of sustainable development strategies. Consequently, policies and incentives aimed at promoting the adoption of electric vehicles and expanding charging infrastructure play a pivotal role in driving market growth and shaping industry dynamics.
The Global EV Charging as a Service market represents a vibrant and dynamic sector at the forefront of the transition towards sustainable transportation solutions. With its focus on innovation, collaboration, and scalability, this industry is poised to play a central role in shaping the future of mobility, driving forward the adoption of electric vehicles, and fostering a cleaner, greener transportation ecosystem.
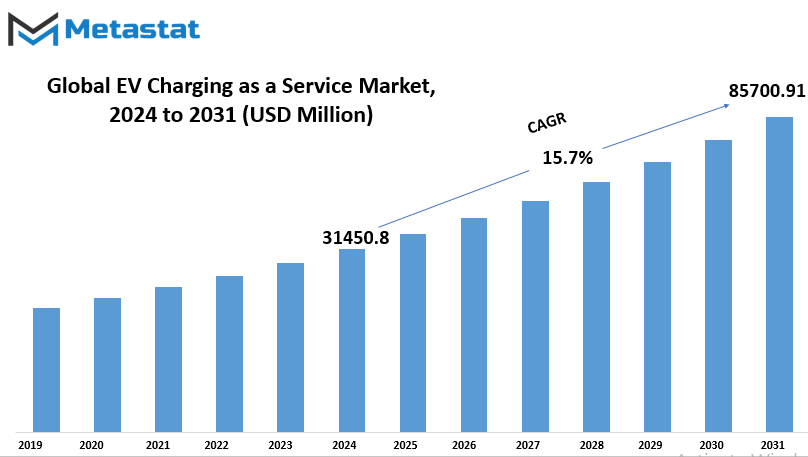
Global EV Charging as a Service market is estimated to reach $85700.91 Million by 2031; growing at a CAGR of 15.7% from 2024 to 2031.
GROWTH FACTORS
The Global EV Charging as a Service market is witnessing significant growth, primarily fueled by two key factors. Firstly, the rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) on a global scale is contributing to the increasing demand for convenient and widespread charging solutions. As more consumers opt for EVs due to their environmental benefits and technological advancements, the need for efficient charging infrastructure becomes paramount.
Secondly, supportive government policies, incentives, and investments in EV charging infrastructure are further propelling market growth. Governments around the world are recognizing the importance of transitioning towards sustainable transportation systems and are thus providing various incentives to both consumers and businesses to promote the adoption of EVs and the development of charging infrastructure.
However, despite these growth factors, there are challenges that could potentially hinder the market's expansion. One such challenge is the high initial infrastructure investment and ongoing operational costs associated with establishing and maintaining EV charging networks. The significant financial commitment required may deter some stakeholders from investing in charging infrastructure, particularly in regions with limited resources.
Another challenge is interoperability issues between different EV models and charging networks. Compatibility issues can create inconvenience for EV users, as they may encounter difficulties finding compatible charging stations or experience delays in charging their vehicles. Addressing these interoperability challenges is crucial for ensuring a seamless and user-friendly experience for EV owners.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for market growth, particularly through the integration of smart grid technologies and renewable energy sources into EV charging infrastructure. Smart charging solutions can optimize charging processes, reduce energy costs, and enhance the overall efficiency of EV charging services. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power can make EV charging more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
While the Global EV Charging as a Service market faces challenges such as high infrastructure costs and interoperability issues, the rising adoption of electric vehicles and supportive government initiatives continue to drive its growth. By addressing these challenges and leveraging opportunities presented by smart charging integration and renewable energy sources, the market is poised for significant expansion in the coming years.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Technology
The Global EV Charging as a Service market, segmented by technology, encompasses various charging options tailored to the needs of electric vehicle users. These options include Normal Charging, Type 1, CHAdeMO, Combined Charging System, and others.
Normal Charging refers to the standard method of charging electric vehicles using a traditional power outlet. This method is convenient for users who have access to standard electrical outlets at home or in public areas.
Type 1 charging, however, uses a specific connector type prevalent in some regions. It allows for efficient charging of electric vehicles equipped with Type 1 connectors, offering compatibility and ease of use for users in those areas.
CHAdeMO charging represents another technology in the EV charging market. It is a fast-charging method developed by the CHAdeMO Association, primarily used by electric vehicles from Japanese manufacturers. This technology enables rapid charging, reducing the time required to replenish the battery and enhancing the convenience of electric vehicle ownership.
The Combined Charging System (CCS) is a versatile charging solution designed to accommodate various charging scenarios. It integrates both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) charging capabilities, providing flexibility and interoperability for electric vehicle charging infrastructure. CCS technology is increasingly adopted by manufacturers and supported by an expanding network of charging stations worldwide.
Additionally, the market includes other charging technologies and solutions catering to specific needs and preferences of electric vehicle users. These may include proprietary charging systems developed by individual manufacturers or innovative charging technologies emerging in the rapidly evolving electric vehicle ecosystem.
The segmentation of the Global EV Charging as a Service market by technology reflects the diverse landscape of electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Each technology offers unique features and benefits, contributing to the overall growth and development of the EV charging market.
Furthermore, the evolution of EV charging technologies is driven by factors such as advancements in battery technology, regulatory initiatives promoting electric vehicle adoption, and the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions. As electric vehicles continue to gain traction worldwide, the need for efficient and reliable charging infrastructure becomes increasingly paramount.
The Global EV Charging as a Service market encompasses a variety of charging technologies tailored to meet the needs of electric vehicle users. From standard charging methods to fast-charging solutions, the market offers diverse options to support the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and foster the transition towards a sustainable transportation ecosystem.

By Voltage Level of Charging
The Global EV Charging as a Service market encompasses a wide array of services aimed at facilitating electric vehicle (EV) charging for consumers worldwide. This market operates on different voltage levels, including Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 charging options.
At Level 1, charging stations provide basic charging capabilities for electric vehicles. These stations typically utilize a standard household outlet, delivering a low level of power to recharge EV batteries. While Level 1 charging is convenient for overnight charging or for topping up EV batteries during the day, it’s relatively slow compared to higher voltage options.
Moving up to Level 2 charging, the market offers faster charging solutions suitable for both residential and commercial settings. Level 2 chargers require higher voltage outlets and provide increased power output compared to Level 1 chargers. This results in quicker charging times, making Level 2 charging ideal for users who need to charge their EVs more rapidly, such as during work hours or while running errands.
Level 3 charging represents the highest voltage level available in the EV Charging as a Service market. Also known as DC fast charging or rapid charging, Level 3 chargers deliver significantly higher power outputs than Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. These stations are typically found along highways and major transportation routes, offering EV drivers the ability to recharge their vehicles quickly during long journeys. Level 3 charging is essential for reducing charging times and promoting widespread adoption of electric vehicles by addressing concerns about range anxiety.
Each voltage level in the EV Charging as a Service market caters to different consumer needs and usage scenarios. Level 1 charging provides a convenient option for slow, overnight charging, while Level 2 charging offers faster charging suitable for various residential and commercial applications. Level 3 charging stands out as the fastest option, enabling rapid charging for long-distance travel and addressing concerns about EV range limitations.
As the demand for electric vehicles continues to grow globally, the EV Charging as a Service market plays a crucial role in supporting this transition. By offering charging solutions at different voltage levels, providers can meet the diverse needs of EV owners and contribute to the widespread adoption of electric transportation. Additionally, advancements in charging infrastructure and technology are driving improvements in charging efficiency, convenience, and accessibility, further bolstering the growth of the EV Charging as a Service market.
The Global EV Charging as a Service market encompasses various charging solutions categorized by voltage levels, including Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 charging options. Each level caters to different charging needs and usage scenarios, contributing to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles worldwide. As the market continues to evolve, innovations in charging infrastructure and technology will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of electric transportation.
By Charging Point Type
The market for Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging as a Service operates on a global scale, catering to the growing demand for electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Within this market, there are different types of charging points available to consumers. These charging points are categorized into two main types: Alternate Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC).
The Alternate Current (AC) segment, also known as Normal Charging, is a prevalent option for electric vehicle owners. In 2022, this segment held a considerable value of 16,193.3 million USD. AC charging points are commonly found in residential areas, workplaces, and public parking spaces, offering a convenient and accessible charging solution for electric vehicle users.
However, the Direct Current (DC) segment, often called Supercharging, is another important component of the EV charging market. Valued at 7,321.5 million USD in 2022, DC charging points provide a faster charging experience compared to AC counterparts. These charging stations are typically located along highways, major roads, and strategic locations, allowing electric vehicle owners to quickly recharge their vehicles during long journeys.
Both AC and DC charging points play vital roles in supporting the adoption and proliferation of electric vehicles worldwide. While AC charging offers convenience for daily charging needs, DC charging provides a rapid charging solution for drivers requiring quick turnaround times. The combination of these two charging technologies contributes to the overall accessibility and usability of electric vehicles, encouraging more individuals to make the switch to sustainable transportation options.
The Global EV Charging as a Service market encompasses various charging point types, with AC and DC segments representing significant portions of the market. These charging options cater to the diverse needs of electric vehicle users, ensuring accessibility and convenience in charging infrastructure as the world transitions towards a more sustainable future.
By Application
The global market for EV charging services can be categorized based on its application into private and public sectors. This division reflects the varied settings where electric vehicle (EV) charging is needed and utilized.
In the private sector, EV charging services cater to individual consumers, residential areas, and private organizations. These settings often involve home charging stations or charging facilities within company premises. Private EV charging services offer convenience and accessibility to EV owners, allowing them to charge their vehicles at their homes or workplaces, thereby integrating EV charging seamlessly into their daily routines.
On the other hand, the public sector encompasses charging services provided by governments, municipalities, and commercial entities in public spaces such as parking lots, streets, and shopping centers. Public EV charging services aim to address the needs of EV owners who require charging facilities while on the go or in public areas where they do not have access to private charging options. These public charging stations play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of electric vehicles by alleviating range anxiety and enhancing the overall accessibility of EVs.
The distinction between private and public EV charging services underscores the diverse requirements of EV owners and the importance of catering to their needs across different environments. While private charging services focus on residential and corporate settings to provide convenient charging solutions for individual EV owners and fleets, public charging services aim to create a widespread infrastructure that supports EV adoption on a larger scale by offering accessible charging options in public spaces.
Overall, the division of the global EV charging market into private and public applications reflects the multifaceted nature of EV charging services and highlights the significance of addressing the diverse charging needs of EV owners across various settings. By offering tailored solutions for both private and public environments, the EV charging industry can contribute to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and the transition towards a sustainable transportation ecosystem.8
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The global market for Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging as a Service is analyzed based on its geographical distribution into regions including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East & Africa.
North America stands as a prominent player in the global market for EV Charging as a Service. The region's advanced infrastructure and strong presence of key market players contribute significantly to its market share. With increasing government initiatives to promote electric vehicles and establish robust charging networks, North America continues to witness substantial growth in this sector.
Europe emerges as another significant region in the global EV Charging as a Service market. The continent's progressive stance towards sustainable transportation and stringent emissions regulations drives the demand for EV charging solutions. Countries like Germany, Norway, and the Netherlands lead the adoption of electric vehicles, fostering the expansion of charging infrastructure across the region.
Asia-Pacific showcases immense potential for the EV Charging as a Service market. Rapid urbanization, rising pollution levels, and government incentives for electric mobility fuel the market growth in countries like China, Japan, and India. The region's large consumer base and increasing awareness about environmental conservation further accelerate the adoption of EV charging services.
South America is also witnessing a gradual uptake of EV Charging as a Service solutions. Growing environmental concerns and efforts to reduce dependency on fossil fuels propel the demand for electric vehicles and associated charging infrastructure in countries like Brazil and Argentina. However, the market in this region is still in its nascent stage compared to other regions.
The Middle East & Africa region is gradually embracing the shift towards electric mobility. With rising concerns about air pollution and efforts to diversify energy sources, several countries in the region are investing in EV infrastructure development. Although the market is relatively smaller compared to other regions, it holds potential for significant growth in the coming years.
Overall, the global market for EV Charging as a Service exhibits a diverse landscape across different regions. While mature markets like North America and Europe lead in terms of adoption and infrastructure development, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East & Africa present lucrative opportunities for market players. As governments worldwide continue to prioritize sustainability and decarbonization, the demand for EV charging solutions is expected to soar across all regions, driving further growth and innovation in the industry.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The global market for Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging as a Service is witnessing significant participation from various key players. These companies are actively involved in providing charging solutions for electric vehicles, contributing to the growth and development of the industry.
Among the prominent players in this sector are Tesla Inc., Volkswagen AG, BYD Co. Ltd., Stellantis NV, Toyota Motor Corporation, and Ford Motor Company. These companies have established themselves as leaders in the EV Charging as a Service market, each bringing its own unique strengths and offerings to the table.
Tesla Inc. stands out as a pioneer in the electric vehicle industry, known for its innovative approach to charging infrastructure. With its extensive network of Superchargers and Destination Chargers, Tesla has played a significant role in shaping the EV charging landscape.
Volkswagen AG, a major player in the automotive industry, has also made substantial investments in EV charging infrastructure. Through its subsidiary, Electrify America, Volkswagen is expanding its network of fast chargers across the United States, making EV charging more accessible to consumers.
BYD Co. Ltd., a Chinese multinational specializing in electric vehicles and batteries, is another key player in the EV Charging as a Service market. With its expertise in battery technology, BYD is developing efficient charging solutions to support the growing demand for electric mobility.
Stellantis NV, formed through the merger of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles and PSA Group, is committed to electrifying its vehicle lineup. The company is investing in charging infrastructure to complement its expanding range of electric and hybrid vehicles.
Toyota Motor Corporation, a leader in hybrid technology, is also making strides in the electric vehicle space. With initiatives like the Toyota Mirai and plans to introduce more electric models, Toyota is actively engaging in the development of EV charging infrastructure.
Ford Motor Company, known for its commitment to sustainability, is ramping up its efforts in the EV market. With the introduction of electric versions of popular models like the Mustang and F-150, Ford is investing in charging infrastructure to support the adoption of electric vehicles.
These key players in the EV Charging as a Service market are driving innovation and competition in the industry. By expanding charging networks, developing new technologies, and collaborating with stakeholders, they are paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable future of transportation.
EV Charging as a Service Market Key Segments:
By Technology
- Normal Charging
- Type 1
- CHadeMo
- Combined Charging System
- Others
By Voltage Level of Charging
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
By Charging Point Type
- Alternate Current (Normal Charging) • Direct Current (Super charging)
By Application
- Private
- Public
Key Global EV Charging as a Service Industry Players
- Tesla Inc.
- Volkswagen AG
- BYD Co. Ltd.
- Stellantis NV
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Ford Motor Company
- ABB Group
- ChargePoint, Inc.
- Shell International BV
- Schneider Electric
- BP Chargemaster
- Eaton Corporation
- Siemens AG
- AeroVironment, Inc
- General Electric Company
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential






 US: +1-(714)-364-8383
US: +1-(714)-364-8383






