MARKET OVERVIEW
The Global Dark Fiber market is at an extraordinary point of synergy within telecommunications and data infrastructure. As the world finds a growing appetite for high-speed connectivity along with private network solutions, the communication paradigm has continuously been pushed to a transformation. Dark fiber networks at present simply represent that level of transformation, with a growing demand now expected to usher in a lot more new roles than previously imagined.
The Global Dark Fiber market will not only serve as a backup solution for data transmissions or reserve infrastructure for future expansions; it will offer ultra-low latency and high bandwidth support for large-scale technologies. Companies that tackle data-heavy applications like advanced AI models, high-frequency trading systems, and immersive media will naturally gravitate towards dedicated fiber-optic lines to sidestep the constraints imposed by shared networks. That will embed dark-fiber networks more into the next generation digital strategies' core realm.
The industry views an incoming change of ownership in that light. This infrastructure will be strategically considered rather than being passive. Companies, governments, and institutions that want to maintain control over their network pathways for reasons of data security, performance reliability, and autonomy will begin to consider dark fiber other than just a passive resource but an operational asset key to their processes. This shift is going to bring major changes to how contracts are agreed upon and how public-private partnerships are going to be shaped.
In addition, the Global Dark Fiber market is expected to sweep eastward from urban centres into less developed rural communities where digital divide issues would act as deterrents to accessing dependable internet services. This new sweep would not just be driven by government action; it is also backed by investments from private players ever hungry to widen their physical footprints, including data centre providers, content delivery networks, and major cloud service vendors. Forces that demand uninterrupted and secure flow of data will push further investments into long-haul dark fiber routes across so far uncharted terrain.
With environmental issues assuming greater importance in the realm of technological planning, future developments in this market will look at energy-efficient deployment practices. From reducing signal amplification points to leveraging AI-based monitoring for proactive maintenance, the focus will shift to responsible expansion. Innovations that reduce physical and carbon footprints of fiber installations will become ingrained in the lexicon of long-term network planning.
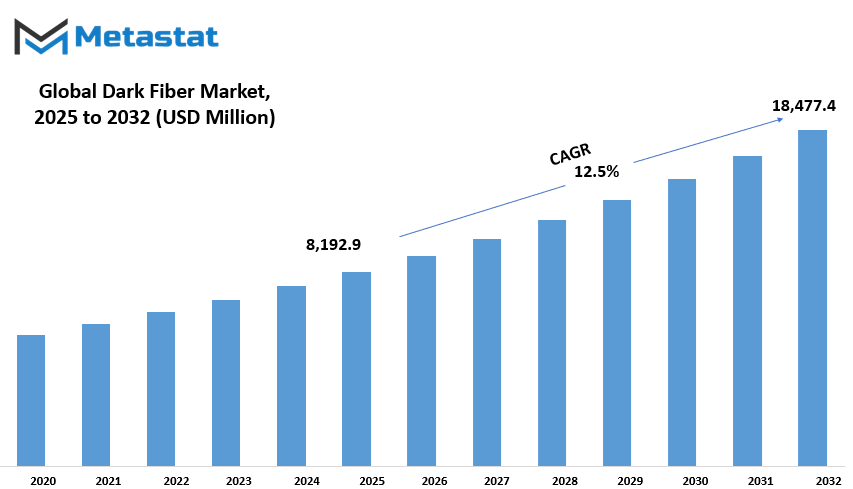
Global Dark Fiber market is estimated to reach $18,477.4 Million by 2032; growing at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2025 to 2032.
GROWTH FACTORS
The major push for establishing the Global Dark Fiber Market has arisen from a need for high-bandwidth communications and fast data transfer services. With a growing number of industries, businesses, and government agencies benefiting from digital operations, the demand for reliable and fast internet solutions continues to develop. While most enterprises need private and secure network infrastructure today, this has brought dark fiber to the forefront of attractive options. Such private networks allow even greater control of organization data, an assurance to have especially when dealing with sensitive or confidential information. This way, dark fiber is being perceived more and more as one not only better but safer for critical communications.
Simultaneously, several factors in the market can retard growth. One such obstacle is the high initial investment on the active side of dark fiber networks. This contrasts with traditional leased lines, whereby dark fiber requires a major investment upfront in the secondary infrastructure before anybody can actually make use of it. This investment not only entails the physical cables but also the purchase of equipment to light those cables as well as maintenance. Another barrier is regulatory in nature. Operating and deploying dark fiber networks normally requires an even slower and more complex process of securing permissions and access to installation on public or private land. These regulatory and rights-of-way concerns limit the speed and ease of expansion for companies, especially in certain regions.
An optimistic dimension still surrounds the dark fiber market view notwithstanding these challenges. Arguably, its most exciting growth has been witnessed in the wake of 5G proliferation. As 5G deployment gathers momentum, it would require a resilient backhauling network, something dark fiber can efficiently provide. Furthermore, with the rise in use of IoT devices in different sectors, the need for high-capacity, low-latency connectivity has also increased tremendously. Dark fiber would therefore be, in fact, regarded as a huge beneficiary.
All in all, there remain some hindrances, but dependence on secure, high-speed data connections in a digital-first world clearly suggests that dark fiber will have a pivotal role in the network infrastructure of the future. The lure of 5G rollout and booming application demand for IoT will provide dark fiber with more acres of opportunities in the near future.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Fiber Type
The Global Dark Fiber market is on a steady growth trajectory as many companies and service providers look for faster and secure data connectivity. This growth is determined by a number of factors, but the fiber type is one of the important reasons because it has a major influence on performance and application suitability. The Fiber Type market is segmented as Single Mode Fiber, Step-index Multimode, and Graded-index Multimode. Among these, Single Mode has a huge chunk valued at $4066.9 million. This is the fiber transmitting the signal over long distances with low loss consumption, so here it is mainly useful for telecom networks, data centers, and enterprise solutions at a large level.
Single Mode fiber has a smaller core, and a single light path to reduce interference, increasing distance data will travel without degradation. Today all workloads from all industries have increased, causing this feature to become a preferred attribute for long-distance transmission. Step-index Multimode Fiber on the other hand, gives the best performance for transmission over short distances. It possesses a core with a uniform index of refraction but doesn't have high bandwidth support for long distances. This type is less expensive and easier to install and is therefore mostly used for small networks or in buildings where the distance is limited.
Graded-index Multimode Fiber sits in between. It has a core which has gradually changing refractive index from the center outward. This not only causes lesser signal loss but also improves performance gains than Step-index for medium distances. It is to be seen in places where performance is needed above what Step-index provides but at the same time, Single Mode will be too much.
There are varying requirements from region to region and industry to industry regarding types of fibers. For example, data center would acquire Single Mode because of its high speed and efficiency, whereas office buildings or campuses would use Multimode, for cost and ease of use. Most of the time or often, the determining factors are cost, distance, and what types of traffic are expected.
As advances in technology such as 5G and cloud computing pave the way for billions more devices in the IoT, the demand for fiber connections that are consistently high between many elements of the modern connected experience will increase. Each fiber type has strengths and weaknesses that cover different sections of the market. Knowing what they do will shed light on how and why the Global Dark Fiber market is expanding and, more importantly, why fiber selection remains a pivotal element in any infrastructure architecture plan.
By Network Type
The global dark fiber market develops at a steady pace regarding the network type. The market is broadly divided into two categories: Metro and Long-haul. Metro networks are used for intra-city and interfacial communication. These networks serve short distances between buildings, offices, and data centers in a specific city or area. Because of the increasing demand for fast internet connectivity, improved communication systems, and smart city initiatives, demand for metro dark fiber is growing. The more organizations put their operations into the cloud and take advantage of data-heavy applications, the higher the need comes to obtain solid fast connectivity. Transmission in metro networks makes that achievable because it entices a premium and reliable-level performance in congested and data-based environments.
On the contrary, bulk networks cross-country and often take data to faraway lands and cities. An essential part of the data infrastructures that connect both the major hubs and serve the international and transnational data commutations is indeed a part of the long-haul segment. The segment also poses a stable demand for the long haul as the global internet traffic continues to increase. Investment in long-haul dark fiber is made for commercial purposes by large corporates, telecommunication companies, and service providers who want to move bulk data at very high security and with low latency. With the increasing number of video streams, online meetings, and online services availed, the pressure on the existing networks increases deeper. Therefore, companies are pushed to increase their long-haul infrastructure using dark fiber to meet the demands for the future.
Both metro and long-haul segments are important, but each fulfills a different purpose. Metro networks are designed to cover the whole area densely and at shorter distances, while long-haul networks typically support widespread, long-term communication cover. This facilitates selection of an ideal type of network according to the needs of a certain company, a local internet provider focusing on metro dark fiber to increase the speed and coverage within a certain area, while a multinational tech company investing in long-haul dark fiber will be doing so to connect its offices spread all over the world.
Broadly, hence the above-the-dark fiber market in the world has created network types of Metro and Long-haul that presuppose different types of infrastructures required for keeping up with the ever-increasing demand for growing digitization. The rising data consumption, thus, keeps investments in both segments important and great for the current and future needs of businesses and individuals alike.
By Material
The increasing demands for high-speed and secure communication networks drive the steady growth of the global dark fiber market. Dark fiber is defined as an unused optical fiber that is available to be used in fiber-optic communication. Companies and service providers lease or buy this fiber to create their private networks. This provides better control over the flow of information, improves security, and allows independent management of large data volumes. The demand continues to rise, considering the increasing number of data centers and cloud-based services in addition to the ramp-up from the 5G network angle. All of these rely on a strong and reliable communication infrastructure, making dark fibers a significant player in the digital world today.
When looking at the market by material, it is differentiated into further categories: glass and plastic. Glass fiber is used mostly in systems, being efficient and of good performance over long distances. It can transmit signals for long distances with slight loss and is best suited for the core networks and large installations. Glass is preferred by many telecoms and larger companies for its reliability and durability. However, plastic fiber is often used for distances that are shorter. It is less cumbersome to handle and install, thus well suited for small networks and in-building applications. While not as good as glass for long-distance applications, plastic remains a viable economical option in many scenarios. Depending on the actual needs and budgetary consideration, each of the materials would find its way in the market.
Increased digital transformation will fuel the demand for better and faster communication channels. Thus, more organizations are beginning to invest in dark fiber. The fact that these allow companies to upgrade their networks without carrying out fresh construction works gives them an added advantage in their ability to adapt to future technologies. More government entities and private companies are also seeing this arena as a means to expand Internet coverage to unserved or underserved areas like some rural locations. This has helped the growth of the dark fiber market even further.
In overall consideration, the outlook for the global dark fiber market appears bullish with glass and plastic fibers playing centre stage in different applications. Dark fiber will endure offering capacity, speed, and control demanded by modern systems with increased data transfer over networks every passing day. With increasing relevance in everything from corporate activities to public service components, this market is expected to experience continuous growth.
By Application
All of these lead us to a certain conclusion, namely, that dark fiber shows a continuous growth in the global market mainly due to the onset of high and well-performing communication systems. Dark Fiber, for example, is that unused optical fiber which is available for use in fiber-optic communication. Companies and organizations are increasingly turning to dark fiber to meet their high-speed connectivity needs since dark fiber has been known to offer security, more control, and high-performance levels. When we look at the market based on how dark fiber is applied, it could be classified into some of the vital areas as: Telecom, Oil & Gas, Military & Aerospace, BFSI, Medical, Railway, and Others.
Telecom is very large in the holding shares since high-speed internet and better mobile networks have proven future growth. Dark Fiber is used to expand networks and handle the rapidly increasing number of users for telecom companies. This rise in demand for data is just going to multiply, hence keeping this segment growing in the years to come. Safe and efficient communications at long and sometimes dangerous distances can be had with the dark fiber in Oil and Gas. Fast and secure data transmission is a must for monitoring equipment and supporting seamless operations in the field.
The Military and Aerospace depend on dark fiber for high bandwidth communicating securely. Such industries need reliable communication systems for various operations, which dark fiber fulfills. Similarly, in the BFSI sector, the need for secure and rapid data transfer cannot be emphasized too strongly. Banks deal with millions of transactions every day, and dark fiber thus becomes instrumental in creating an efficient and secure environment for their data.
Dark fiber is increasingly being utilized in the medical field since hospitals and the likes are going through transformation to the world of digital records and high-resolution imaging and telemedicine. Connections that are both faster and more reliable will assist in improving the management and delivery of patient data, thereby ensuring better healthcare. The Railway sector will also accrue benefits in dark fiber technology, where it will contribute to real-time communication, signaling, and monitoring systems towards improved safety and efficiency. Lastly, government services, as well as educational institutions, have also put dark fiber into their usage to enhance their data infrastructure.
Therefore, going by what has been described, dark fiber will apparently continue with a constant increase in the global market owing to the necessity of emerging high and efficient communication systems.
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
$8,192.9 million |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
$18,477.4 Million |
|
Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032 |
12.5% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
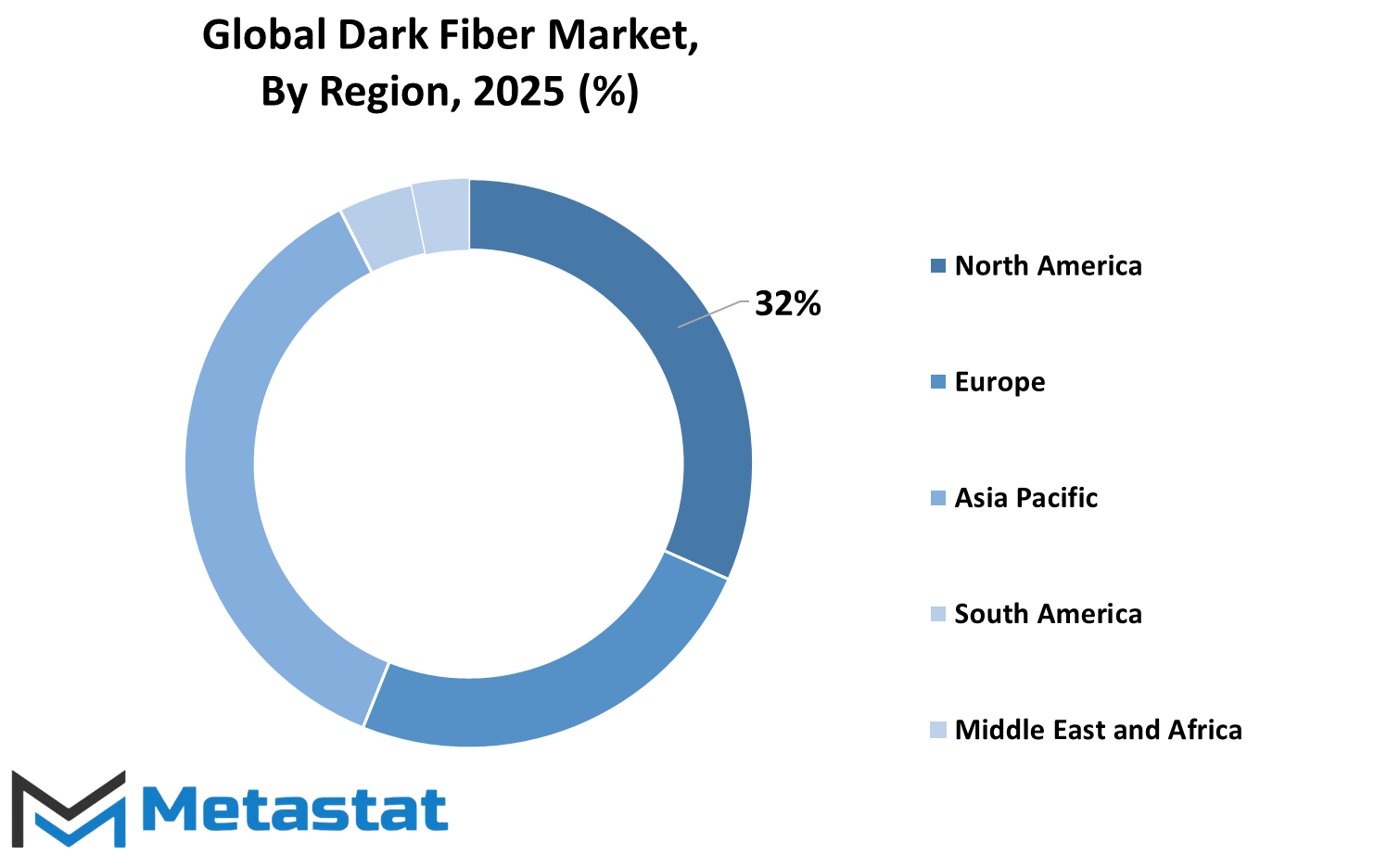
The global Dark Fiber market can be subdivided into five regions according to geography: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East and Africa. Every region is playing a significant role in establishing Dark Fiber networks by fueling the expansion of data centers and increased internet use as well as creating higher investments in telecommunications infrastructure.
North America is still one of the major contributors of the market. The United States, Canada, and Mexico make the core of this region. Among these countries, the United States leads by demand and infrastructure development since several companies spend their resources on advanced networking solutions. Gradual growth can also be observed in Canada and Mexico, especially in the urban areas where people have greater needs for high-speed internet access and secure data transmission.
The market in Europe would comprise the UK, Germany, France, Italy, and the Rest of Europe. These countries have placed more emphasis on digital transformation, which now serves as a solid push toward deploying high-capacity fiber networks. Both Germany and the UK have continued their consistent efforts to improve fiber infrastructure, many government initiatives include provisions for private sector investment. Furthermore, France and Italy are following with similar advances intended to enhance broadband connectivity and boost expanding digital services.
This includes India, China, Japan, and South Korea under Asia Pacific along with the rest of Asia Pacific. The market is increasing rapidly due to the increased demand for cloud services, the implementation of 5Gs, and the rising internet penetration in this region. Key markets are China and India because of their growing populations and technology industries, while Japan and South Korea are adopting technologies and now have advanced network systems, which in turn drive demand for dark fiber even higher. Other countries in the region are also starting to realize that there is an importance to strengthening their digital infrastructures.
Brazil and Argentina emerge as the two major markets of South America, helped at present by the initiatives of digitalization in business and public services. Though a little behind in large-scale fiber deployments, the region has considerably started to improve; however, the demand for reliable and faster internet connectivity grows stronger in many regions. The Rest of South America is slowly seeing progress because of the efforts of both local governments and private players to upgrade existing networks.
The Middle East and Africa comprise the GCC Countries, Egypt, South Africa, and the Rest of Middle East and Africa. The increasing momentum about fiber optic technologies among these regions continues to increase. Smart city development and digital connectivity are the main investments of GCC countries, while efforts are underway in South Africa and Egypt to expand their broadband coverage toward economic growth.
COMPETITIVE PLAYERS
The dark fiber market has been continuously growing over the years owing to the demand for high-speed interconnecting internet data storage along with improved performance of networks. Dark fiber, in simple terms, refers to the unused fiber-optic cables that have already been laid but are not presently in use. Cost effective benefit of these cables is that a company can expand its communication infrastructure without having to lay new cables. As consumption of data is continuously multiplying because of digital transformation, cloud computing, video streaming and increasing usage of smartphones, many businesses are now leasing or procuring dark fiber to meet their growing requirements for bandwidth.
The growing demand has brought several key players to the fore. Companies such as AT&T Inc., Colt Technology Services Group Limited, Eurofiber, and Consolidated Communications are some of the many working actively to deliver better dark fiber solutions. GTT Communications, Inc., Lumen Technologies, and Verizon Partner Solutions have also all made efforts to improve accessibility and reliability in their fiber networks. Windstream Intellectual Property Services, LLC and Zayo Group, LLC are some other major names driving innovation in the market. As a result, the expanding data centers and the emergence of 5G will increase the demand for secure and fast connectivity which will help the dark fiber providers.
Important players include Microscan Infocommtech Private Limited, Orange S.A, and Axione investing in improvement of the already present models of infrastructure. Sipartech, Altice, Relined B.V, and Koninklijke KPN NV have been searching for ways to provide more flexible and scalable solutions to clients. Smaller companies like TReNT Glasvezel and GasLINE GmbH & Co. KG are also making their entries felt around the market, usually focusing on regional needs or specialized services. German providers like Inexio Beteiligungs GmbH, Bouygues Energies & Services, Open Grid Europe GmbH, REACOM GmbH, and DB broadband GmbH are still growing their networks, while GlobalConnect Group and euNetworks increase the interconnections across borders. Also, major parts are 1&1 Versatel GmbH and AFIBER, which are providing competitive dimensions and variety in the industry.
With more businesses understanding the importance of dedicated fiber networks as well as how much control over their data traffic adds value, the market for dark fiber should continue to expand. As these companies further develop and imagine the future, so too will their destinies shape how data moves across regions and countries.
Dark Fiber Market Key Segments:
By Fiber Type
- Single Mode
- Step-index Multimode Fiber
- Graded-index Multimode Fiber
By Network Type
- Metro
- Long-haul
By Material
- Glass
- Plastic
By Application
- Telecom
- Oil & Gas
- Military & Aerospace
- BFSI
- Medical
- Railway
- Others
Key Global Dark Fiber Industry Players
- AT&T Inc.
- Colt Technology Services Group Limited
- Eurofiber
- Consolidated Communications
- GTT Communications, Inc.
- Lumen Technologies
- Verizon Partner Solutions
- Windstream Intellectual Property Services, LLC
- Zayo Group, LLC
- Microscan Infocommtech Private Limited
- Orange S.A
- Axione
- Sipartech
- Altice
- Relined B.V
- Koninklijke KPN NV
- TReNT Glasvezel
- GasLINE GmbH & Co. KG
- Inexio Beteiligungs GmbH
- Bouygues Energies & Services
- Open Grid Europe GmbH
- REACOM GmbH
- GlobalConnect Group
- euNetworks
- DB broadband GmbH
- 1&1 Versatel GmbH
- AFIBER
WHAT REPORT PROVIDES
- Full in-depth analysis of the parent Industry
- Important changes in market and its dynamics
- Segmentation details of the market
- Former, on-going, and projected market analysis in terms of volume and value
- Assessment of niche industry developments
- Market share analysis
- Key strategies of major players
- Emerging segments and regional growth potential





 US: +1 3023308252
US: +1 3023308252






